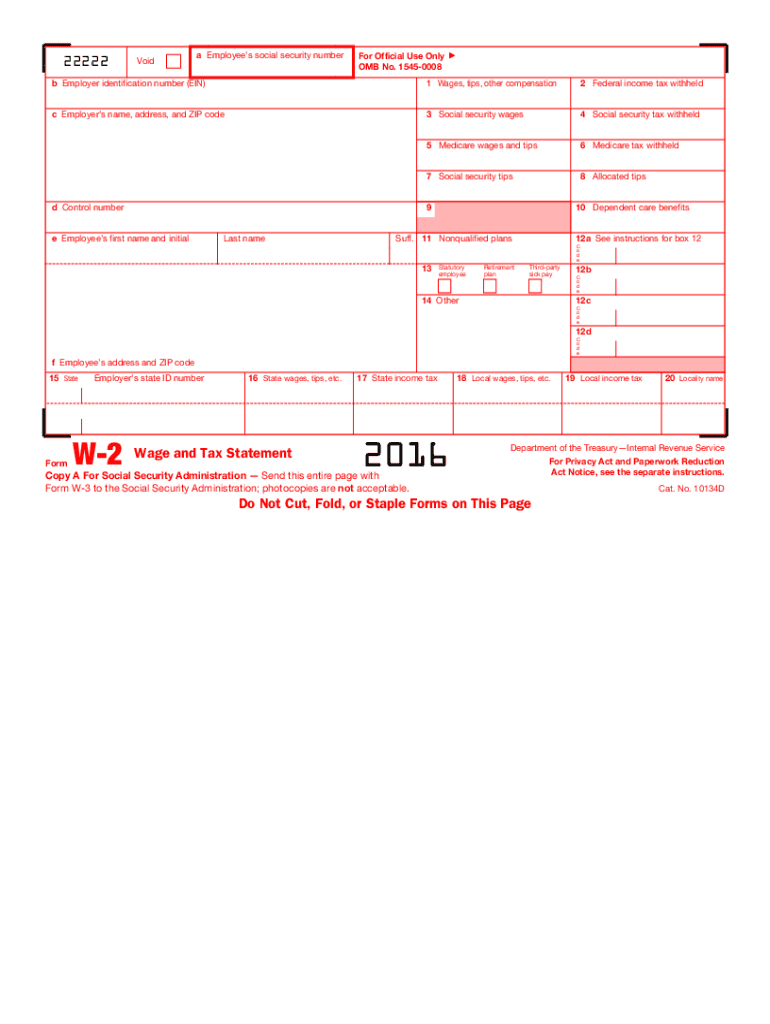
Definition and Purpose of the 2016 W-2 Form
The 2016 W-2 Form is a critical tax document used in the United States by employers to report wages paid to employees and the taxes withheld from them. It's officially known as the "Wage and Tax Statement" and plays a pivotal role in the annual tax filing process for both employees and employers. Each employer is required to furnish a W-2 form for every employee who received any form of remuneration during the year, including wages, tips, and other compensation.
Components of the Form
- Employee's Personal Information: Includes name, address, and Social Security Number (SSN).
- Employer's Information: Contains the employer's name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- Income Details: Reports wages, tips, and other forms of income earned by the employee.
- Tax Withholdings: Lists federal, state, and local taxes withheld, as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Obtaining the 2016 W-2 Form
To obtain a 2016 W-2 Form, employees should first contact their employers. Employers are required to issue copies to employees no later than January 31 of the following year. If misplaced or not received, employees can request a duplicate from the employer. For those unable to retrieve it from the employer, the IRS can be contacted for assistance after February 14.
Alternate Sources
- Online Access: Many employers offer electronic access to W-2 forms through payroll services or employee portals.
- Payroll Services: Companies using payroll services like ADP or Paychex often provide digital download options for W-2 forms.
Steps to Complete the 2016 W-2 Form
- Gather Required Information: Collect accurate employee details and financial data.
- Fill Employee and Employer Sections: Enter names, addresses, and identification numbers.
- Input Earnings and Withholdings: Record wages and taxes withheld in the respective boxes.
- Double Check for Accuracy: Ensure all entries are correct to avoid IRS penalties.
- Distribute Copies: Provide the employee with copies B, C, and 2 for filing with federal, state, and local tax returns.
Filing Copies with SSA
Employers must send Copy A of the W-2 Form to the Social Security Administration. This can be done electronically or via mail, depending on the employer's preference and capabilities.
Legal Use of the 2016 W-2 Form
The W-2 Form is legally mandated as part of the reporting process to comply with IRS requirements. It helps reconcile the amount of the taxes withheld from an employee's paycheck and the amount paid to the IRS.
Employee Responsibilities
- Ensure accuracy of personal and financial data on the form.
- Use the W-2 to complete personal tax returns accurately.
- Report any discrepancies immediately to the employer to correct the information before the filing deadline.
Key Elements of the 2016 W-2 Form
The 2016 W-2 Form consists of several critical elements that serve specific purposes:
- Wages, Tips, Other Compensation (Box 1): Total taxable income.
- Federal Income Tax Withheld (Box 2): Amount withheld for federal taxes.
- Social Security Wages (Box 3): Income subject to Social Security Tax.
- Medicare Wages and Tips (Box 5): Total income subject to Medicare tax.
Additional Elements
- State and Local Information (Boxes 15-20): State and local tax details, including wages and withholdings specific to the region.
IRS Guidelines for the 2016 W-2 Form
The IRS provides specific guidelines regarding the preparation and submission of W-2 forms:
- Scannable Forms Required: Forms must be scannable; therefore, precise printing and accurate data are mandatory.
- Electronic Filing: Encouraged for employers with more than 250 W-2 forms to file.
Addressing Errors
Employers should promptly correct any errors using Form W-2c, which is the corrected version of the Wage and Tax Statement.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Timely submission of the 2016 W-2 Form is crucial for compliance:
- Employee Distribution Deadline: January 31 of the following year.
- SSA Filing Deadline: January 31 for both paper and electronic submissions.
Late Submission Consequences
Failure to meet these deadlines can result in penalties imposed by the IRS based on the duration of the delay and the number of employees affected.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with W-2 filing requirements can lead to several penalties:
- Failure to Furnish Correct Payee Statements: Charges per form that increases over time.
- Intentional Disregard Penalties: Significantly higher for intentional failures to file.
Avoiding Penalties
To avoid penalties, ensure accurate preparation and timely submission of forms, adhere to IRS instructions, and maintain good communication with both employees and the IRS.