Definition & Meaning
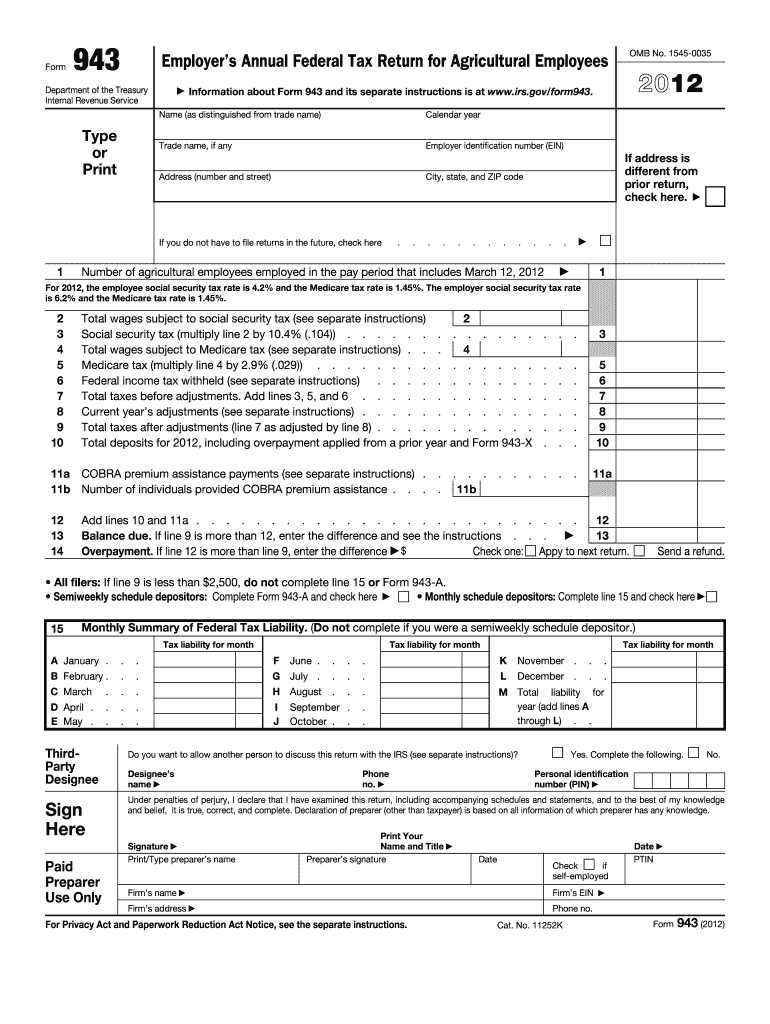
Form 943 for 2012 is the Employer's Annual Federal Tax Return specifically designed for agricultural employees. It serves as a mandatory reporting tool for employers to communicate wages paid to agricultural workers and the corresponding federal taxes withheld. The form also calculates the total taxes owed, ensuring that agricultural employers fulfill their obligations to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). By capturing essential data, the form aids in annual tax reconciliation, providing critical insights into employment taxation specific to the agricultural sector.
Steps to Complete the 943 Form 2012
-
Gather Required Information: Begin with your Employer Identification Number (EIN), employee wage data, and details about tax withholdings for the year.
-
Input Total Wages: Record the total wages paid to agricultural employees during the year broken down by different categories if necessary.
-
Calculate Taxes Owed: Use the provided IRS guidelines on the 943 form to compute the federal taxes owed based on the wage data. This includes accounting for Social Security and Medicare taxes.
-
Utilize Form 943-V Payment Voucher: If a payment is required, complete and attach Form 943-V to facilitate the payment process of the taxes owed.
-
Review and Confirm Details: Double-check all entries to ensure accuracy, particularly the tax calculations and the filled fields. Ensure that all data aligns with year-end payroll records.
-
Sign and Date: As the employer, provide a signature to authenticate the information on the form, affirming its accuracy and completeness.
How to Use the 943 Form 2012
Using Form 943 involves annual completion by employers who paid remuneration to agricultural workers. This includes those involved in farming operations like crop production, livestock raising, and others. Employers must accurately report this income to comply with federal regulations. The form aids in systematic tax calculation and payment submission, ensuring that the employer's contributions to Social Security and Medicare are current and correctly attributed throughout the fiscal year.
Who Typically Uses the 943 Form 2012
Form 943 primarily applies to business entities involved in agriculture, such as:
- Farm owners or operators who employ fieldhands, harvest workers, or livestock caretakers.
- Agricultural cooperatives handling worker payrolls.
- Businesses and individuals that meet the IRS's definition of agricultural employers.
These users engage with Form 943 to fulfill their federal tax obligations efficiently and to ensure compliance with employment tax laws relevant to the agricultural sector.


Required Documents
Completing Form 943 necessitates several documents:
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): Essential for form submission as it identifies the business entity.
- Employee Payroll Records: Provide comprehensive data on wages paid throughout the year.
- Year-End Summary of Tax Withholdings: Information regarding federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare withholdings.
- Previous Year's Tax Documents: Use last year's filings as a reference to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Ensuring availability of these documents accelerates form completion and reduces the potential for errors.
Filing Deadlines / Important Dates
For the 2012 tax year, Form 943 was due by January 31, 2013. Timely filing is crucial to avoid penalties and interest. Employers who made timely deposits and full payments on all taxes due could extend the filing deadline to February 10, 2013, reflecting the IRS's adherence to biannual deposit schedules for some agricultural employers.
Form Submission Methods (Online / Mail / In-Person)
Employers can opt for various submission methods:
- Electronic Filing: Use IRS-authorized e-file services for efficient and easy submission.
- Mail: Send completed forms and payments through the postal service using IRS-provided addresses specific to geographic locations and payment requirements.
- In-Person Submission: Deliver the form to an IRS office if preferred; although electronic and mail methods are typically encouraged for efficiency.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to file Form 943 or to file by the due date can result in penalties from the IRS. These fines accrue based on the degree of lateness and the amount of tax due. Understanding and adhering to filing deadlines is essential to mitigate potential financial penalties, preserve business reputation, and prevent accumulation of interest on unpaid tax liabilities.