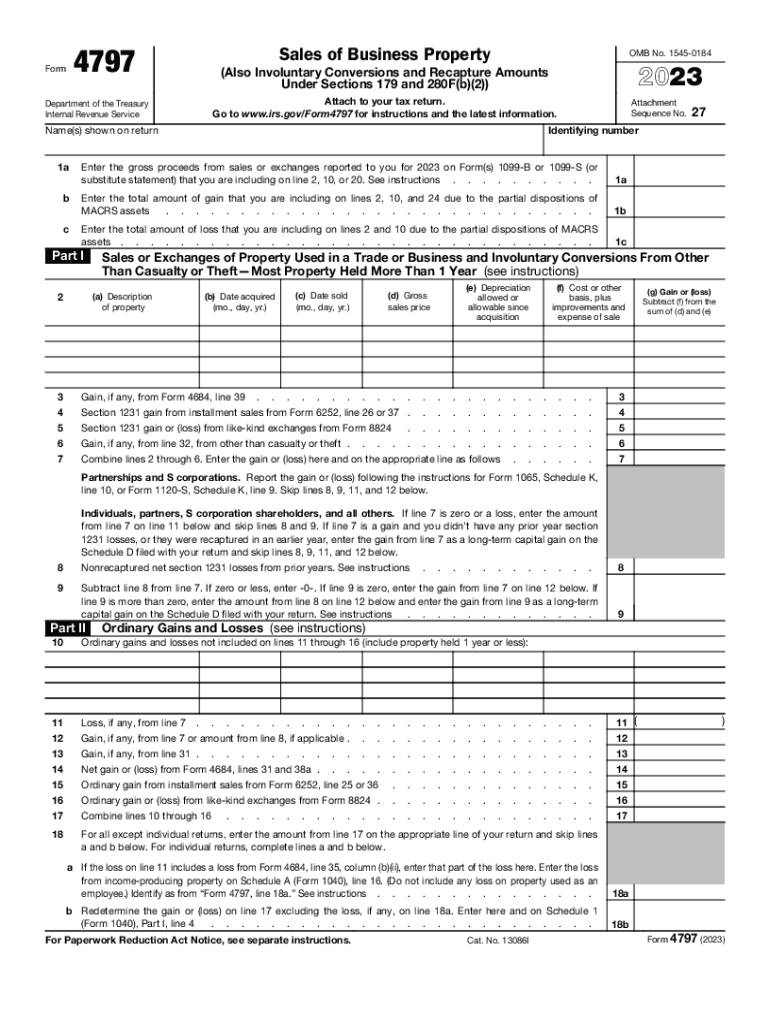
Definition and Purpose of Form 4797
Form 4797, titled "Sales of Business Property," is utilized by taxpayers to report the sale, exchange, or involuntary conversion of business property. This form captures essential information relating to gains and losses, providing a comprehensive overview of transactions involving property used in a business. The form encompasses various types of business property, including real estate and equipment, which are significant for accurate tax declaration.
Important Functions of Form 4797
- Reporting Gains and Losses: Taxpayers must declare gains or losses from the sale or exchange of business assets, ensuring transparency in financial reporting.
- Depreciation Recapture: The form addresses the recapture of depreciation previously claimed on the property, affecting the overall tax liability.
- Involuntary Conversions: In instances where property is disposed of due to circumstances beyond the taxpayer's control, such as theft or natural disasters, Form 4797 facilitates the reporting of such involuntary conversions.
How to Complete and Use Form 4797
Filling out Form 4797 involves several steps that require careful consideration to accurately reflect property transactions. Each section of the form must be completed with precise details to ensure compliance with IRS guidelines.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Gather Necessary Information: Before starting the form, collect all relevant details, such as the sale price, depreciation taken, and any relevant expenses.
- Identify Type of Transaction: Determine whether the transaction is a sale, exchange, or involuntary conversion, as these influence the specific lines to complete.
- Complete Relevant Sections: Fill in sections for Part I (Sales or Exchanges of Property), Part II (Ordinary Gains and Losses), or Part III (Involuntary Conversions) as appropriate.
Example of Completing Part I
- If you are reporting a sale, include the gross proceeds from the sale, the adjusted basis of the property, and calculate any gain or loss.
- If your asset was depreciated, ensure you address any recapture under Section 1245 or Section 1250, where applicable.
- Review Your Entries: After completing the form, double-check all entries for accuracy and completeness, which is crucial for avoiding penalties.
Who Needs to File Form 4797?
The requirement to file Form 4797 generally applies to individuals and entities that engage in transactions involving business property. Common filers include:
- Business Owners: Sole proprietors who sell or exchange property used in their business need to report the transaction.
- Partnerships and Corporations: These entities use Form 4797 to report gains or losses on sales of business property or partnerships that hold real estate.
- Real Estate Investors: Individuals engaged in the sale of rental properties must complete the form when they dispose of such assets.
Key Elements and Terms Related to Form 4797
Understanding specific terms and elements within Form 4797 is vital for accurate reporting and compliance.
- Gross Proceeds: The total amount received from the sale, which forms the basis for calculating gains.
- Adjusted Basis: This value represents the original cost of the asset adjusted for deductible expenses, depreciation, and improvements.
- Recapture Tax: Applies to certain transactions involving depreciated property, requiring taxpayers to pay tax on previously deducted depreciation at ordinary income rates.
Filing and Submission Methods for Form 4797
Form 4797 can be submitted through several methods, providing flexibility for taxpayers to choose their preferred filing process.
Available Submission Options
- Electronic Filing: Taxpayers can e-file Form 4797 through IRS-approved tax software, seamlessly integrating it into their overall tax return.
- Mail Submission: The form can also be printed and mailed to the appropriate IRS address, as specified in the form instructions.
- In-Person Filing: Although less common, individuals may also submit their forms in person at local IRS offices, allowing for immediate confirmation of receipt.
Important Considerations
- Ensure that all submissions are complete, including supporting documentation and schedules needed for specific transactions.
- For electronically filed returns, ensure your software is compatible with IRS guidelines for the current tax year.
With a comprehensive understanding of Form 4797, taxpayers can accurately report their business property transactions, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards while minimizing the risk of penalties.