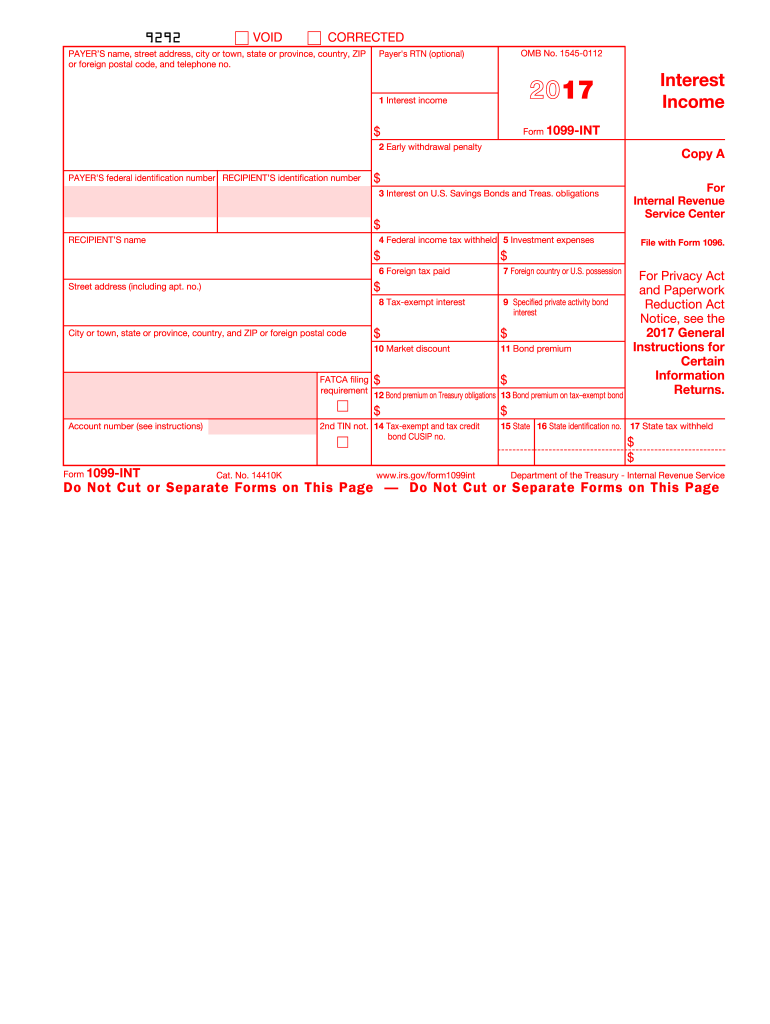
Definition & Meaning
The 1099-INT form is a document used by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to report interest income paid to taxpayers. Specifically for the year 2017, this form serves a critical function in tax reporting for individuals who have received interest payments from financial institutions or investment entities. Interest income includes payments from savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and other financial instruments, which must be reported as part of the taxpayer's annual tax return. The form ensures that individuals accurately account for all interest earnings and pay the appropriate taxes on them.
How to Use the 1099-INT 2017 Form
To use the 1099-INT 2017 form effectively, it is essential to first understand the information it captures. The form typically includes details such as the total interest income earned for the year, federal tax withheld, and any early withdrawal penalties incurred. Taxpayers should gather any documents from banks or financial institutions that issued interest payments. When filing taxes, this form is referenced to ensure all interest income is accounted for, which determines the total tax liability or refund. Accuracy is vital to avoid the risk of underreporting income, which could result in fines or penalties.
Steps to Complete the 1099-INT 2017 Form
- Gather Information: Collect all necessary documents, including bank statements and any prior correspondence related to interest earnings.
- Enter Personal Details: Ensure that the taxpayer's name, address, and Social Security number are correctly entered.
- Report Interest Income: Complete Box 1 for Interest Income to reflect the total interest earned during the calendar year.
- Withholding Taxes: If applicable, fill in Box 4 to report any federal income tax withheld.
- Check for Mistakes: Review the completed form for accuracy, verifying all figures and information.
- Submission: Submit the form electronically if using a software platform like DocHub, or mail it to the IRS if submitting manually.
Important Terms Related to 1099-INT 2017 Form
- Payer: The entity, usually a financial institution, responsible for paying interest.
- Payee: The individual or entity receiving interest payments.
- Interest Income: Earnings accumulated from investments or savings, mandatory to report on the 1099-INT.
- Federal Withholding: Any income tax withheld by the payer from interest payments, often found in Box 4.
- Early Withdrawal Penalty: Fees incurred for withdrawing funds from certain financial products before maturity, reported in Box 2.
Filing Deadlines / Important Dates
Understanding deadlines is crucial for compliance with IRS regulations. For the 1099-INT form covering the year 2017, payers were required to furnish copies to recipients by January 31, 2018, and submit them to the IRS by April 2, 2018, for electronic filing. Failing to meet these deadlines could result in heightened accuracy penalties or additional filing liabilities. Taxpayers should be vigilant about these deadlines to ensure timely and correct submissions.
IRS Guidelines
The IRS provides comprehensive guidelines on how to complete and file the 1099-INT. These guidelines emphasize the importance of accuracy and completeness in reporting. The IRS also mandates that certain criteria be met for issuing these forms, such as interest income thresholds and specific types of interest-bearing accounts. The guidelines serve to clarify who needs to file the form and how it should be reported on one's tax returns to avoid conflicts or penalties.
Who Typically Uses the 1099-INT 2017 Form
This form is primarily used by entities such as banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions responsible for paying interest to customers. Any individual or organization receiving interest income exceeding $10 within the tax year should expect to receive a 1099-INT. It is particularly relevant for those with significant savings or investments, retirees drawing income from CDs, or businesses managing multiple interest-generating accounts.


Required Documents
When preparing to fill out a 1099-INT form, having the proper documentation is essential for accuracy. The necessary documents include end-of-year financial statements from payers, previous years' tax returns for reference, and any records of federal tax withholdings applied to interest earnings. Collecting these documents ensures that all interest income and related deductions are thoroughly and accurately reported, helping to facilitate a smooth filing process.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to file the 1099-INT form on time, or submitting incomplete or inaccurate information, can lead to IRS-imposed penalties. Penalty amounts vary based on the degree of non-compliance and the duration of the delay. It's imperative for both payers and recipients to adhere to the guidelines and ensure the form is completed accurately to avoid potential fines, interest charges, or further legal action by the IRS.
Examples of Using the 1099-INT 2017 Form
Consider a scenario where a taxpayer has been receiving interest income from multiple savings accounts. Each financial institution would issue a separate 1099-INT form reflecting the interest payments over the year. The taxpayer would need to aggregate these forms when calculating total interest income for their tax return. This enables an accurate representation of their financial earnings, influences their tax bracket, and helps determine their overall tax obligation for the year.