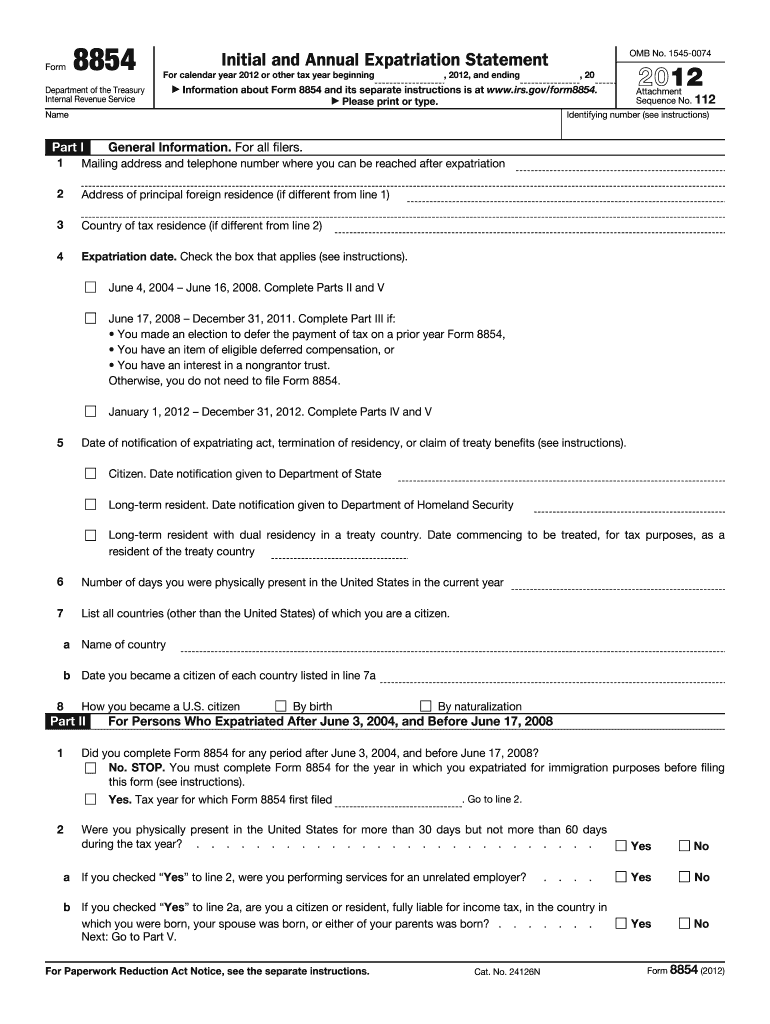
Definition and Purpose of Form 8854
Form 8854, known as the Initial and Annual Expatriation Statement, serves as an official document for U.S. citizens and long-term residents who choose to expatriate. This form collects detailed information about the individual's expatriation process, including the expatriation date, tax residency status, and the individual's compliance with tax obligations. It plays a crucial role in managing taxes on income, assets, liabilities, and helps in deferring taxes on specific properties upon expatriation. The form ensures that all necessary tax liabilities are addressed when an individual decides to sever their official fiscal ties with the United States.
How to Use Form 8854 Effectively
Proper utilization of Form 8854 can be essential for accurate reporting and compliance:
- Information Gathering: Before filling out the form, gather all relevant financial and personal information, including your tax residency status and details of your income, assets, and liabilities.
- Filling Sections: Pay close attention to each section to ensure all fields are accurately completed, reflecting your expatriation status and fiscal changes.
- Compliance Review: Verify that all the information provided complies with both the expatriation rules and tax regulations to avoid potential penalties.
Steps for Completing the 2012 Form 8854
- Prepare Documents: Collect your personal and financial documents, including financial statements and previous tax returns.
- Enter Personal Information: Start by filling out the personal identification section, ensuring your name, address, and Social Security Number (SSN) are correct.
- Expatriation Information: Provide the exact date of your expatriation and explanations for your change in tax status.
- Financial Disclosure: List your assets and liabilities in detail, ensuring accuracy for each category.
- Review and Verify: Double-check all entries for correctness and compliance with IRS expatriation guidelines.
- Submit the Form: Follow specified IRS procedures to submit the form, either electronically or by mail.
Key Elements of Form 8854
- Personal Identification: Basic details such as name, address, and SSN.
- Expatriation Date: Crucial for determining the start of the expatriation process.
- Income and Assets: Detailed declaration of income streams, properties, and other financial holdings.
- Tax Compliance: Assurance of meeting all prior tax obligations before expatriation.
Eligibility Criteria for Filing
- U.S. Citizens and Long-Term Residents: Individuals who meet the criteria for tax purposes and plan to relinquish their citizenship or residency.
- Threshold Limits: Financial thresholds that may mandate filing depending on asset and income levels.


Legal Use and Constraints of Form 8854
Form 8854 must be used in compliance with U.S. tax laws regarding expatriation. Filing accurately and timely ensures compliance; failure leads to penalties. Legal constraints prohibit falsification or omission of required information on this form.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
- General Filing: Typically aligned with the tax filing season deadlines, though specific expatriation events might prescribe customized dates.
- Extensions: Seek an extension if necessary, following IRS guidelines, to avoid non-compliance penalties.
IRS Guidelines for Completing the Form
The IRS provides specific instructions for completing Form 8854, including detailed guidance on each section, definitions of technical terms, and how to report expatriation accurately. Familiarity with these guidelines ensures proper filing and adherence to regulatory expectations.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
- Monetary Fines: Financial penalties may be imposed for late filing or inaccurate information.
- Legal Consequences: Potential legal actions for severe or willful misrepresentations on the form.
Ensure compliance by cross-verifying information, adhering to deadlines, and using IRS resources for guidance.