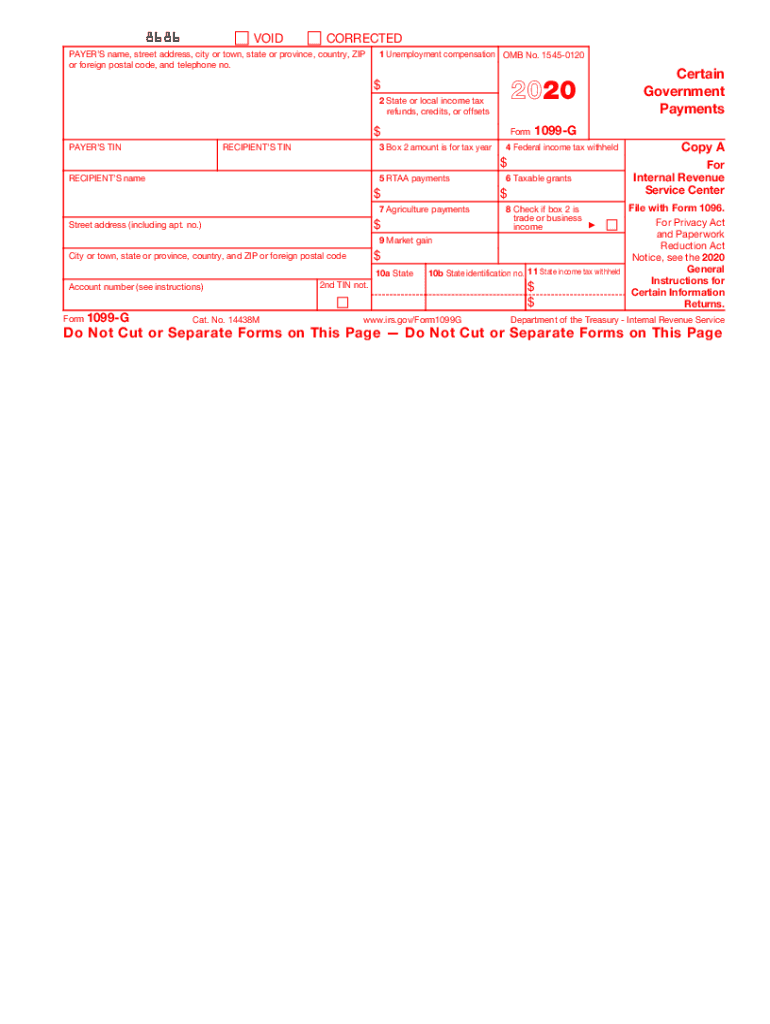
Definition & Understanding: Form 1099-G
Form 1099-G is a tax document used by the IRS to report certain types of government payments. It is primarily issued for payments like unemployment compensation, state or local income tax refunds, and agricultural payments. The form ensures that individuals who receive these payments report them on their federal income tax return. It is mandatory for recipients to use this form to accurately reflect such income, as it affects the total income reported and may result in adjustments to tax liability.
How to Obtain the 1099-G
Individuals can obtain Form 1099-G through various means, often directly from the government agency that issued the payment. Typically, state revenue agencies or departments of labor will issue the form at the end of the tax year. These agencies typically offer options to receive the form electronically via their website or mail it to the recipient's address. Accessing the form online often requires creating an account on the agency's website and verifying personal details, ensuring secure handling of sensitive information.
Steps to Complete the 1099-G
Completing Form 1099-G involves several straightforward steps:
- Verify Receipt: Ensure that all payments received that should be listed are accurately accounted for.
- Check Information: Cross-check the form’s details, including the payer’s information, payment amounts, and any withheld taxes, for errors.
- Report on Tax Returns: Transfer information from Form 1099-G to the appropriate sections of your federal tax return. Payments could affect your total taxable income.
- File with IRS: Submit the completed tax return, including data from the Form 1099-G, to the IRS by the deadline.
Ensuring each step is meticulously followed helps prevent discrepancies that could lead to audits or penalties.
Who Typically Uses the 1099-G
Form 1099-G is commonly used by a variety of individuals and entities:
- Unemployed Individuals: Those who receive unemployment benefits, which must be reported as income.
- Taxpayers Receiving Refunds: Individuals who receive state or local tax refunds or credits from a previous tax year.
- Farmers: Recipients of agricultural payments or benefits must report these earnings.
- Government Program Beneficiaries: Participants in various government programs that distribute funds requiring reporting.
Understanding the target audience for Form 1099-G is crucial for proper compliance and accurate tax reporting.

Key Elements of the 1099-G
Form 1099-G includes several critical components:
- Payer Information: Details about the government agency issuing the payments.
- Recipient Information: Ensures the correct tax identification number and address for reporting.
- Box Entries: Specific boxes are used for different types of payments, such as unemployment compensation (Box 1) and state tax refunds (Box 2).
- Tax Withheld: Any federal income tax withheld must be noted and reported.
Accurate completion of these elements is necessary for legal compliance and for recipients to properly file their taxes.
IRS Guidelines for Form 1099-G
The IRS has set guidelines surrounding Form 1099-G to ensure compliance and uniformity. These include:
- Mandatory Reporting: Agencies must report specific payments made to individuals during the tax year.
- Filing Deadlines: Issuers must send copies to recipients by January 31 and file them with the IRS by February 28.
- Accuracy Requirements: Both issuers and recipients must verify the accuracy of reported information to avoid penalties.
By adhering to IRS guidelines, taxpayers and government agencies can prevent common issues associated with tax filing and form submissions.
Filing Deadlines & Important Dates
Key dates related to Form 1099-G are crucial for compliance:
- January 31: Deadline for issuers to send the form to recipients.
- February 28: Paper submissions of the form must be filed with the IRS.
- March 31: Electronic submissions deadline for IRS filing.
Timely receipt and submission allow individuals to meet their federal tax obligations and avoid unnecessary fines or interest from late reporting.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with the rules surrounding Form 1099-G can result in penalties:
- Late Filing: Delays in filing by issuers can incur fines.
- Incorrect Information: Errors may lead to penalties if corrected forms are not resubmitted promptly.
- Failure to Furnish: Not providing recipients with their form can result in issuer penalties.
Understanding the consequences of non-compliance emphasizes the importance of careful handling and timely submission of Form 1099-G.
Important Terms Related to the 1099-G
Familiarizing oneself with the terminology related to Form 1099-G can aid in comprehension and proper handling:
- Unemployment Compensation: Payments made during periods of joblessness.
- Tax Withholding: Amount withheld for federal income tax from payments.
- Payer Identification: Entity providing the taxable payment, typically a government agency.
Accurate understanding and usage of these terms ensure clear communication and compliance with tax laws.