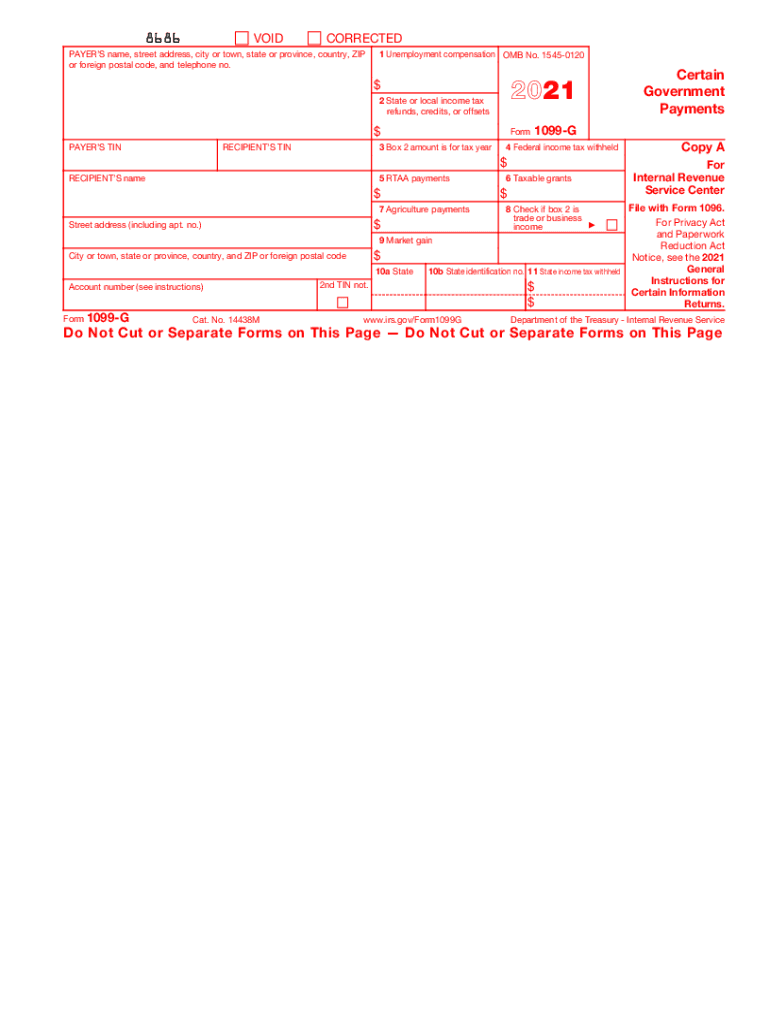
Definition & Purpose of Form 1099-G
Form 1099-G is issued by government agencies to report certain types of government-generated income. This includes unemployment compensation, state and local income tax refunds, agricultural payments, and taxable grants received during the tax year. Understanding this form is crucial for accurately reporting income on your federal tax return and ensuring compliance with IRS requirements.
Understanding Key Components
- Unemployment Compensation: Box 1 reports unemployment benefits, which are taxable income.
- State or Local Income Tax Refunds: Reported in Box 2 and must be declared if you itemized deductions in the previous year.
- Taxable Grants and Agricultural Payments: Shown in Box 6 and Box 7, respectively, indicating funds received from federal or state programs.
How to Use Form 1099-G for Tax Filing
Form 1099-G details the income that must be reported on your federal tax return. Each type of income reported corresponds to specific tax lines and calculations.
Filing Instructions
- Review the Form for Accuracy: Verify your personal information and income amounts.
- Report on Federal Tax Return: Include reported amounts on the appropriate lines:
- Use IRS Schedule 1 for unemployment compensation.
- State tax refunds are reported only if you itemized deductions in the prior year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Neglecting to report income because the form was not received.
- Miscalculating taxes owed on refunds if you did not itemize deductions.
Steps to Obtain Form 1099-G
Receiving the 1099-G is typically straightforward but requires awareness of state procedures.
Methods to Receive the Form
- Mail: Forms are usually sent by January 31. If not received by February, contact the issuing agency.
- Online Access: Many states offer electronic access through their tax department websites.
Troubleshooting Missing Forms
- Contact the Issuer: If you haven’t received the form by mid-February, reach out to the specific agency, such as the state unemployment office.
- Access Online Portals: Explore state websites for any downloadable options.
Steps to Complete Form 1099-G
For those required to fill out sections of a 1099-G, such as agencies or preparers, accuracy is essential.
Completing the Form
- Enter Payee's Information: Fill in the recipient’s name, address, and taxpayer identification number.
- Report Payment Information: Enter details on unemployment compensation, state tax refunds, and other relevant payments.
- Verify State Information: Ensure accuracy in reporting state income distributions and identifiers.
Ensuring Accuracy
- Double-check calculations for errors.
- Confirm alignment with agency records to prevent mismatches on recipients' returns.
IRS Guidelines for 1099-G
The IRS provides detailed guidelines to help ensure correct handling of Form 1099-G.
General IRS Instructions
- Filing Requirements: All government payments over $10 must be reported.
- Record Keeping: Retain a copy of all issued forms for at least three years for potential audits.
Additional Compliance Details
- Electronic Filing: The IRS encourages electronic submission through the FIRE system to streamline processes.
- Accuracy Penalties: Inaccurate filings could result in financial penalties or increased scrutiny.
Important Terms Related to Form 1099-G
Familiarity with specialized terminology can aid in understanding and using Form 1099-G correctly.
Key Terms
- "Reemployment Compensation": Another term for unemployment benefits.
- "State Refund Offset": This refers to overpayment adjustments that may affect refund totals.
- "Grantor": The entity, usually a government agency, that disburses grants or payments.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Not adhering to 1099-G filing requirements can attract significant penalties.
Avoiding Penalties
- Timely Reporting: Meet all deadlines to avert late fees.
- Error Corrections: Amend forms quickly if discrepancies arise.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Fines increase with the duration of non-compliance.
- Potential for audits and heightened scrutiny on future filings.
Software Compatibility and Submission Options
Utilizing tax software can streamline the process of filing with a 1099-G.
Compatible Software Solutions
- TurboTax and QuickBooks: Both offer integrated solutions for importing and using 1099-G data.
- Software features include guided prompts and suggestions on handling uncommon scenarios or state-specific issues.
Submission Methods
- Paper Filing: Traditional but less efficient; still viable for less complex returns.
- Online Filing: Recommended for quicker processing and accessibility. Most state and federal tax systems support e-filing.
Comprehending the intricacies of Form 1099-G fosters accurate tax reporting and reduces potential legal or financial complications. This intricate understanding not only assists taxpayers in fulfilling their obligations but also empowers them with the knowledge to optimize their approach toward tax season nuances.