Definition and Purpose of Form 1040-ES
Form 1040-ES, also known as the Estimated Tax for Individuals form, is an essential document required by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for the payment of estimated taxes. This form is used by individuals, including sole proprietors, partners, and S corporation shareholders, who expect to owe taxes of $1,000 or more when their returns are filed. It helps taxpayers calculate their estimated tax amounts for income not subject to withholding, such as self-employment earnings, dividends, interest, and rent.
- Purpose: Helps taxpayers pay estimated taxes quarterly.
- Audience: Nonresident aliens and taxpayers with income beyond wages.
How to Obtain Form 1040-ES
Form 1040-ES can be easily obtained from various sources to ensure taxpayers have the tools needed to calculate their taxes.
- IRS Website: The most common way to access the form is through the official IRS website where it’s available for download.
- By Mail: Request a paper copy by using the order form feature on the IRS website.
- In Person: Visit local IRS offices for physical copies.
- Software Programs: Tax filing software often includes this form for user convenience.
Key Elements of Form 1040-ES
Several critical components must be understood when using Form 1040-ES to ensure compliance with IRS requirements.
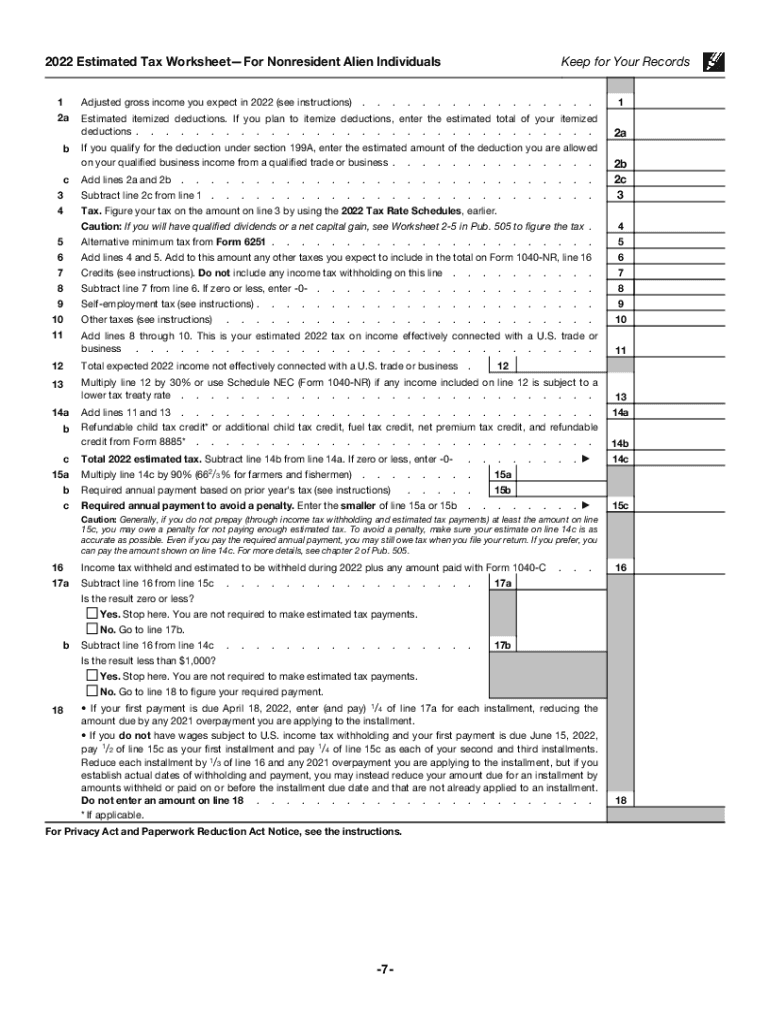
- Estimated Tax Worksheet: Guides taxpayers through the calculation of tax liabilities.
- Tax Payment Coupons: Used for mailing payments if not paying electronically.
- Instructions for Farmers and Fishermen: Special provisions for these groups due to fluctuating income.
- Schedule A for Adjustments: Details required adjustments to income and credits.
Steps to Complete Form 1040-ES
Completing Form 1040-ES involves calculations and entering data accurately.
-
Calculate Estimated Tax:
- Use previous year's tax return as a baseline.
- Account for expected changes in income.
-
Fill Out the Estimated Tax Worksheet:
- Requires input on expected income, deductions, and credits.
-
Determine Payment Amounts:
- Calculate quarterly installments.
-
Make Payments:
- Utilize provided Payment Vouchers.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Timely payments are crucial to avoid penalties. Here's a breakdown of key filing dates.
-
Quarterly Deadlines:
- April 15
- June 15
- September 15
- January 15 (following year)
-
Special Dates for Farmers and Fishermen: Only one payment by January 15 for certain conditions.
IRS Guidelines for Using Form 1040-ES
The IRS provides comprehensive guidelines to aid in understanding the submission process and the responsibilities of taxpayers.
- Follow Instructions: Carefully review the form’s instructions for accuracy in submission.
- Tax Rate Changes: Review any changes in tax laws affecting the current tax year.
- Record Keeping: Maintain copies of all payments and forms for personal records.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to make estimated tax payments, or owing insufficient amounts, can lead to penalties.
- Underpayment Penalty: Imposed for insufficient estimated tax payments.
- Late Payment Fee: Charged if payments are made after the due date.
Who Typically Uses Form 1040-ES
This form is designed for individuals who earn income not typically subject to withholding:
- Self-Employed Individuals: Such as freelancers and independent contractors.
- Investors: Those who earn dividends or interest income.
- Business Owners: With pass-through income from S corporations or partnerships.
Through detailed understanding and punctual submission, Form 1040-ES helps ensure compliance with tax obligations and avoids the inconvenience of late penalties.