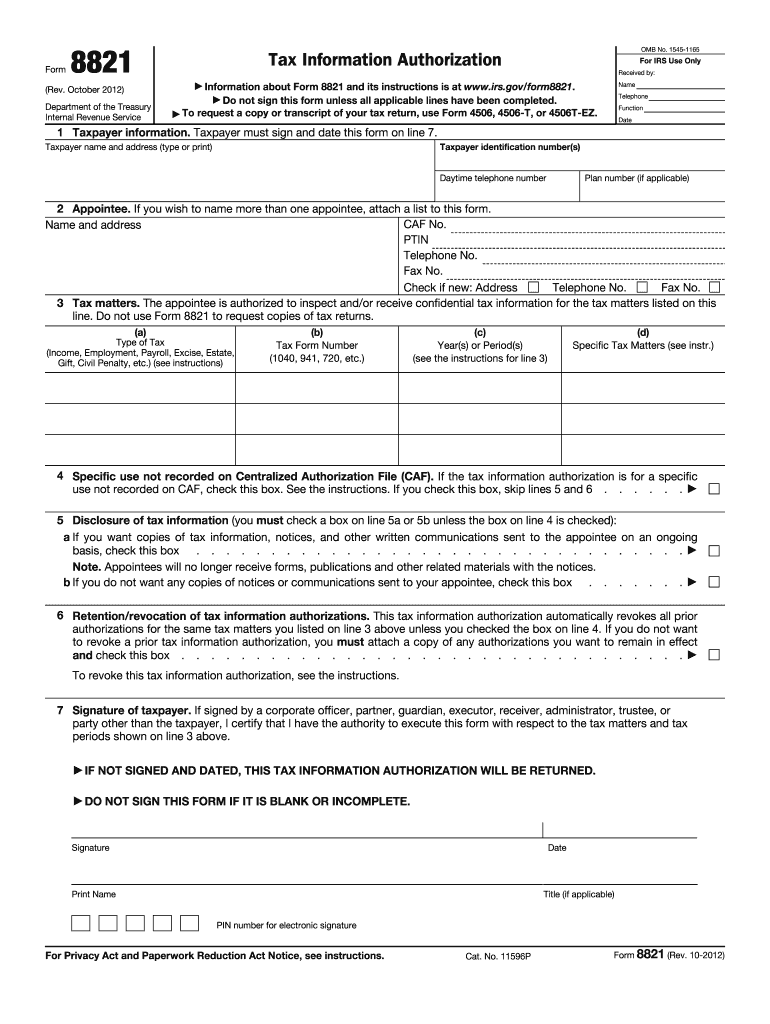
Definition and Purpose of the 2012 Form 8821
Form 8821, also known as Tax Information Authorization, is a document utilized by taxpayers to authorize individuals or entities to access their confidential tax information held by the IRS. The form does not grant the appointee the authority to represent the taxpayer in dealings with the IRS; rather, it strictly allows them to inspect and obtain information on behalf of the taxpayer. This can include details about federal tax returns, tax accounts, and communications related to the taxpayer’s tax matters.
Key Features of Form 8821
- No Representation Authority: Unlike other forms that allow representation, such as Form 2848, Form 8821 limits the appointee's role to information access only.
- Taxpayer Identification: The form requires the taxpayer’s personal identification details, including name, address, and Social Security number or Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- Appointee Information: Taxpayers must provide identification for appointees, including the name, address, and a designated telephone number.
How to Complete the 2012 Form 8821
Completing Form 8821 involves several critical steps to ensure the effective authorization of tax information access. A thorough understanding of these steps is essential to minimize errors and ensure compliance.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Download the Form: Access the 2012 Form 8821 from the IRS website or through authorized providers.
- Fill in Taxpayer Information:
- Provide the taxpayer's name and address.
- Include the Social Security Number or EIN for identification.
- Appointee Details:
- Enter the appointee’s name and address.
- It is also essential to include a phone number for communication.
- Specify Tax Matters:
- Indicate the specific tax matters for which the authorization is valid, such as income taxes, estate taxes, or excise taxes.
- Sign and Date: The taxpayer must sign the form to validate the authorization and include the date of signing. If submitted electronically, ensure compliance with IRS electronic filing requirements.
Important Considerations
- The form should be filed within 120 days of the taxpayer’s signature.
- Clearly define which tax years or periods the authorization covers.
- Include only the relevant appointee's details to avoid confusion.
Filing and Submission Methods for Form 8821
Form 8821 can be submitted to the IRS through various methods, each with its own requirements and timelines.
Submission Methods
- By Mail: Print the completed form and send it directly to the specified IRS office based on the given instructions. The mailing address is determined by the state of the taxpayer's residence.
- Fax: In some cases, the IRS allows Form 8821 to be submitted via fax. Taxpayers should verify eligibility and ensure they are sending it to the correct fax number provided on the form.
- Electronic Submission: For taxpayers using electronic filing services, it may be possible to submit Form 8821 electronically through integrated platforms that support IRS forms.
Important Deadlines
- It is crucial to remember that Form 8821 must be submitted to the IRS within 120 days of signing the form. If it is submitted later, regardless of the method, the authorization may not be effective, necessitating the completion of a new form.
Who Typically Uses the 2012 Form 8821
The use of Form 8821 is prevalent among various taxpayers, each with distinct needs for accessing tax information.

Common Users Include:
- Individuals: Taxpayers who need family members or trusted friends to access their tax information without granting full representation.
- Tax Professionals: Accountants or tax advisors who need specific tax information to assist clients with tax filing or audit preparations.
- Businesses: Business owners who may designate employees or external service providers to review tax matters.

Specific Scenarios
- Alice, a retired individual, may use Form 8821 to allow her son access to her tax documents for straightforward inquiries, ensuring he cannot act on her behalf.
- A small business may appoint an accountant to review past tax returns to prepare for an upcoming audit, relying on Form 8821 for necessary access.
Legal Guidelines and Compliance for Using Form 8821
Understanding the legal framework surrounding Form 8821 is essential for ensuring compliance and proper use.
Legal Use of Form 8821
- Adherence to IRS Regulations: The use of Form 8821 must comply with IRS guidelines about tax information access. Appointees should only receive information pertinent to the specified tax matters.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements: While Form 8821 allows access to information, it does not obligate the appointee to maintain confidentiality beyond their standard professional ethics.
- Limitations: The appointee cannot represent or negotiate tax matters with the IRS; this limitation is vital to ensure that the taxpayer retains ultimate control over their representation.
Protecting Sensitive Information
- Verification: Taxpayers should verify the credentials of the appointee before authorizing access to ensure trust and minimize the risk of information misuse.
- Monitoring Access: Taxpayers can consider tracking interactions by staying informed about information accessed by the appointee.
This comprehensive understanding equips users with essential knowledge about completing, submitting, and leveraging Form 8821 effectively while navigating the relevant legal context and compliance requirements.