Definition & Meaning
The 2001 W-2 form, officially titled "Wage and Tax Statement," is a critical document used in the United States tax system. Employers issue this form to employees, detailing their annual wages and the amount of taxes withheld throughout the fiscal year. While the form's primary function is to document earnings and withholdings, it also contains important information such as social security and Medicare taxes. This comprehensive record is essential for both employees and the IRS to ensure accurate tax calculations and compliance.
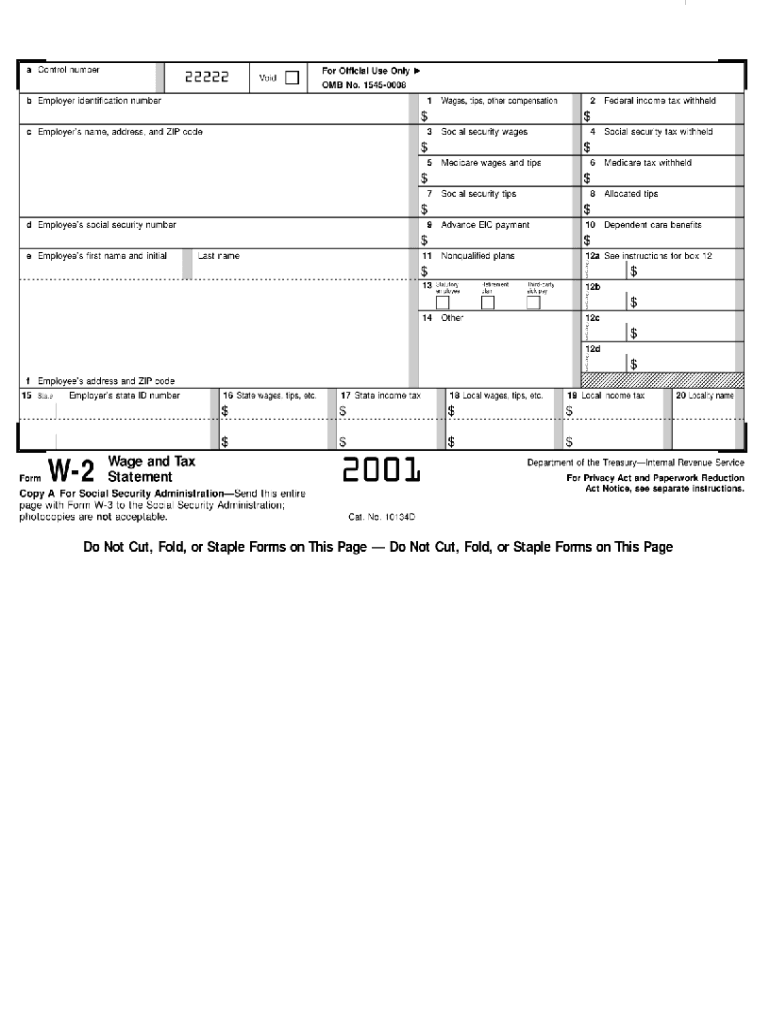
Key Elements of the 2001 W-2 Form
Understanding the key elements of the 2001 W-2 form is crucial for accurate tax reporting. The form includes:
- Employee Information: This section features the employee's full name, address, and social security number, identifying the taxpayer accurately.
- Employer Information: Provides the employer's name, address, and identification number, linking the document to the correct business entity.
- Wage Details: Displays total earnings, including salaries and tips, which are crucial for calculating tax liabilities.
- Tax Withholding: Breaks down federal income tax, social security, and Medicare taxes deducted from the employee's paychecks.
- Box 12 Codes: Contains codes related to specific benefits or deductions, providing additional tax-related information.
- State and Local Taxes: Reflects any taxes withheld at the state or local levels, offering a comprehensive view of the individual's tax situation.
How to Obtain the 2001 W-2 Form
Employees generally receive their W-2 form by January 31st of the following year, allowing them ample time to file their taxes. Obtaining the 2001 W-2 form may involve:
- Direct from Employer: Employers are required to provide this form by mail or electronic delivery.
- Online Self-Service: Some companies offer digital access through employee portals.
- Requesting Copies: If the form is lost, employees can request a duplicate from their employer's payroll department.
- Contacting the IRS: If the form is not provided, contacting the IRS may prompt employer compliance.
Steps to Complete the 2001 W-2 Form
Filing taxes with a W-2 form requires careful completion to ensure accuracy. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Verify Personal Information: Check that your name, address, and social security number are correct.
- Review Wage and Tax Details: Ensure all earnings and taxes withheld are accurately reported.
- Consider Box 12 Codes: Familiarize yourself with any codes present in Box 12, as they may affect your tax return.
- Calculate State and Local Details: Be aware of any taxes withheld for state and local purposes.
- Submit with Tax Return: Use the form to complete your 1040 or 1040EZ and submit by the tax deadline.
IRS Guidelines
Adhering to IRS guidelines is essential when handling the W-2 form. Important considerations include:
- The form must be filed with your income tax return by the April 15th deadline.
- Keeping a copy of the form for personal records is highly recommended.
- Correcting any errors on the W-2 promptly, typically by contacting your employer.
Filing Deadlines / Important Dates
Timely submission of the 2001 W-2 form is crucial for compliance. Key dates to remember include:
- January 31: Deadline for employers to distribute W-2 forms to employees.
- April 15: Standard deadline for individuals to file their tax returns with the IRS.
- October 15: Deadline extension for tax return filing if a request was made by April 15.
Digital vs. Paper Version
The choice between digital and paper versions of the W-2 form offers flexibility:
- Digital Version: May be preferred for its convenience and ease of access. Often available through employer portals and allows for seamless integration with tax software.
- Paper Version: Traditional method, useful for those who prefer hard copies or lack digital access.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with W-2 form requirements can result in significant penalties:
- For Employees: Inaccurate reporting may lead to penalties from the IRS, emphasizing the importance of accuracy in a tax return.
- For Employers: Fines for failing to provide W-2 forms or submitting incorrect information, stressing the need for timely and correct distribution.
Understanding and handling the 2001 W-2 form with care ensures accuracy in your tax filings and prevents potential legal and financial issues.