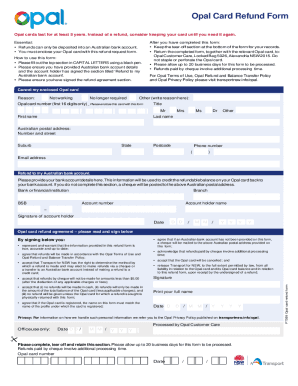
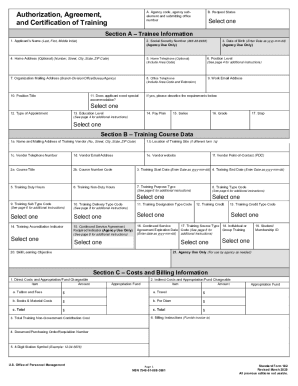
Definition & Meaning
The term "gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric: MFgwCgYEVQgBAQICAf8DSgAwRwJAW2sNKK9AVtBzYZmr6aGjlWyK3XmZv3dTINen TWSM" refers to an asymmetric cryptographic key, which is often used in secure communications to encrypt or authenticate information. This specific key likely plays a role in governmental or large-scale organizational processes where data integrity and security are paramount. Unlike symmetric keys, which use the same key for both encryption and decryption, asymmetric keys operate with a pair of keys: one public and one private. This dual-key nature enhances security by allowing encryption without exposing the private decryption key.
How to Use the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric
To use the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric key, determine its purpose within your workflow. Generally, such keys are integral in operations requiring the secure transmission of data, such as document signing or user authentication. Implement the key in your security protocols by configuring your software system to recognize and utilize it for encryption tasks. Ensure that the public part of the key is distributed appropriately, maintaining the confidentiality of the private key at all times. Use advanced software or cryptographic libraries known for supporting asymmetric cryptography to handle these keys efficiently.
Common Use Cases
- Document Signing: Apply the private key to sign documents electronically, ensuring authenticity.
- Secure Communications: Enable encrypted messaging services, where only intended recipients with the correct key pair can decipher messages.
- Access Control: Restrict system access by verifying the identity of users via unique key-pair associations.
Steps to Complete the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric
Using the key effectively involves several steps:
- Identification: Ensure that the key aligns with your security needs and organizational standards.
- Configuration: Set up your system to use the key appropriately, ensuring compatibility with your encryption software.
- Testing: Perform tests to confirm that encryption and decryption are functioning as intended.
- Deployment: Implement the key in live systems while continuously monitoring for potential security breaches.
Why Should You Use gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric
Utilizing the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric offers unparalleled security benefits. Asymmetric keys are essential in environments requiring robust data protection, such as government agencies or large corporations dealing with sensitive information. Their application reduces the risk of data interception during transmission and ensures that any shared data remains confidential and untampered with. These keys also facilitate compliant electronic transactions, creating legally binding digital signatures that replace the need for physical counterparts.
Key Elements of the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric
Understanding the components and functionality of the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric is crucial:
- Security: High level of security due to distinct encryption and decryption keys.
- Scalability: Suitable for managing complex systems where multiple users need secure access.
- Flexibility: Supports various protocols and services in digital communications.
- Interoperability: Can integrate with existing security infrastructure without major overhauls.
Important Terms Related to gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric
Familiarize yourself with key cryptographic terminology to effectively use this form:
- Encryption: The process of converting data into a coded form to prevent unauthorized access.
- Decryption: Reversing encryption to access the original data.
- Public Key: A key that can be shared openly to enable encrypted communication.
- Private Key: A secure, confidential key used to decrypt data encoded with the corresponding public key.
Security Implications
The security of the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric is paramount. All individuals handling the key must enforce strict access controls to prevent unauthorized parties from compromising the system. Regular audits and security updates are essential to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of the keys. Furthermore, make use of secure channels for key distribution to avoid interception during transmission.
Examples of Using the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric
Practical scenarios for this form include:
- Enterprise Authentication Systems: Use the key to authenticate user logins securely.
- Encrypted Email Services: Exchange sensitive information through email without fear of interception.
- Verifying Transactions: Securely verify and complete transactions electronically, essential for e-commerce and banking systems.
Compatibility with Software Systems
To effectively deploy the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric, ensure compatibility with encryption software like OpenSSL, which supports advanced cryptographic actions. Many enterprise-level security systems, such as those used by financial institutions, are equipped to handle such keys seamlessly. Integrating the key with these systems often requires technical consultation with IT specialists to leverage its full potential while ensuring system integrity.
Conclusion
The comprehensive utility of the gov Originator-Key-Asymmetric lies in its secure communication capabilities, adaptable to various organizational needs. By integrating it with your current systems, you ensure a robust level of data security, conforming to modern cryptographic standards. This key represents a cornerstone in any secure encryption strategy where the protection of data is critical.