Definition and Purpose of VA Form 763
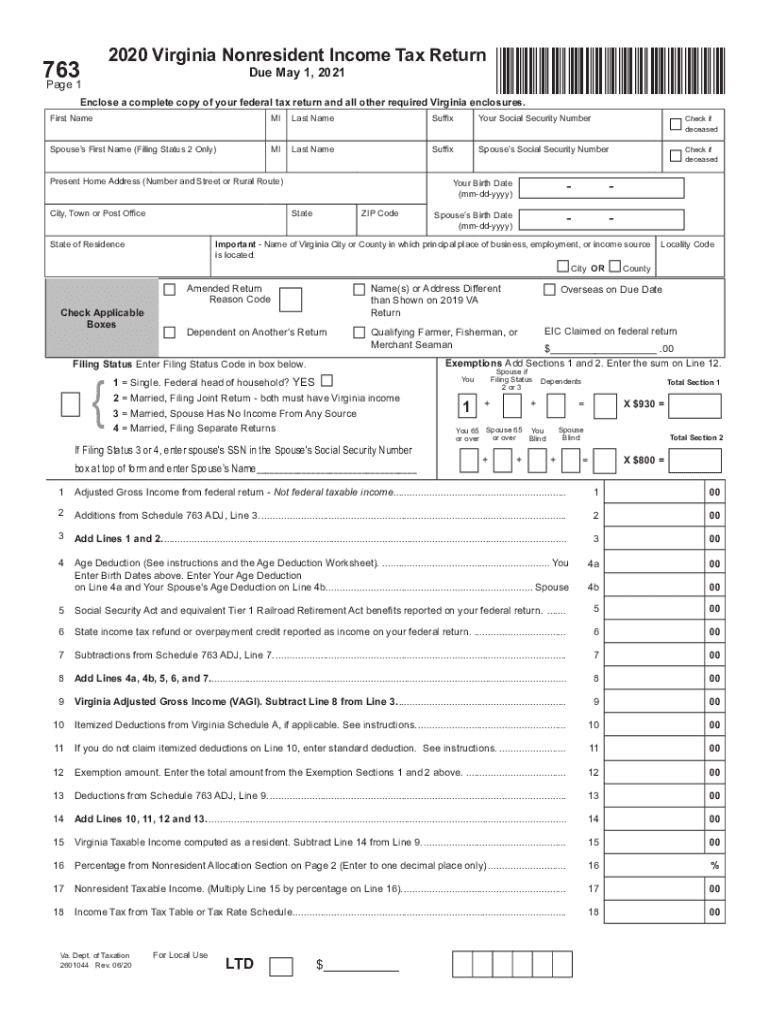
VA Form 763, also known as the Virginia Nonresident Income Tax Return, is utilized by nonresidents of Virginia who earn income within the state during the tax year. This form is vital for ensuring that individuals comply with Virginia's tax laws, as it allows the state to collect taxes on earnings generated from sources within its jurisdiction. By filing this form, nonresidents declare their income, deductions, and credits applicable under Virginia tax regulations. Understanding its purpose helps individuals navigate tax responsibilities and avoid potential penalties.
Who Typically Uses VA Form 763
A range of individuals may need to use the VA Form 763. Specifically, this form is designed for:
- Nonresidents: Individuals who live outside Virginia but earn income from Virginia sources, such as wages, rents, or investment income.
- Part-time Residents: Those who may reside in Virginia for a portion of the year but do not qualify as full-time residents according to state law.
- Self-employed Individuals: People who operate their businesses and derive income from customers in Virginia.
- Students: Nonresident students attending institutions in Virginia who earn income while studying, either through employment or internships.
Each of these groups must demonstrate compliance with Virginia's tax laws by accurately reporting income earned within the state.
Steps to Complete the VA Form 763
Filing the VA Form 763 requires a series of specific steps that ensure accuracy and compliance. The following is a detailed breakdown of the process:
- Gather Required Information: Collect all necessary documents, including W-2 forms, 1099 forms, and any other records of income earned in Virginia. Additionally, compile documentation for deductions and credits.
- Fill Out Personal Information: Enter your name, address, and Social Security number at the top of the form. Ensure this information is accurate to prevent delays.
- Report Your Income: List all sources of income earned in Virginia. Include wages, dividends, interest income, and any rental income. Calculate total income accurately.
- Claim Deductions and Credits: Review the deductions available to nonresidents on the form, such as personal exemptions or specific credits that may apply. Include these in your calculations to determine your taxable income.
- Calculate Virginia Tax Owed: Utilize the tax tables provided to find the appropriate tax rate based on your taxable income. Multiply your taxable income by this rate to determine the total tax owed.
- Complete Signature Section:Make sure to sign and date the form, affirming that the information provided is true to the best of your knowledge. An unsigned return will be considered incomplete.
Following these steps accurately will facilitate a smooth filing process, reducing the risk of errors that could lead to penalties.
Key Elements of VA Form 763
Understanding the key elements of the VA Form 763 is essential for proper completion. The following components are vital:
- Personal Information Section: This captures your identity and residency status, crucial for determining filing requirements.
- Income Reporting: Detailed sections require the reporting of various income sources, which informs the state of your earnings for the tax year.
- Deduction and Credit Lines: Specific lines within the form allow for deductions and credits to be entered, affecting the overall taxable income and tax liability.
- Tax Calculation Table: This section simplifies calculating how much tax is owed based on the taxable income reported.
- Signature Requirement: Ensures accountability for the information reported; submitting without a signature may delay processing or require the form to be resubmitted.
Each of these elements serves a distinct function, collectively ensuring compliance and accuracy in tax reporting.
Important Dates and Filing Deadlines for VA Form 763
Filing deadlines for the VA Form 763 are crucial for ensuring compliance with state tax laws. Key dates include:
- Regular Filing Deadline: The VA Form 763 typically must be filed by May first of the year following the tax year in question, aligning with the federal filing deadline for individual income tax returns.
- Extensions: Residents may apply for an extension, which allows additional time to file. However, it is essential to pay any tax owed by the original deadline to avoid penalties.
- Penalties for Late Filing: Noncompliance with the filing deadline can result in financial penalties and interest accruing on unpaid taxes, so timely submission is vital.
Being aware of these dates helps taxpayers maintain on-time compliance and avoid surprises regarding penalties or interest on unpaid taxes.
Important Terms Related to VA Form 763
Familiarity with key terms associated with the VA Form 763 enhances understanding and usage of the form. Important terms include:
- Nonresident: An individual who does not reside in Virginia but earns income from Virginia sources.
- Taxable Income: The amount of income subject to tax after deductions and exemptions are subtracted.
- Deductions: Specific amounts that taxpayers can subtract from their gross income to reduce their taxable income, impacting total taxes owed.
- Credits: Direct reductions in tax liability that can lower the total amount owed.
- Filing Status: The classification that affects the tax rate and eligibility for certain deductions (e.g., single, married, head of household).
Understanding these terms aids taxpayers in accurately completing and filing the VA Form 763 while fully complying with Virginia tax regulations.