Keep track of your 2 of liabilities on Balance Sheet Templates and boost your record precision and relevancy. Ensure your business transparency and effortlessly modify, fill out, and store your documents in your DocHub account.

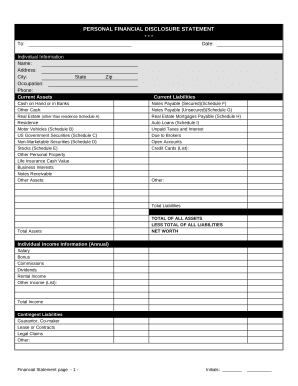
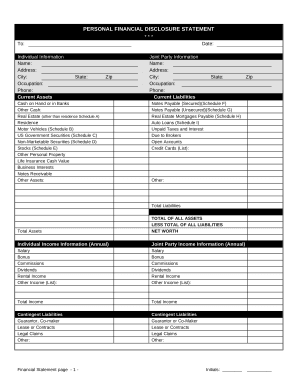



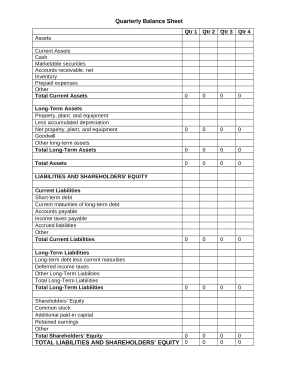


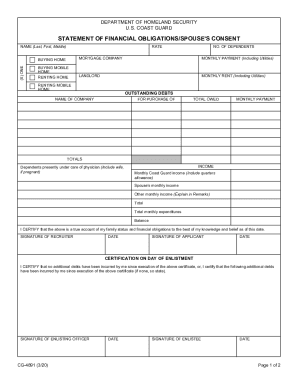
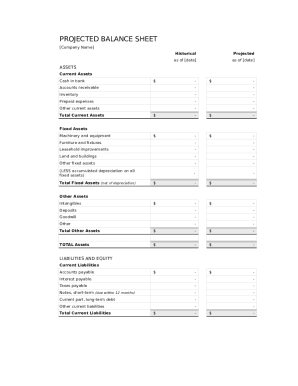
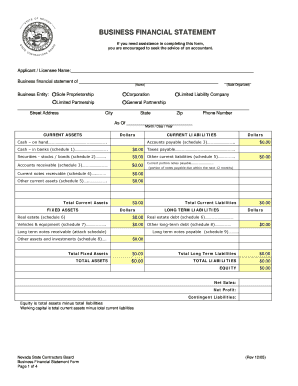



Speed up your file administration using our 2 of liabilities on Balance Sheet Templates library with ready-made templates that suit your needs. Access the document template, alter it, fill it, and share it with your contributors without breaking a sweat. Start working more effectively with your documents.
How to use our 2 of liabilities on Balance Sheet Templates:
Discover all of the opportunities for your online document administration with our 2 of liabilities on Balance Sheet Templates. Get your totally free DocHub account today!