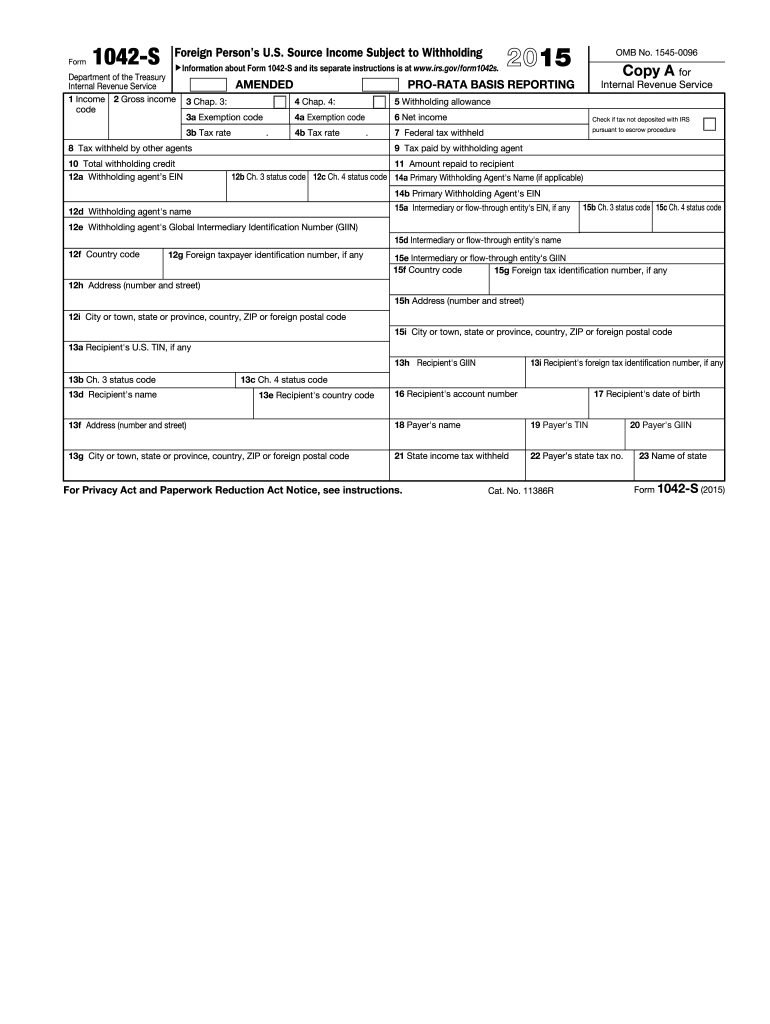
Definition and Meaning of Form
Form 1042, specifically for the 2015 tax year, is the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) form used to report income that is subject to withholding for foreign persons. This form primarily deals with U.S.-sourced income payments made to nonresident aliens, foreign corporations, and other foreign entities. It details various types of income such as interest, dividends, rents, and royalties that are subjected to tax withholding at the source.
The term "withholding" refers to the process whereby the payer (withholding agent) deducts tax from the payment made to a foreign recipient, remitting that tax directly to the IRS. This ensures that nonresident aliens and foreign entities meet their tax obligations on income earned in the United States. Understanding how Form 1042 operates is crucial for compliance with U.S. tax laws, allowing individuals and entities to properly report and remit tax obligations.
Key Elements of the Form
Form 1042 is structured with several key components that facilitate accurate reporting and compliance. The essential elements of the form include:
- Identification of Withholding Agent: This section requires details about the entity or individual responsible for withholding tax on payments made to foreign persons.
- Recipient Information: Here, details about the foreign recipient—including name, address, and identification numbers—must be provided. Proper identification ensures the correct taxation and reporting of income.
- Types of Income: The form includes sections to report various types of income categorized under U.S. tax law. Common income forms reported include dividends, interest, and rents.
- Exemption Codes: If applicable, exemption codes can indicate whether the income is exempt from withholding due to specific tax treaty benefits, which can significantly reduce tax liability.
- Total Amounts Withheld: This part summarizes the total amount withheld from payments as well as any tax that was remitted to the IRS.
Each of these sections is integral to ensuring the withholding agent accurately reports income for foreign persons. Misreporting can result in penalties and complications with both the IRS and foreign recipients.
How to Use the Form
Using Form 1042 effectively involves a clear understanding of the reporting process. The following steps outline how to appropriately utilize this form for compliance.
-
Determine Filing Requirement: Assess whether you, as a withholding agent, are required to file Form 1042. This generally applies when you pay U.S.-sourced income to foreign recipients.
-
Gather Necessary Information: Collect all relevant information about the withholding agent, recipients, and the types and amounts of income being reported. Accurate data collection is crucial to avoid errors in filing.
-
Complete the Form: Fill out the form completely, ensuring all sections are filled in accurately based on gathered information. Pay attention to exemption codes and ensure the withholding amounts align with the correct income types.
-
File the Form: Submit Form 1042 to the IRS by the appropriate deadline, typically by March 15 of the following year after the payments were made. Review IRS guidelines to confirm the deadline specific to each tax year.
-
Maintain Records: Keep copies of Form 1042 and related documentation for your records. The IRS recommends retaining these files for at least four years in case of an audit.
These steps encourage compliance and accurate reporting, which protect both the withholding agent and the foreign recipients from potential issues with the IRS.
Steps to Complete the Form
Completing Form 1042 involves a series of methodical steps to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with federal tax laws. Here are detailed steps for effective completion:
-
Part A: Identify the Withholding Agent
- Enter the name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN) of the withholding agent. If a business entity, ensure the legal name matches IRS records.
-
Part B: Provide Recipient Details
- Fill out the information for each foreign individual or entity receiving U.S. sourced income, including their name, address, and TIN if applicable.
-
Part C: Report Types of Income and Withholding
- Use specific lines for various income types, providing a breakdown of total amounts paid and amounts withheld for each income source.
-
Part D: List Exemption Codes
- If the recipient is claiming a reduced withholding rate under a tax treaty, list the applicable exemption codes as detailed in IRS guidelines.
-
Review and Certify the Information
- Before submission, review all entries for accuracy, ensuring there are no discrepancies or missing data. Certify the form by signing and dating, affirming the information is true and accurate.
-
Submit the Completed Form
- File Form 1042 electronically or by mail, ensuring adherence to IRS regulations on submission methods, and retain a copy for your records.
These steps offer a structured approach to completing Form 1042, minimizing errors and ensuring compliance with U.S. tax regulations.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates for Form
Understanding the important deadlines associated with Form 1042 is crucial for timely compliance. The general deadlines for filing Form 1042 are as follows:
-
Filing Deadline: Form 1042 must be filed with the IRS by March 15 of the year following the year in which U.S. source income was paid. For example, income paid in 2015 must be reported by March 15, 2016.
-
Payment Deadline: Any tax withheld from payments must also be remitted to the IRS by the same deadline of March 15. Failure to remit by this date can incur interest and penalties.
-
Form 1042-S: If required, issuers must provide Form 1042-S, which reports income information to recipients, by March 15 as well. This is a critical document for recipients, containing the income figures and taxes withheld.
Being aware of these dates is essential for withholding agents to maintain compliance and prevent unnecessary penalties or complications with the IRS.
Important Terms Related to Form
Understanding key terminology associated with Form 1042 can enhance clarity and compliance when dealing with U.S. tax matters involving foreign persons. Here are some significant terms to know:
-
Withholding Agent: The individual or entity responsible for withholding tax on payments made to foreign persons. This can include businesses, payroll departments, or individuals making payments.
-
Nonresident Alien: An individual who is not a U.S. citizen and does not meet the criteria to be classified as a resident for tax purposes. Nonresident aliens often have specific tax obligations related to U.S. income.
-
Exemption Code: A code utilized on the form that indicates the reason for any tax exemption or reduced withholding rates. This often relates to treaties between the U.S. and other countries that may affect taxation rates in certain situations.
-
U.S.-Sourced Income: Income that is generated from sources within the United States, including wages, dividends, royalties, and interest. Such income is subject to U.S. tax laws, regardless of the residency status of the recipient.
-
Tax Treaty: Agreements between the United States and foreign governments that establish rules for taxation on income. They often provide benefits such as reduced withholding rates or exemptions on certain types of income.
Understanding these terms not only aids in the proper completion of Form 1042 but also serves to clarify the legal framework governing tax obligations for foreign recipients in relation to U.S. income.