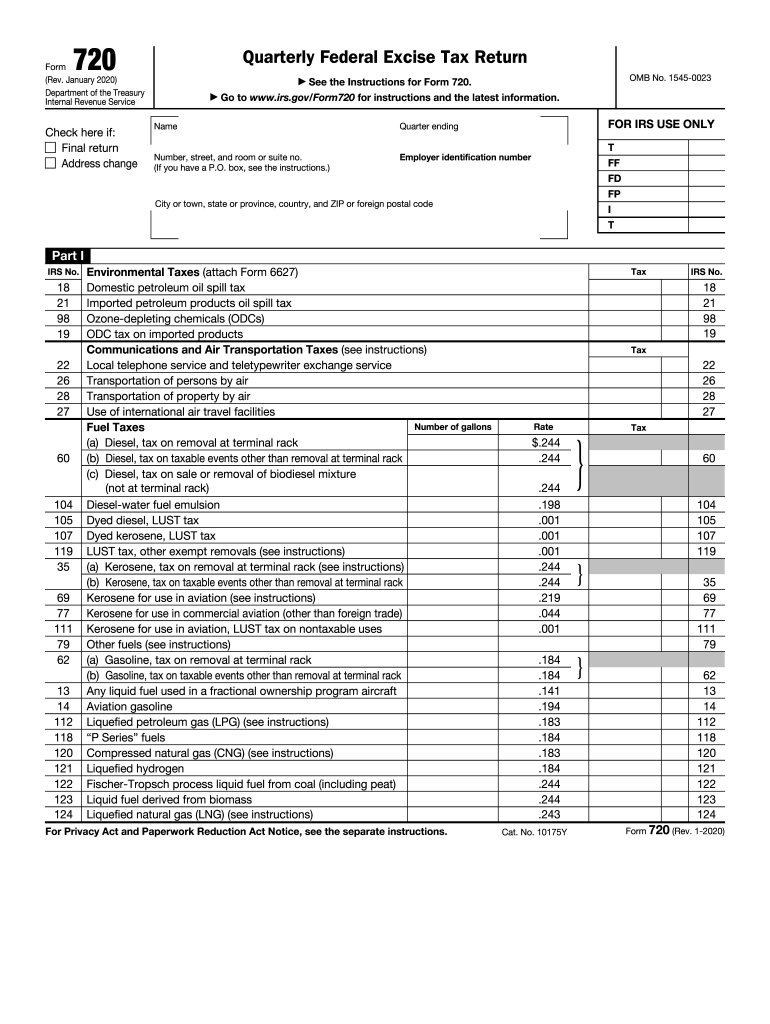Definition and Purpose of Form 720
Form 720, also known as the Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return, is a tax form utilized by businesses in the United States to report and pay federal excise taxes. These taxes apply to various products, services, and activities, including environmental taxes, fuel taxes, and other specific excise taxes mandated by federal law. The purpose of Form 720 is multifaceted:
- Tax reporting: Businesses must report their liabilities associated with federal excise taxes each quarter, ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
- Payment submission: The form serves as the mechanism for businesses to submit payments for any owed excise taxes.
- Refund claims: The form also allows taxpayers to claim refunds for overpaid excise taxes, enabling them to recover funds when applicable.
Understanding this form is critical for businesses engaged in excise-taxable activities, as failure to file correctly can result in penalties.
Steps to Complete Form 720
Filing Form 720 entails several systematic steps to ensure accuracy and compliance. The following outlines the general process for completing this form:
- Gather necessary information: Before completing the form, compile relevant financial data including total sales figures, eligible tax amounts, and previous payments.
- Obtain the form: Form 720 can be accessed through the IRS website or obtained through tax preparation software that supports federal tax filings.
- Fill out the form: Input the required data into the designated sections:
- Report specific excise taxes due based on business activities.
- Include any claims for refunds if applicable.
- Calculate the total amount owed or that will be refunded.
- Sign and date the form: Ensure you provide a signature and date to validate the submission.
- File the form by the due date: Submit the form either electronically or via postal mail, adhering to prescribed deadlines to avoid penalties.
Following these steps meticulously ensures that your Form 720 is complete and correctly submitted.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Filing deadlines for Form 720 are strategically set to align with quarterly tax reporting periods. Businesses must adhere to the following schedule to avoid late penalties:
- First Quarter: For taxes accrued from January 1 to March 31, the form is due by April 30.
- Second Quarter: For taxes from April 1 to June 30, the deadline is July 31.
- Third Quarter: Taxes accrued from July 1 to September 30 must be filed by October 31.
- Fourth Quarter: For the period from October 1 to December 31, the filing deadline is January 31 of the following year.
It is crucial to mark these dates on your calendar to avoid late payments or filed returns, which can result in fines or increased scrutiny from the IRS.
Key Elements of Form 720
Form 720 consists of several key components that taxpayers must complete accurately. Understanding these elements is essential for successful filing:
- Identifying information: This includes the business name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN), which helps the IRS to correctly process the return.
- Tax liability reporting: Various lines on the form designate distinct excise taxes. Each line corresponds to different products and services, like:
- Fuel taxes
- Air transportation taxes
- Communications taxes
- Payment calculations: Businesses are required to calculate total tax owed based on the reported liabilities and include any payments made during the quarter.
- Signature section: A signature is required to validate the accuracy of the information provided.
Ensuring that all these elements are filled out correctly can prevent complications or audits from the IRS.
Legal Use and Compliance of Form 720
The legal use of Form 720 is governed by IRS regulations that outline the requirements for excise tax reporting. Several compliance aspects are particularly noteworthy:
- Due diligence: Businesses must ensure they understand their liability under federal excise tax laws. This includes knowing which taxes are applicable to their operations.
- Accurate reporting: Incorrect information can lead to severe penalties, including fines and interest on unpaid taxes. Compliance is essential to maintain good standing with the IRS.
- Record keeping: It is vital to retain copies of submitted forms and related documentation for at least three years in case of an audit.
By adhering to the compliance aspects of Form 720, businesses can effectively mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
Important Terms Related to Form 720
Familiarity with specific terms associated with Form 720 can enhance understanding and facilitate smoother filing:
- Excise tax: A tax imposed on specific goods, services, or activities. It can be a major source of revenue for the federal government.
- Quarterly tax return: A periodic reporting requirement where taxpayers submit returns every three months to report and pay tax liabilities.
- Refund claim: A request made by a taxpayer to recover overpaid excise taxes. This can be reported on Form 720 when applicable.
- IRS: The Internal Revenue Service, the U.S. government agency responsible for tax collection and enforcing tax laws.
Being well-acquainted with these terms supports clearer communication and understanding of the excise tax process.