Overview and Purpose of State of Maine Taxes
The primary purpose of the state of Maine taxes is to generate revenue for the state's budget, supporting public services such as education, infrastructure, and healthcare. Maine employs a progressive tax system, meaning that tax rates increase with higher income brackets. Individuals, corporations, and other entities in Maine must comply with these tax regulations to maintain legal standing and contribute to the state’s growth.
Understanding Taxable Income in Maine
Taxable income in Maine includes wages, salaries, and other earned income, as well as interest, dividends, capital gains, and pension income. Residents of Maine are taxed on their worldwide income, while non-residents are taxed solely on income derived from sources within Maine. It is crucial to understand what constitutes taxable income when filing taxes to ensure compliance and accuracy.
- Residency Determination: Maine distinguishes between residents, part-year residents, and non-residents, each with different tax obligations.
- Common Deductions and Credits: Maine offers deductions and credits such as the Property Tax Fairness Credit and the Earned Income Tax Credit.
How to Obtain and Use Tax Forms
Tax forms for Maine can be obtained online from the Maine Revenue Services website or through tax software. These forms include detailed instructions for reporting income, deductions, and credits.
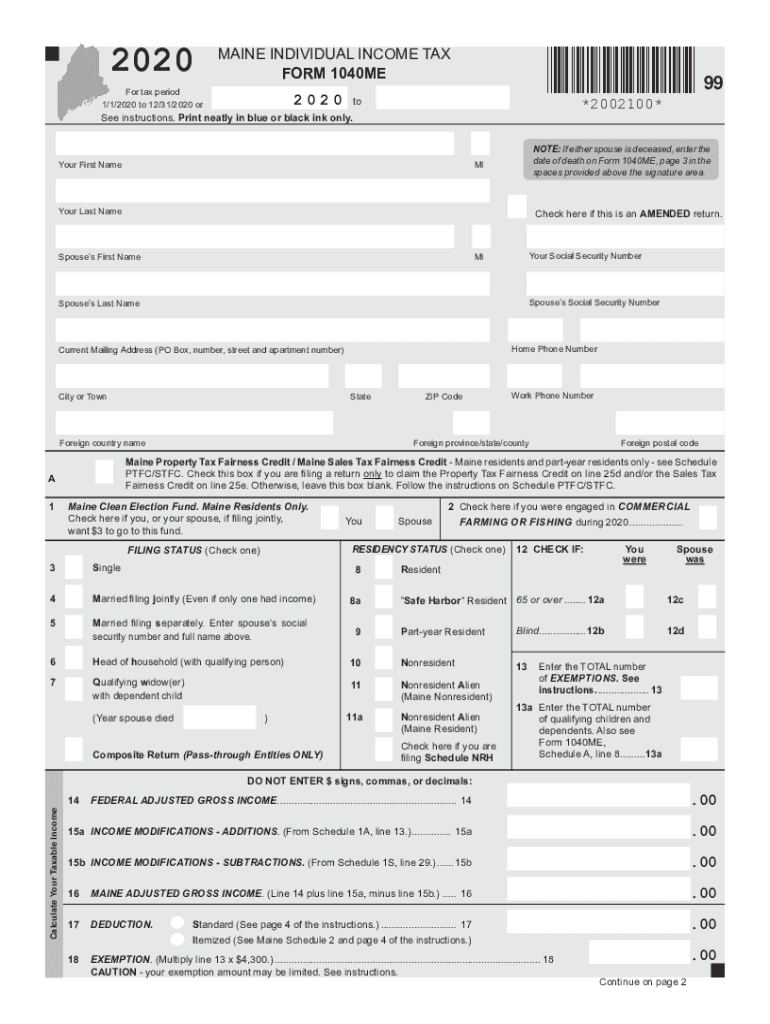
Filling Out the 1040ME
The 1040ME is the primary form for individual income taxes in Maine. It encompasses various sections to input personal data, calculate tax liabilities, and claim deductions or credits.
- Personal Information: Includes fields for name, address, social security number, and filing status.
- Income Reporting: Sections for various types of income, including wages, interest, and investment income.
- Calculation of Tax Liability: Use the form's tax tables and worksheets to calculate the amount owed.
Steps to Complete State of Maine Taxes
Completing the state of Maine taxes involves several key steps, from gathering necessary information to submitting the completed forms.
- Collect Required Documents: Gather documents such as W-2s, 1099s, and records of deductions or credits.
- Determine Filing Status: Choose a status based on your marital situation and household.
- Complete the 1040ME Form: Fill out each section according to your documentation.
- Calculate Taxes and Payments: Use worksheets and tax tables to determine your tax liability and any payments due.
- Submit the Form: Choose between online submission, mailing, or in-person filing at a tax office.
- Keep Copies: Retain copies of all filed documents for at least three years.
Important Deadlines and Submission Methods
Taxpayers in Maine should be aware of important deadlines and submission methods to avoid penalties.
Key Filing Dates
- Regular Deadline: Maine state taxes are typically due on April 15th, similar to federal taxes.
- Extensions and Late Filing: Extensions can be requested if additional time is needed, but interest may still accrue on unpaid taxes.
Submission Options
- Online Filing: Most tax software supports Maine state tax filing and provides direct submission to the Maine Revenue Services.
- Mailing: Paper forms can be mailed to the designated address provided by the Maine Revenue Services.
- In-Person Submission: Visiting a tax office allows for direct submission and the opportunity to ask questions.
Legal Obligations and Penalties for Non-Compliance
Understanding the legal requirements for Maine's tax system is essential for compliance and avoiding penalties.
Penalties for Late Filing or Payment
Failure to file or pay taxes on time can result in penalties and interest. It's important to comply with deadlines to avoid additional charges.
- Filing Penalties: Late filing may incur a penalty calculated as a percentage of unpaid taxes.
- Payment Penalties: Interest accrues on unpaid taxes from the due date until payment is made.
Variants and Alternatives to Tax Forms
Taxpayers may require different forms depending on their status or income sources.
Form Variants
- Non-Resident and Part-Year Resident Form: Special forms exist for those who lived in Maine for only part of the year or earned income within the state as non-residents.
- Alternative Filing for Seniors: Some forms offer simplified filing options for seniors with specific income profiles.
Taxpayer Scenarios and Software Compatibility
Different taxpayers in Maine may have specific considerations based on their profile.
Common Scenarios
- Self-Employed Individuals: Must account for additional taxes such as self-employment tax and may use specific deductions.
- Retirees: State-specific exemptions may apply to pension or retirement income.
Software Compatibility
- Tax Software: Tools like TurboTax and H&R Block support Maine tax forms and facilitate accurate filing.
- Integration with Federal Filing: Ensure software links state forms with federal tax forms for consistency.
Key Elements and Common Terms in State of Maine Taxes
Familiarity with common terms and key elements can simplify the tax filing process.
Definitions
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): A crucial figure used to determine taxable income.
- Filing Status: Impacts tax rates and eligibility for certain deductions.
Essential Components
- Deduction and Credit Listings: Understand which deductions and credits are available to maximize tax benefits.
- Tax Table Usage: Reference Maine’s tax tables for accurate calculation of tax liabilities based on income.
Each block provides detailed insight into the complexities and requirements of filing state taxes in Maine, helping to ensure compliance and accurate completion of tax obligations.