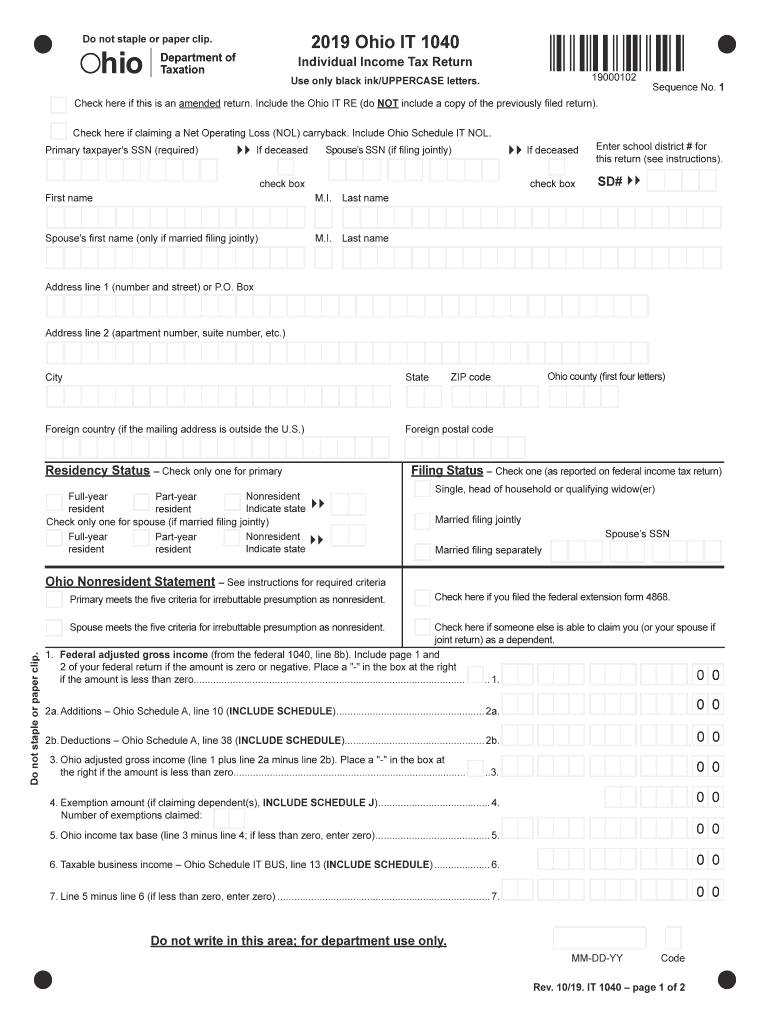
Definition and Purpose of Ohio IT 1040
The Ohio IT 1040 is a state-specific individual income tax return form used by Ohio residents to report their income, claim deductions and credits, and calculate their overall tax liability for a given tax year. It is structured to accommodate various income sources and residency statuses, making it applicable for a diverse taxpayer base. The form guides taxpayers in complying with Ohio's state tax requirements, ensuring accurate financial reporting and tax payments.
How to Obtain the Ohio IT 1040
Taxpayers can access the Ohio IT 1040 form through multiple avenues to facilitate ease of filing. The form can be downloaded directly from the Ohio Department of Taxation's official website, where it is available in both printable and fillable PDF formats. Additionally, individuals can pick up a physical copy of the form at local tax offices or libraries. Many tax preparation software solutions and services also provide access to the Ohio IT 1040, integrating it into their workflow for seamless digital filing.
Steps to Complete the Ohio IT 1040
- Gather Necessary Documents: Collect your W-2s, 1099s, and any other relevant tax documents that reflect your income sources and deductions.
- Personal Information Section: Fill out your personal details, including your name, address, and Social Security number.
- Residency Status Declaration: Declare whether you are a full-year, part-year, or non-resident.
- Report Income: Enter all income details, including wages, salaries, interest, dividends, and business income.
- Deductions and Credits: Claim eligible deductions and credits to reduce your taxable income.
- Calculate Tax Liability: Follow the instructions to compute your state tax liability based on the given tables and formulas.
- Payment Instructions: Include payment if taxes are owed or choose a refund method if a refund is due.
- Review and Submit: Double-check all entries, ensure signatures are in place, and submit the form using the chosen submission method.
Key Elements of the Ohio IT 1040
- Personal Information: Essential for identification and processing, this includes the filer’s name, address, and personal identification numbers.
- Income Details: A comprehensive section capturing various income types, crucial for total income calculation.
- Tax Deductions and Credits: Specific lines to enter deductions and credits that can lower the taxable income.
- Payment and Refund Instructions: Clear instructions on how to handle tax payments or how refunds will be processed, including payment plans if owing.
Eligibility Criteria for the Ohio IT 1040
Ohio residents and certain non-residents with income sourced from Ohio need to file the IT 1040. Eligibility is primarily determined by income level and residency status. Even if one is not required to file an Ohio IT 1040, filing might be beneficial to claim any withholding refunds or tax credits. Part-year residents must report income earned while residing in Ohio, while non-residents must file if they have Ohio-sourced income.


Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
The Ohio IT 1040 follows federal tax deadlines, generally due by April 15 of each year, coinciding with the IRS deadline unless an extension is filed. It's crucial to adhere to this timeline to avoid late fees or penalties. If April 15 falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. Taxpayers may request an extension, but this does not delay payment of any taxes owed.
Required Documents for the Ohio IT 1040
- W-2 Forms: For employment income.
- 1099 Forms: For other income types such as freelance work or investment earnings.
- Documentation for Deductions/Credits: Receipts or proof for eligible educational expenses, property taxes, or charitable contributions.
- Ohio State Tax Withholding Statements: To verify taxes withheld in Ohio.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to file the Ohio IT 1040 or to pay owed taxes can result in penalties, including late fees and accrued interest on unpaid taxes. The state can also impose additional penalties for fraudulent filings or substantial underpayment of taxes. It is vital for taxpayers to ensure that all sections of the form are completed accurately and submitted timely to avoid such consequences.