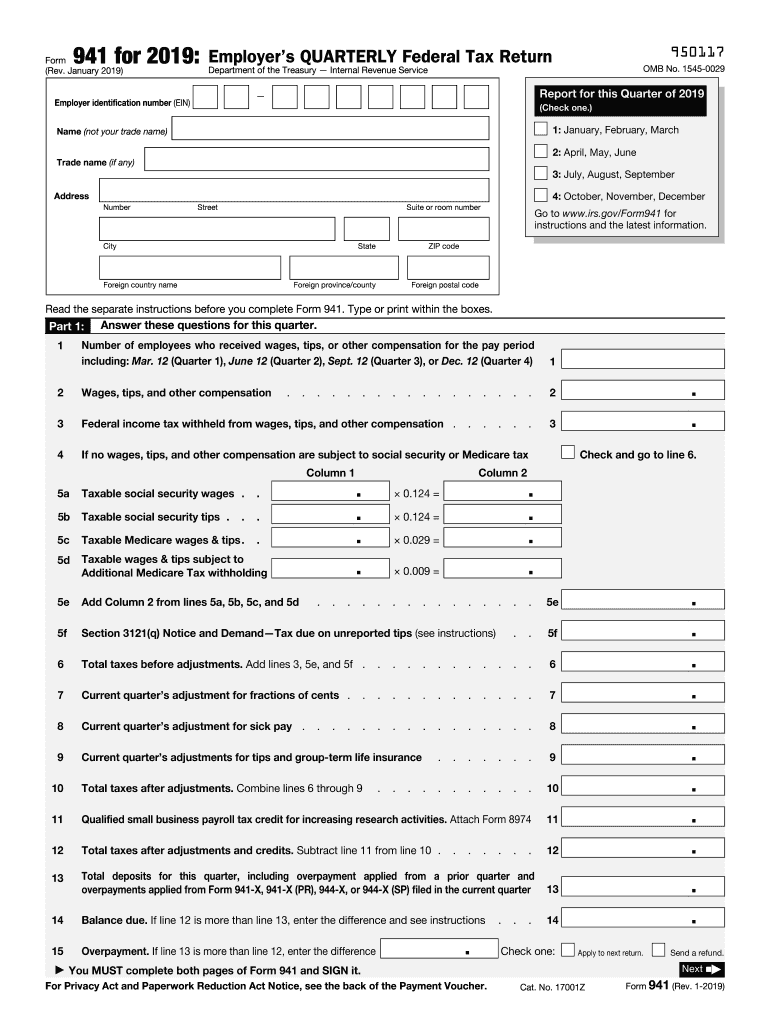
Definition and Purpose of Form 941
The Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return, formally known as Form 941, is a crucial document used by employers to report wages, tips, and other compensation paid to employees. Additionally, it captures the federal income tax withheld from employees' paychecks, along with social security and Medicare taxes owed. This form aids the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in tracking payroll tax liabilities and ensuring compliance with federal tax regulations.
Employers must file Form 941 four times a year, covering each calendar quarter. This schedule demands reporting not only for wages but also providing detailed information about employee counts and taxable wages. Additionally, employers must report any adjustments or payments made during the quarter. The precise structure of Form 941 includes various sections designated for these different elements, making it a comprehensive tax-filing tool.
Understanding the components and purpose of Form 941 is essential for employers, as inaccuracies or omissions can lead to penalties or additional scrutiny from the IRS.
Steps to Complete Form 941
Successfully completing Form 941 involves several structured steps that ensure all required information is correctly reported.
-
Gather Necessary Information:
- Collect payroll information for the quarter, including wages, tips, and the names and identification numbers of employees.
- Compile data regarding federal income tax withheld, social security, and Medicare taxes.
-
Fill Out the Basic Information:
- Provide your business name, address, and employer identification number (EIN) at the top of the form.
- Confirm the reporting period by marking the correct quarter.
-
Report Employee Wages:
- In Section 1, report the total number of employees during the quarter and calculate total wages subject to federal withholding.
-
Calculate Taxes Owed:
- Move to Section 2 to enter the amounts of federal income tax withheld, social security tax, and Medicare tax. This section also provides a space for any adjustments that may affect your tax liability.
-
Review and Sign:
- Carefully review all entries for correctness and sign the form, certifying that all information is accurate. Employers can designate someone else to sign, but they must provide their name and title on the form.
Form 941 must be filed electronically or mailed to the appropriate IRS address by the established deadlines to avoid penalties.
Important Terms Related to Form 941
Form 941 incorporates several key terms that are essential for accurate completion and compliance.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): A unique identifier assigned to businesses by the IRS, essential for filing Form 941.
- Taxable Wages: The gross earnings on which federal withholding tax is calculated, including salaries, bonuses, and tips.
- Social Security Taxes: Payroll taxes used to fund the social security program, which provides benefits for retirees and disabled individuals.
- Medicare Taxes: Taxes that finance Medicare, the federal health insurance program for individuals aged sixty-five and older, as well as younger people with disabilities.
- Employment Tax: A category encompassing various taxes that employers must withhold from employee wages, including federal income tax, social security, and Medicare taxes.
Familiarity with these terms is critical, as they inform the calculations and reporting required on Form 941.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates for Form 941
Adhering to deadlines when filing Form 941 is essential to avoid late fees and penalties.
-
Quarterly Filing Schedule:
- For the first quarter (January, February, March), the due date is April 30.
- The second quarter (April, May, June) is due on July 31.
- The third quarter (July, August, September) must be filed by October 31.
- The fourth quarter (October, November, December) deadlines fall on January 31 of the following year.
-
Employer Payments: Employers must make payroll tax deposits regularly, adhering to either monthly or semi-weekly deposit schedules. Missing these deadlines may incur penalties, compounded by interest on unpaid amounts.
Staying informed about these crucial deadlines helps businesses maintain compliance with IRS regulations and promotes smooth operational workflow.
Digital and Paper Versions of Form 941
Form 941 is available in both digital and paper formats, providing employers with flexible filing options depending on their preferences.
-
Digital Version: The electronic filing option via IRS e-File is recommended for its speed and convenience. It allows for automatic calculations and easier submission, reducing human error. Many tax preparation software solutions, such as TurboTax or QuickBooks, also provide the capability to electronically file Form 941.
-
Paper Version: A printable Form 941 is accessible through the IRS website for those who prefer traditional methods. This paper form must be mailed to the appropriate address, which can lead to longer processing times. Employers should ensure they send the form well before the deadline to accommodate possible mail delays.
Choosing between the digital and paper versions depends on business preferences and operational capacities, but leveraging digital solutions can enhance accuracy and efficiency.
Legal Use of Form 941
Form 941 plays a critical role in the legal obligations imposed on employers by the Internal Revenue Code. Understanding its legal implications ensures compliance with federal tax laws.
-
Legal Obligation: All employers who pay wages for services performed must file Form 941. This includes those who may not withhold taxes due to insufficient salaries but still engage employees.
-
Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to file Form 941 or incorrect reporting can result in significant penalties, including fines and interest charges on unpaid taxes. Legal repercussions can affect business standing and operations.
-
Retention of Records: Employers must maintain accurate records reflecting payroll activity and taxes reported on Form 941 for at least four years. This record-keeping is crucial for any future audits or disputes.
Understanding the legal requirements connected with Form 941 helps employers navigate their responsibilities and avoid costly penalties.
Examples of Using Form 941
Real-world scenarios illustrate the practical application of Form 941 and its significance for compliance.
-
Small Business Example: A small retail store with five employees pays bi-weekly wages. They must complete Form 941 at the end of each quarter, reporting the total wages paid and taxes withheld. Any changes in employee status or wages during the quarter must be accurately reported to avoid discrepancies.
-
Corporation Scenario: A corporate entity hires seasonal workers during the summer. They must accurately report these wages on the Form 941, ensuring that the tax liabilities reflect the temporary employment status. Adjustments may be needed if employee hours fluctuate significantly.
These examples demonstrate the importance of Form 941 in workforce management, ensuring that all obligations are met timely and accurately.