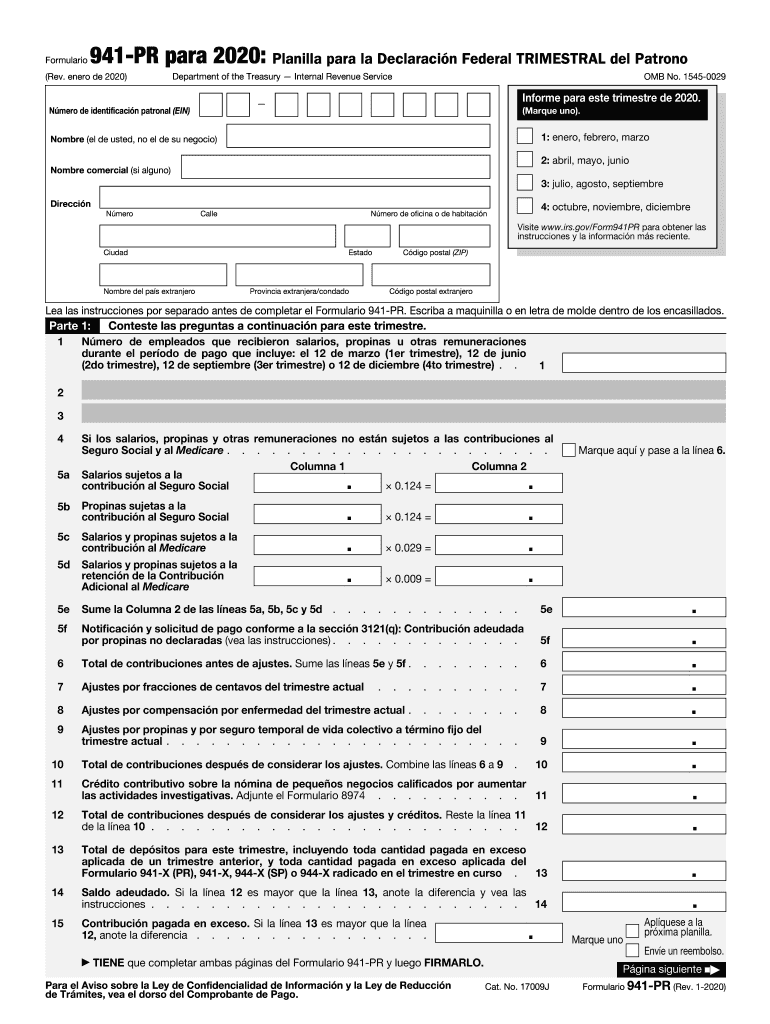
Understanding the 941 Form for 2020
The 941 Form for 2020 is a quarterly tax return used by employers in the United States to report wages paid to employees, along with employee and employer contributions to Social Security and Medicare taxes. It's a critical document for ensuring compliance with federal tax obligations related to payroll. This form captures details about withheld federal income taxes, as well as the employer's share of Social Security and Medicare taxes. Proper completion and timely submission are essential to avoid penalties and ensure accurate tax records.
How to Use the 941 Form for 2020
Using the 941 Form involves several steps that require careful attention to detail. Employers should gather all payroll information from the specific quarter before beginning. This includes total wages, taxable wages, federal income tax withheld, and the employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes. The form has multiple sections, each of which requires precise information. The main sections include employee counts, wages paid, tax liabilities, and adjustments for sick pay or fringe benefits. Employers must complete each section accurately and verify all totals before submission to avoid discrepancies.
Key Elements of the 941 Form
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): This is a unique number assigned to businesses by the IRS for tax purposes, necessary for form identification.
- Reported Wages and Tips: The total amount of wages and tips paid during the quarter, as well as taxable social security and Medicare wages.
- Adjusted Tax Liability: Adjustments for sick leave, tips, or group term life insurance benefits are documented in this section.
- Deposits and Payment Slips: Indicating the amount already deposited with the IRS and any balance due with the form.
Steps to Complete the 941 Form
Filling out the 941 Form requires careful calculation and reporting:
- Gather Payroll Data: Assemble all pay records for the quarter.
- Calculate Taxes: Determine total wages, federal tax withholding, and payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare.
- Complete the Identification Section: Provide business name, address, and EIN.
- Enter Financial Details: Fill out accurate figures in Sections 1-12 for wages and taxes.
- Adjust and Verify: Address any applicable adjustments for third-party sick pay or COBRA credits.
- Finalize and Review: Double-check calculations and ensure all fields are complete.
- Submit the Form: File electronically for efficiency or mail to the IRS.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
The 941 Form must be filed quarterly. The deadlines are typically the end of the month following the end of the quarter:
- First Quarter: April 30
- Second Quarter: July 31
- Third Quarter: October 31
- Fourth Quarter: January 31 (of the following year)
Who Typically Uses the 941 Form
Employers with employees subject to income tax withholding, Social Security, and Medicare taxes are required to file the 941 Form. This includes corporations, non-profits, limited liability companies, and partnerships engaging workers who receive regular compensation. Self-employed individuals may need to use different forms, such as the 1040-ES, for estimated taxes.


IRS Guidelines on the 941 Form
The IRS provides detailed instructions for completing the 941 Form to minimize errors. Employers must ensure they follow the provided guidelines, which cover everything from calculating tax liability to the proper method for reporting adjustments. The instructions emphasize accuracy in reporting figures and provide tips for avoiding common mistakes, such as transposing numbers or miscalculating tip allocations.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to file the 941 Form on time or underpaying taxes can result in penalties. The IRS imposes fines based on the delay length or the payment shortfall. To mitigate these risks, employers should maintain accurate records and consider using reliable accounting software to track payroll taxes.
Software Compatibility
For convenience, many businesses use software like TurboTax or QuickBooks to assist with completing and filing the 941 Form. These platforms streamline the data entry and calculation process and often include e-filing options. They offer built-in reminders for deadlines, automatic error checking, and detailed guides, supporting compliance and accuracy.
Differences between Digital and Paper Versions
There are two main ways to file the 941 Form: electronically via the IRS e-file system or by mail using the paper form. Digital submission is generally faster, enabling quicker processing and receipt confirmation. In contrast, paper filings may take longer to process and require manual checks. Electronic filing is highly recommended for businesses looking to simplify their tax processes.
Examples of Using the 941 Form
Consider a business with ten employees paying $50,000 in wages for a quarter. Using the 941 Form, the business would report the total wages and calculate applicable Social Security and Medicare taxes. They'd then declare federal tax withholdings and deduct any previous tax deposits to determine any due balance. Data from preceding closing months would be used to ensure accuracy, and the completed form would offer a clear view of the business's payroll tax responsibility for that period.