Definition and Meaning of PR
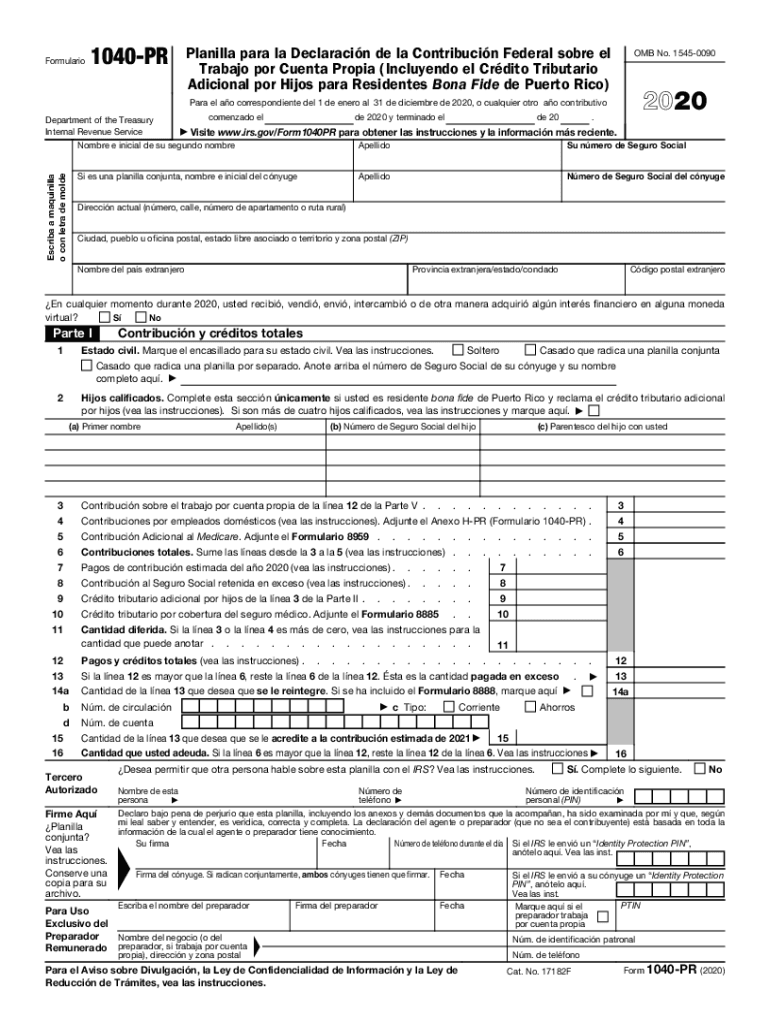
The PR form, specifically the Form 1040-PR, serves as a federal tax return for individuals in Puerto Rico who are self-employed. This form is crucial for reporting income generated from self-employment to the IRS. The 1040-PR includes sections for reporting earnings, claiming deductions, and calculating self-employment taxes, making it essential for compliance with U.S. tax regulations.
In particular, the Form 1040-PR differs from the standard federal Form 1040 due to its specific focus on individuals living and working in Puerto Rico. It is designed to accommodate the unique aspects of Puerto Rican taxation, providing guidelines on how residents can claim education credits, child tax credits, and other pertinent deductions. Understanding the 1040-PR is vital for those who are self-employed, as it helps ensure that tax obligations are met accurately.
Steps to Complete the PR Form
Completing the 1040-PR form involves several important steps to ensure accurate reporting and compliance. The following are the steps required when filling out the form:
- Obtain the Form: Access the 1040-PR from the IRS website or request a paper version from the IRS.
- Gather Required Documents:
- A copy of your previous year’s tax returns.
- Records of all self-employment income and expenses.
- Any relevant 1099 forms received during the tax year.
- Fill Out Personal Information: Enter your name, address, and Social Security number at the top of the form.
- Report Income:
- List all income earned from self-employment and any other sources.
- Include additional earnings such as interest or dividends.
- Claim Deductions:
- Identify eligible deductions related to self-employment, including business expenses.
- Keep thorough records to support deductions claimed.
- Calculate Tax Liability: Use the provided sections of the form to determine the self-employment tax owed.
- Sign and Date: Make sure to sign and date the form before submission.
Following these steps can help ensure that the form is completed accurately and submitted on time.
Important Terms Related to PR
When dealing with the 1040-PR form, several key terms are essential for understanding the context and requirements of Puerto Rico’s tax laws:
- Self-Employment Tax: A tax consisting of Social Security and Medicare taxes primarily for individuals who work for themselves.
- Tax Credits: Reductions in the total tax due, which may include credits like the Child Tax Credit or the Earned Income Tax Credit.
- Filing Status: Refers to the category (e.g., single, married filing jointly) chosen by the taxpayer affecting tax rates and credits.
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): An individual’s total gross income minus specific deductions; it is used to determine eligibility for various tax deductions and credits.
- Estimated Payments: Pre-paid amounts made towards expected tax liability, often required for self-employed individuals.
Understanding these terms is crucial for accurately completing the PR tax form and engaging with other aspects of tax filing.
IRS Guidelines for Filing PR
The IRS provides specific guidelines for filing the Form 1040-PR that are essential for compliance and accuracy. Key guidelines include:
- Eligibility: The form is designated for Puerto Rican residents who earn a net self-employment income of $400 or more during the tax year.
- Filing Deadline: The usual deadline for filing the 1040-PR is April 15, aligning it with the standard federal tax deadline. However, extensions may be available.
- Record Keeping: Taxpayers are advised to maintain robust records of all income and expenses to support the figures entered on the form. This includes receipts, bank statements, and invoices.
- Signature Requirements: The form must be signed and dated by the taxpayer or their representative; failure to do so can result in processing delays or rejections of the return.
- Electronic Filing: While paper filing is an option, electronic submission is encouraged for faster processing and confirmation of receipt.
Adhering to IRS guidelines is crucial for avoiding penalties and ensuring that filings are processed efficiently.
Who Typically Uses the PR Form?
The Form 1040-PR is primarily utilized by individuals in Puerto Rico who are self-employed. This includes a variety of professionals and business owners, such as:
- Freelancers: Individuals who offer services independently, including writers, consultants, and graphic designers.
- Small Business Owners: Owners of sole proprietorships or partnerships that operate within Puerto Rico.
- Gig Economy Workers: Those engaged in short-term or project-based work through platforms like Uber, Airbnb, or similar services.
- Real Estate Agents: Professionals who depend on commissions as a significant portion of their income.
Understanding who uses the 1040-PR helps in recognizing the diverse nature of self-employment in Puerto Rico, which requires careful documentation and compliance with specific tax regulations.

Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Timely submission of the 1040-PR is essential for compliance with U.S. tax laws. Key dates include:
- Initial Filing Deadline: The 1040-PR must usually be filed by April 15 of each year.
- Extensions: Taxpayers may request an extension, typically allowing for an additional six months to file, pushing the deadline to October 15.
- Quarterly Estimated Tax Payments: Self-employed individuals may need to make estimated tax payments on a quarterly basis, with deadlines typically on April 15, June 15, September 15, and January 15 of the following year.
Being aware of these deadlines helps ensure that taxpayers can avoid penalties for late filing or payments.