Definition & Meaning
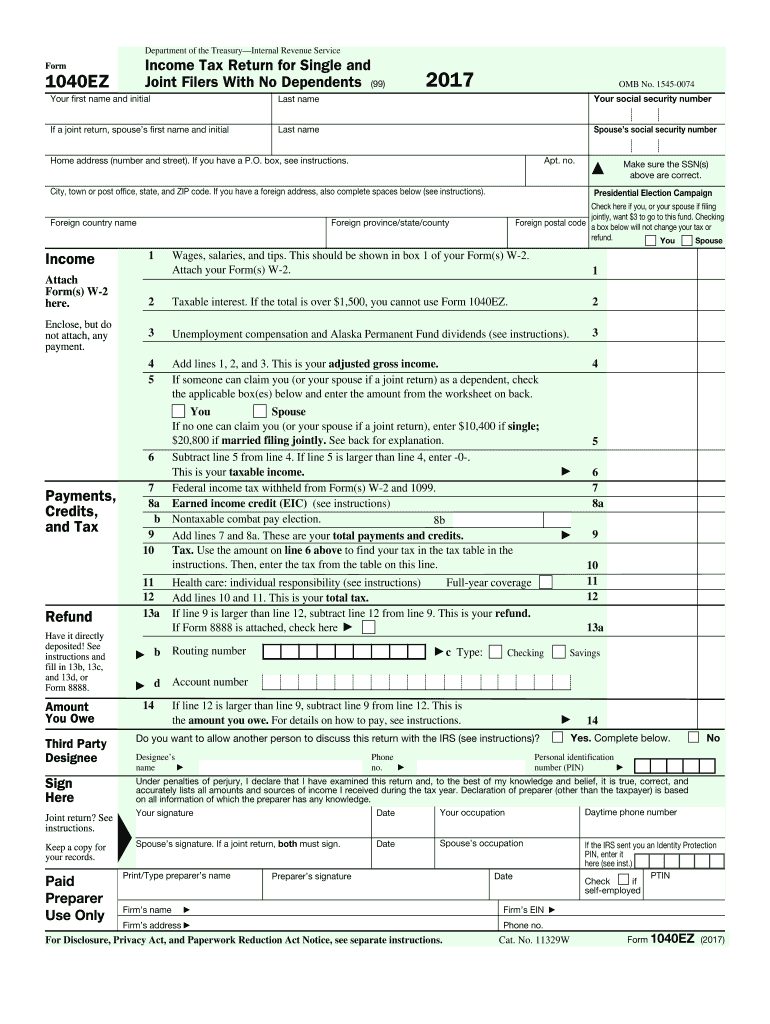
The 1040EZ form was a simplified version of the Individual Tax Return used in the United States. Generally meant for single and joint filers with uncomplicated tax situations, it was designed to streamline the tax filing process by including only the most essential sections. Taxpayers who used the 1040EZ form had straightforward tax affairs, such as a taxable income less than $100,000, no dependents, and no additional credits or deductions outside the most common ones. While the 1040EZ form was convenient for many, it is important to note that it was discontinued after the 2017 tax year and has been replaced by the revamped Form 1040.
Steps to Complete the 1040EZ
-
Personal Information:
- Enter your full name, Social Security Number, and address.
- If filing jointly, include the same details for your spouse.
- Indicate your filing status.
-
Income Reporting:
- Record your total wages, salaries, and tips as shown on your W-2 form.
- Include taxable interest of up to $1,500.
-
Federal Income Tax Withheld:
- Enter the total federal income tax withheld as reported on your W-2.
-
Earned Income Credit (EIC):
- Compute your eligibility for the Earned Income Credit and enter the amount if applicable.
-
Calculate Your Refund or Amount Owed:
- If you overpaid, calculate your refund.
- If additional tax is owed, calculate the amount payable.
-
Signature Section:
- Sign and date the form.
- If filed jointly, ensure your spouse also signs.
How to Obtain the 1040EZ
Although the 1040EZ form is outdated and replaced, taxpayers can still access it for historical reference or previous tax filings. Taxpayers can request a copy through the IRS’s official website. Older physical copies may also be available at libraries or through a professional tax preparer. For current filing, the new Form 1040 should be used.
Eligibility Criteria
To have been eligible to file Form 1040EZ, taxpayers had to meet specific conditions:
- Taxable income below $100,000
- Filing status as single or married filing jointly
- No dependents
- Interest income of $1,500 or less
- No income adjustments, such as student loan interest deductions
- Not claiming credits other than Earned Income Tax Credit
These criteria ensured the 1040EZ form was only used by those with simple tax situations, minimizing errors and ensuring a fast filing process.


Important Terms Related to 1040EZ
Understanding key terms related to Form 1040EZ is essential for comprehending its use:
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): The total gross income minus specific deductions, marking a crucial line item in calculating tax liability.
- Earned Income Credit (EIC): A refundable credit for low to moderate-income working individuals and couples, especially those with children.
- Withholding: Taxes taken from wages by an employer, deemed as prepayments on federal taxes owed for the year.
Legal Use of the 1040EZ
Form 1040EZ served specific legal purposes strictly as defined by IRS guidelines. Its use was limited to qualified taxpayers, and it was necessary that all entries were accurate and verifiable through supporting documents. Any misrepresentation could lead to legal penalties. It is crucial for individuals using such simplified forms to fully understand their qualifications to ensure compliance with tax laws.
Filing Deadlines / Important Dates
The submission deadline for the 1040EZ was aligned with the traditional tax filing deadline, typically April 15. In situations where the 15th fell on a weekend or holiday, the due date would be extended to the next business day. Taxpayers needing more time could apply for an extension, moving the deadline to October 15, although any taxes owed were still due by April. Awareness of these dates was crucial to avoid penalties for late filing or payment.
IRS Guidelines
The IRS provided detailed guidelines on how to fill the 1040EZ form. These included clear instructions on each section of the form, descriptions of qualifying and disqualifying conditions for using the form, and assistance on how to claim credits or report various types of income accurately. IRS guidelines also stressed the importance of safeguarding all tax-related documents to substantiate the information provided, in case of audits or reassessments.