Definition and Meaning
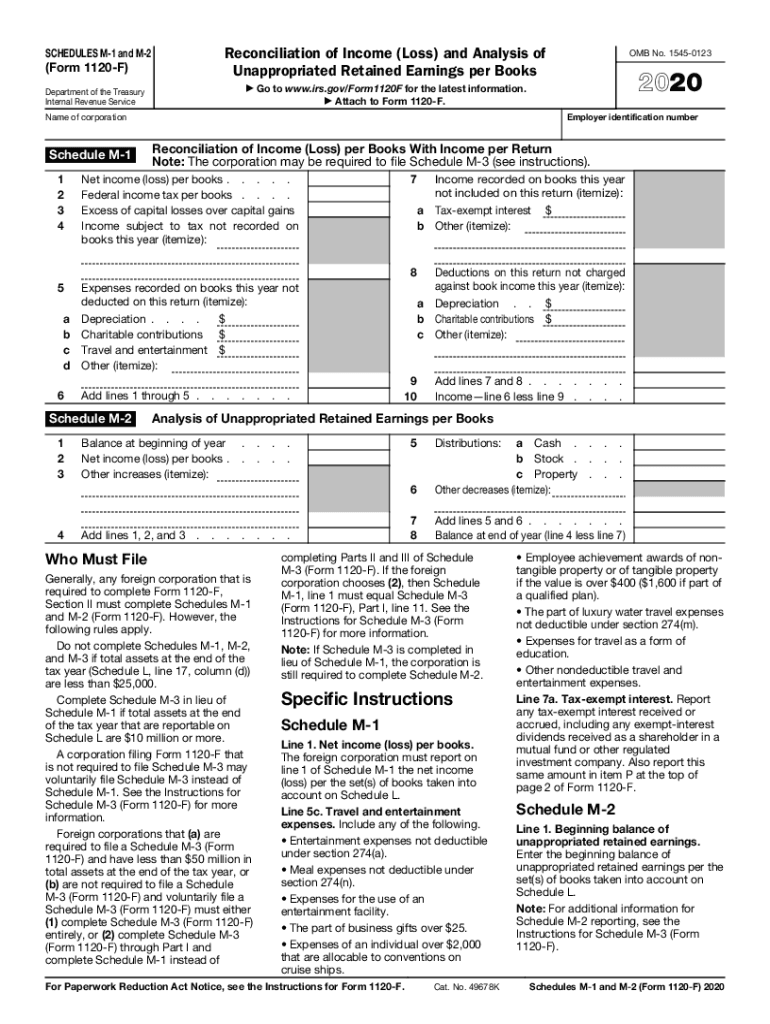
Form M-1 is an essential part of IRS Form 1120-F used by foreign corporations to reconcile their book income with taxable income. This form plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with U.S. tax laws, enabling accurate reporting of financial activities by detailing adjustments to income and expenses. By outlining these reconciliations, Form M-1 assists corporations in understanding their tax obligations and ensuring that all incomes are reported correctly to the Internal Revenue Service.
How to Use Form M-1
Using Form M-1 involves accurately gathering and presenting financial data that reflects your corporation's income tax requirements. Begin by collecting information on book income and then systematically adjust this for the differences that arise due to tax laws. It's crucial to detail all discrepancies clearly and consistently, ensuring that the final taxable income aligns with federal requirements. Double-check calculations and entries for accuracy, considering revisions or amendments where necessary.
Steps to Complete the Form M-1
-
Gather Financial Statements: Collect all relevant income and expense reports that detail your corporation’s financial activities.
-
Identify Discrepancies: Examine financial reports to spot differences between book income and taxable income due to deferrals, adjustments, or deductions allowed.
-
Adjust Book Income: Using the identified discrepancies, adjust your book income accordingly in line with IRS guidelines.
-
Complete the Form: Fill out Form M-1 by clearly listing adjustments and the reconciled figures for your corporation.
-
Review for Accuracy: Ensure that all information is accurately reported and abstraction consistently applied.
-
Submit with Form 1120-F: Attach the completed Form M-1 to Form 1120-F and submit to the IRS by the relevant deadline.
Key Elements of Form M-1
Form M-1 features several crucial components, including:
- Income Reconciliation: Adjusting the book income to reconcile with taxable income as per tax laws.
- Expense Variations: Noting discrepancies in expenses due to different handling in book and tax records.
- Deduction Details: Specifying items that affect the difference between book income and taxable income.
- Adjustment Entries: Additional entries for tax deferrals and discrepancies in reporting that affect reconciliation.
Who Issues the Form
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) issues Form M-1 as part of the compliance requirements for foreign corporations filing Form 1120-F. This issuance is integral for standardizing and systematizing how these corporations report their financial and tax obligations.
IRS Guidelines
The IRS provides detailed instructions to ensure accurate completion of Form M-1. These guidelines emphasize the importance of presenting discrepancies fully and justifying each adjustment. Compliance with these instructions is crucial for avoiding inaccuracies and potential penalties, and ensures thorough documentation of each item affecting reconciliation.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
- Regular Deadline: Submit Form M-1 with Form 1120-F by April 15th, following the tax year, if the corporate year aligns with the calendar year.
- Extension Deadline: If an extension is filed using IRS Form 7004, the submission deadline may move to October 15th.
Adhering to these deadlines is crucial, as late submissions may incur penalties.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Penalties for failing to accurately complete or timely file Form M-1 may include:
- Monetary Fines: Related to inaccuracies or late submission.
- Interest Accrual: On unpaid tax amounts due to discrepancies not reconciled in a timely manner.
- Audits: Increased likelihood of IRS audits due to insufficient or erroneous filings.
Understanding and mitigating these penalties can prevent significant legal and financial repercussions for corporations.