Definition and Purpose of IRS Tax Forms
IRS tax forms are essential documents issued by the Internal Revenue Service to facilitate the process of filing and reporting taxes by both individuals and businesses. A variety of forms exist, each serving specific tax situations and needs. They are designed to capture the critical financial information required for accurate tax assessment. Depending on one's tax situation, the appropriate form must be selected to correctly compute and report income, deductions, and tax payments. Understanding the purpose of these various forms enables taxpayers to choose the right one for their financial scenario, ensuring compliance with federal tax laws.
How to Use IRS Tax Forms
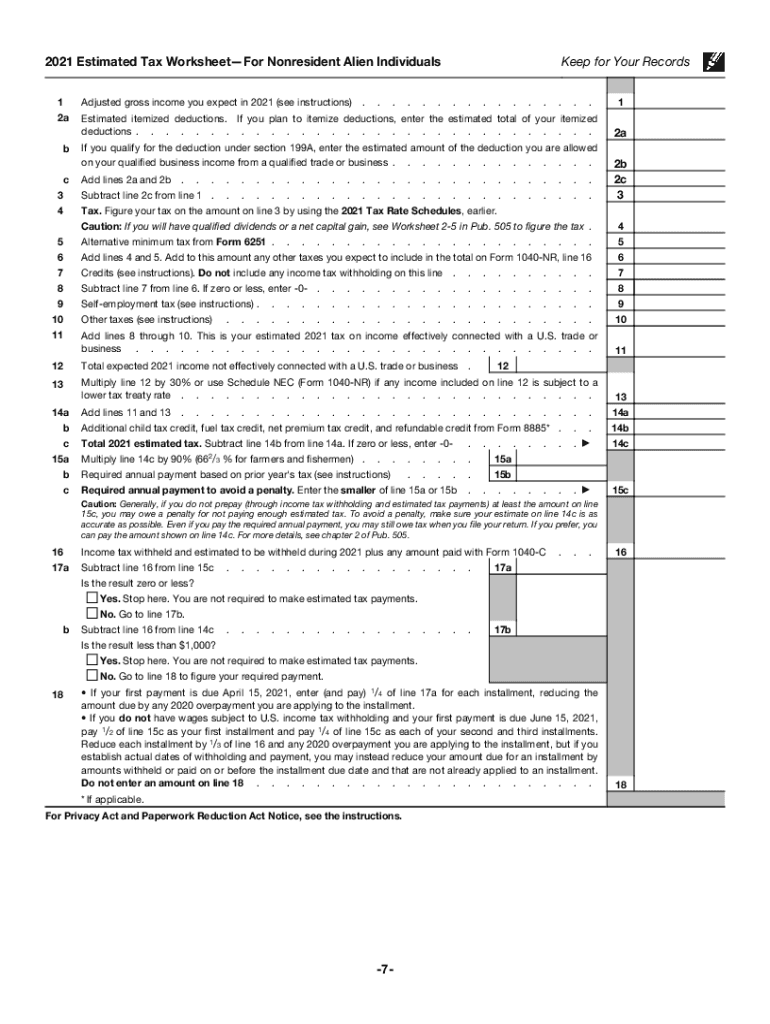
Navigating IRS tax forms can seem daunting, but understanding their structure and function simplifies the process. Begin by selecting the appropriate form for your situation; for instance, the 1040 series is commonly used for individual tax returns. Each form comprises sections where you must input specific details such as personal information, income, deductions, credits, and taxes owed or refunds. Follow the instructions meticulously, which accompany each form, to ensure that all required fields are correctly filled out. Using an organized approach, gather all necessary financial documents beforehand to prevent errors and omissions during the completion process.
Steps to Complete an IRS Tax Form
Completing an IRS tax form involves several precise steps:
- Gather Financial Documents: Collect W-2s, 1099s, receipts, and records of deductions and credits to correctly report income and expenses.
- Choose the Correct Form: Identify which IRS tax form corresponds to your employment status, income type, or filing needs (e.g., 1040 for individuals, 1120 for corporations).
- Read Instructions Carefully: Each form comes with detailed instructions that explain how to fill out each section.
- Complete Personal Information: Accurately enter your personal details, including full name, Social Security number, and filing status.
- Report Income Accurately: Input income figures from various sources as indicated on your financial documents.
- Calculate Deductions and Credits: Deductible expenses and eligible tax credits should be precisely calculated and recorded to reduce taxable income.
- Double-Check for Errors: Ensure accuracy by reviewing all entries to avoid miscalculations or missing information.
How to Obtain IRS Tax Forms
IRS tax forms can be acquired through several convenient methods:
- Online: Download forms directly from the IRS website, where the most current versions are always available.
- Tax Software: Many tax preparation software packages include the ability to access and fill out IRS forms as part of their service.
- Local IRS Office: Visit a nearby IRS office to pick up physical copies of forms needed for filing.
- Mail Order: Request forms to be mailed directly to your residence by calling the IRS forms line.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Awareness of filing deadlines is crucial for timely submission and avoiding penalties. Generally, tax returns are due by April 15th for individuals, unless that date falls on a weekend or holiday, in which case it is pushed to the next business day. For businesses, deadlines may vary depending on the type of entity. Extensions can be requested, granting additional time to file without incurring a late submission penalty. Monitoring any changes in deadlines due to legislative updates or exceptional circumstances, such as natural disasters, is essential in ensuring compliance.
Required Documents for IRS Forms
Certain documents are necessary to accurately complete IRS tax forms:
- Income Statements: W-2 from employers, 1099 forms for freelance or investment income.
- Deductions and Credits Documentation: Receipts, invoices, and statements supporting claimed deductions and tax credits.
- Proof of Taxes Paid: Previous year’s tax return as a reference and records of estimated tax payments made throughout the year.
- Identification Documents: Social Security numbers or taxpayer identification numbers for filers and their dependents.
Legal Use of IRS Tax Forms
Using IRS tax forms correctly and lawfully is the taxpayer's responsibility. Each form is legally binding, requiring truthful and precise reporting of financial information. Misreporting can lead to audits or legal consequences including fines and penalties for tax evasion. Taxpayers are encouraged to seek professional advice or utilize certified tax preparation services to ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid inadvertently providing misleading or incorrect information.
Software Compatibility with IRS Tax Forms
IRS tax forms can often be completed using compatible software such as TurboTax or QuickBooks. These platforms guide users through form selection and completion, providing support for accurate tax preparation while helping minimize errors. They also facilitate electronic filing (e-filing) directly to the IRS. Using software can streamline the submission process, offering additional features like deductions maximization tools, real-time tax refund tracking, and automatic calculations, which are beneficial in ensuring the integrity and correctness of reported tax information.