Definition and Meaning of Reading Level Chart
A reading level chart is a tool used to evaluate and categorize the readability of texts at different proficiency levels. This chart provides educators, parents, and students with a clear understanding of the appropriate reading level for various age groups and grade levels.
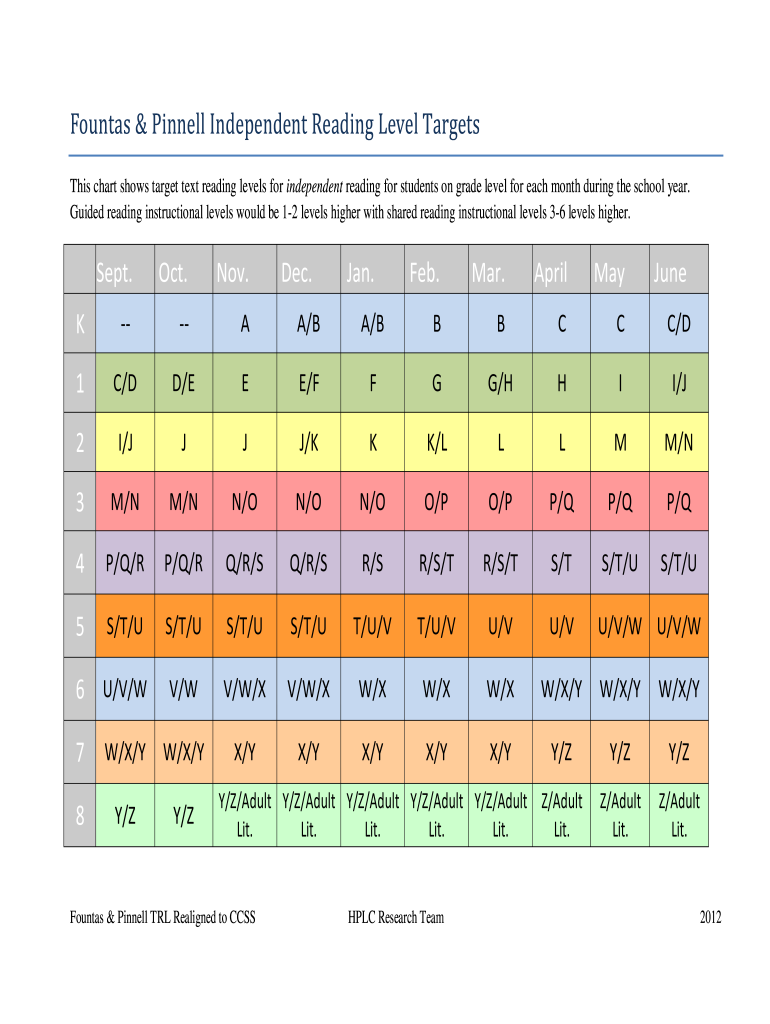
Reading levels are often represented in terms of specific systems, such as the Fountas and Pinnell grading scale or Lexile measures. These systems assign a numerical or alphabetical value to texts, indicating their complexity based on factors such as vocabulary, sentence length, and content.
A well-constructed reading level chart allows users to easily identify the right texts for independent reading, guided instruction, or shared reading experiences. For instance, a reading level chart might indicate that a first-grade student should read at a level A to C, suggesting the text's complexity should align with their developing reading skills.
Understanding the meaning and purpose of reading level charts is crucial for educational professionals and parents alike, ensuring children engage with materials that foster growth without causing frustration.
How to Use the Reading Level Chart Effectively
Using a reading level chart involves several steps that are crucial for selecting appropriate reading materials. This process ensures that students encounter texts that meet their reading abilities, promoting effective learning.
-
Identify the Student's Reading Level: Start by assessing the student's reading ability using standardized tests or teacher evaluations. This assessment helps determine which level of text they should be reading.
-
Select the Appropriate Level from the Chart: Once you have established the reading level, consult the reading level chart to find corresponding texts. For example, if a student is at a Level D on the Fountas and Pinnell scale, select texts with a similar designation.
-
Monitor Progress: After providing reading materials, periodically reassess the student's reading level. As students improve, upgrade their reading materials by moving to higher levels on the chart.
-
Consider Genre and Interests: While the chart provides a framework, it is also essential to consider the student's interests and the genre of texts. Engage them with a variety of genres while still adhering to their reading level.
-
Encourage Reading Across Levels: Occasionally, allow students to explore texts above their identified level to challenge them. This should be accompanied by guidance and support to enhance comprehension.
By following these steps, educators and parents can utilize the reading level chart to foster a positive reading experience that aligns with each student's developmental stage.
How to Obtain a Reading Level Chart
Accessing a reading level chart is straightforward, with various sources available for educators and parents. Here are several methods to obtain an effective reading level chart:
-
Educational Publishers: Many educational publishers provide reading level charts, including the Fountas and Pinnell system. These can often be downloaded from their official websites or requested in print.
-
Online Resources: Numerous educational websites offer free versions of reading level charts. Websites dedicated to literacy resources, teacher tools, and educational guides often provide downloadable PDFs or online interactive charts.
-
Library Access: Local libraries may have physical copies of reading level charts or can assist in obtaining one through interlibrary loans. They often have resources available for educators and parents.
-
Educational Institutions: Schools may provide reading level charts as part of their reading programs or curricula. Additionally, districts may supply teachers with comprehensive charts specific to their instructional materials.
-
Workshops and Professional Development: Educators can attend workshops or professional development events where they may receive reading level charts, along with training on how to implement them effectively in classroom settings.
By utilizing these methods, obtaining a reading level chart becomes a manageable task, allowing educators and parents to support students’ reading needs effectively.
Key Elements of a Reading Level Chart
A reading level chart comprises several critical elements that contribute to its effectiveness as a resource:
-
Level Designation: Each reading level is identified by specific markers, such as letters or numbers, representing different complexity gradients. For example, Fountas and Pinnell uses letters A-Z, while Lexile measures texts with a numerical score.
-
Grade Correlation: Charts typically include grade-level correlations, indicating which grades correspond to specific reading levels. For instance, a Level G text may be appropriate for second-grade readers.
-
Text Examples: Many reading level charts provide sample titles or authors associated with each level. This element assists users in identifying actual reading materials across various genres.
-
Reader Characteristics: Effective charts include information about typical reader characteristics for each level, such as vocabulary complexity, sentence structure, and typical themes found in texts.
-
Use Percentage Indicators: Some charts indicate the percentage of comprehension expected at different levels. This feature helps gauge how well students should understand texts at their designated reading levels.
Understanding these key elements ensures that educators and parents can effectively use reading level charts to match texts appropriately with student reading abilities.
Examples of Using Reading Level Charts in Practice
Utilizing reading level charts in educational settings can enhance instruction and support literacy development. Here are practical examples:
-
Guided Reading Groups: Teachers often use reading level charts to organize guided reading groups, selecting texts that align with each group's reading level. For instance, a second-grade group at Level I will read books that may include titles like "Frog and Toad Are Friends" while discussing comprehension strategies.
-
Independent Reading Assignments: In a classroom, students can choose books from a designated reading level range. For example, students reading at Level J can explore books like "Little Bear". This method enriches their reading experience and encourages autonomy.
-
Parent Workshops: Educators can host workshops for parents, demonstrating how to use reading level charts to select books for home reading. Providing examples helps parents understand the importance of consistent exposure to appropriately leveled texts.
-
Literacy Assessments: Schools can integrate reading level charts into literacy assessments to analyze student progress. By comparing the initial reading level with later assessments, educators can determine growth and adjust instruction.
-
Library Programs: Public libraries can utilize reading level charts for curating book collections for children. Creating sections based on various reading levels facilitates easy access for young readers and helps parents guide their children's selections.
These examples show how effectively integrating reading level charts into various educational contexts can foster a love for reading and promote skill development.