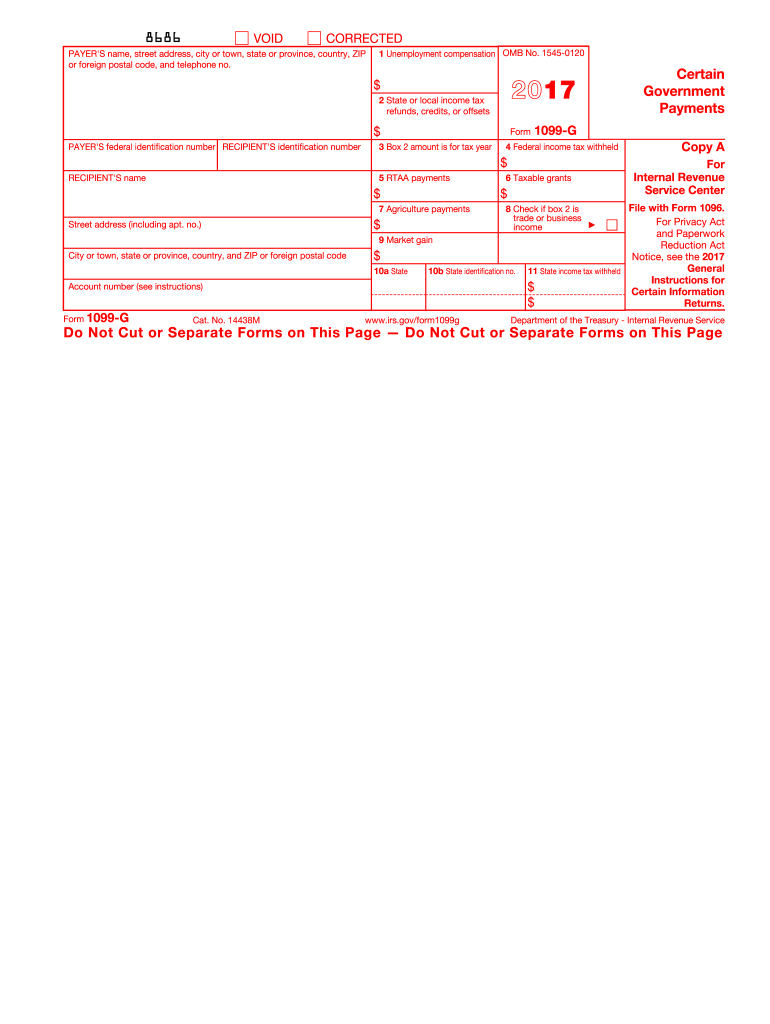
Definition & Overview of the 1099-G 2017 Form
Form 1099-G, issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), is used to report certain types of income received from government sources, primarily for U.S. taxpayers. The "G" in its name signifies "Government," as it reports payments like unemployment compensation and state or local tax refunds. Understanding this form is crucial because these amounts often affect the taxpayer's annual income calculations.
-
Unemployment Compensation: For individuals who received unemployment benefits during 2017, these amounts are reported in Box 1 of the form. Since unemployment compensation is considered taxable income, recipients must include this in their federal tax return to avoid underreporting their earnings.
-
State or Local Tax Refunds: Taxpayers who received a state or local tax refund, credit, or offset may need to report this in Box 2, depending on whether they itemized deductions in previous tax filings. This distinction is essential because it helps determine whether the refund should be considered taxable income.
The form ensures that all pertinent income outside of standard employment wages is properly reported to the IRS, enabling accurate tax assessments.
How to Obtain the 1099-G 2017 Form
Form 1099-G is typically issued directly by the agency or department responsible for distributing the payments. Here’s how taxpayers can obtain their copy:
-
Mail: Usually, the form is mailed to your address by January 31, following the tax year for which the form is relevant. Taxpayers should ensure their address is up-to-date with the issuing agency to avoid delays.
-
Online Access: Many agencies provide digital copies accessible through their websites. Taxpayers may log in to their account, often using specific credentials, to download and print the form.
-
Contacting the Issuer: If the form is not received by early February, contacting the issuing agency by phone or email can help in acquiring a reissued document. Always verify the authenticity of the contact information to avoid phishing scams.
Ensuring timely receipt of Form 1099-G is vital for meeting tax filing deadlines and avoiding potential penalties.
Steps to Complete the 1099-G 2017 Form
Though Form 1099-G itself is filled out by the issuing agency, recipients must understand how to use the information when filing taxes. Here are the steps:
-
Review the Form: Verify that all personal information and reported amounts are accurate. Check details like your name, address, and Social Security Number.
-
Determine Tax Liability: Use the figures in the form to calculate your taxable income. For example, unemployment compensation reported here must be included in your gross income, affecting taxable income based on current tax laws.
-
Report on Federal Tax Return: Enter the figures from Form 1099-G on the corresponding lines in your tax return. For instance, amounts in Box 1 should be reported as unemployment compensation.
-
File on Time: Align with the tax filing deadlines to avoid penalties. Typically, the federal tax filing deadline is April 15, unless an extension is granted.
Accurately completing the integration of Form 1099-G into your tax return ensures compliance with IRS regulations and prevents erroneous tax liabilities.
Who Typically Uses the 1099-G 2017 Form
Form 1099-G is utilized by various taxpayers based on their specific circumstances or income sources. Key users include:
-
Unemployment Benefit Recipients: Those who lost jobs and collected unemployment compensation during 2017 receive this form for tax purposes.
-
Taxpayers with State or Local Tax Refunds: If you itemized deductions in previous years and received a tax refund, this form documents whether this refund needs to be reflected in your tax return.
-
Agricultural Subsidy Recipients: Farmers and agricultural businesses receiving certain subsidies or grants might also use this form as part of their financial documentation.
Understanding the reasons for receiving this form helps taxpayers prepare and file accurate tax returns.


Key Elements of the 1099-G 2017 Form
The 1099-G form contains several critical components that taxpayers should be familiar with for correct reporting:
-
Box 1: Displays total unemployment compensation received. This is a crucial figure for individuals who have been out of work and must be reported on your tax return.
-
Box 2: States the total state or local income tax refunds, credits, or offsets. Whether this amount constitutes taxable income depends on your itemized deduction circumstances from prior tax years.
-
Personal Information: Includes details such as the taxpayer's name, address, and Social Security Number, which should be verified for accuracy.
These elements highlight the importance of the form in accurate income tax reporting and compliance with IRS requirements.
Legal Use of the 1099-G 2017 Form
Form 1099-G serves not only as a statement of income but as a legal document that validates the receipt of certain types of government payments:
-
IRS Compliance: Not reporting or underreporting amounts from the form can lead to penalties, audits, or further legal actions. Ensuring accurate reporting per IRS guidelines safeguards against such issues.
-
Record Keeping: Retaining a copy of your Form 1099-G is crucial for future reference and potential disputes. The IRS can request documentation to verify past filings up to six years.
Understanding the legal implications of Form 1099-G allows taxpayers to manage their financial and tax-related risks effectively.
State-Specific Rules for the 1099-G 2017 Form
Tax regulations and the treatment of certain payments can vary from state to state. Key points to consider include:
-
Different Tax Treatment: While federal tax treatment for unemployment compensation is consistent, specific states might apply additional taxation or exceptions.
-
State Refunds: The implications of receiving a state or local tax refund differ, particularly in states without income tax. It's important to check local regulations to ensure compliance.
Familiarity with both federal and state-specific guidelines can enhance accuracy in filing and prevent unexpected liabilities.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to accurately report amounts from Form 1099-G can result in significant penalties:
-
Late Filing Fees: Missing the federal tax filing deadline without an approved extension could incur fees, compromising an individual’s financial standing.
-
Underpayment Penalties: If payments reported on the 1099-G are not included in taxable income, it may lead to penalties for underpayment of taxes.
Understanding these potential penalties stresses the importance of diligent tax filing and adherence to IRS guidelines related to Form 1099-G.