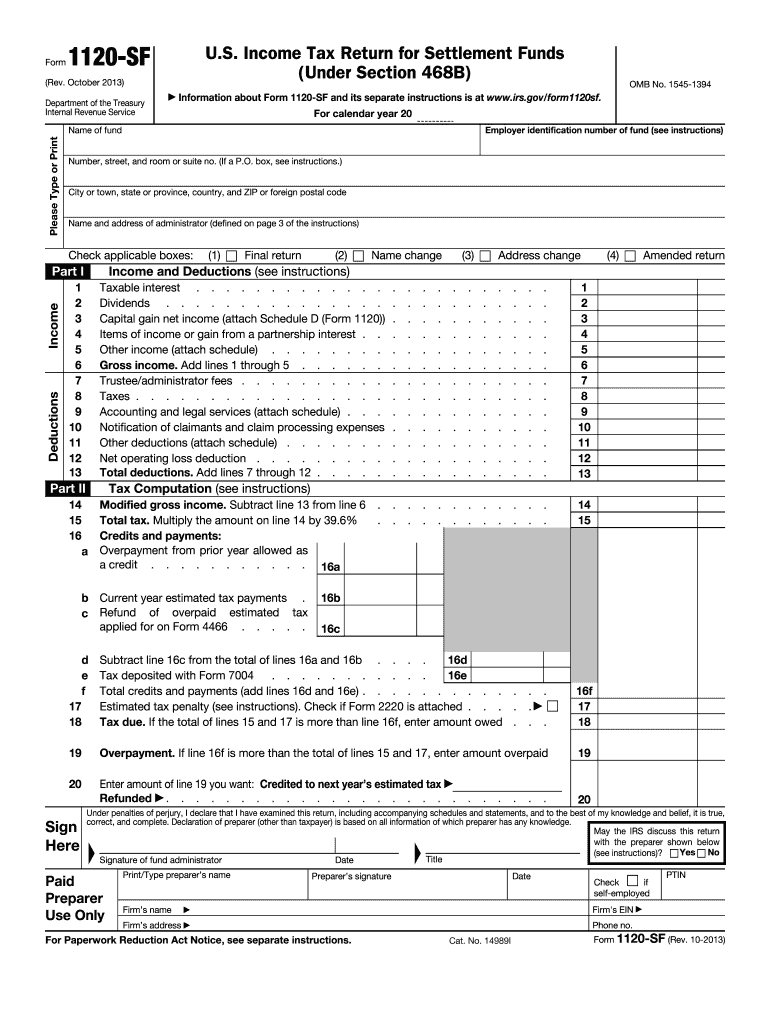
Definition & Meaning of Form 1120-SF
Form 1120-SF, formally known as the U.S. Income Tax Return for Settlement Funds, is a specific tax return required for settlement funds established under Section 468B of the Internal Revenue Code. This form enables settlement funds to accurately report their income, deductions, and computed tax liabilities for a given calendar year.
Settlement funds are created to manage and allocate funds that have been received in settlements involving legal claims. These funds must adhere to specific tax regulations, and the Form 1120-SF is essential for ensuring compliance with IRS requirements. By utilizing this form, funds can provide necessary financial details, including taxable income, deductible expenses, and relevant distributions made to claimants.
The form encompasses important sections such as:
- Identification of the Fund: Essential information about the fund itself, including its name and Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- Income Reporting: Sections designated for reporting various types of income earned by the fund during the year.
- Deductions: Detailed accounts of deductions the fund can claim, which may include administrative expenses and management fees.
- Balance Sheets: A space for presenting the fund's financial position at the end of the tax year.
How to Use the Form 1120-SF
Completing Form 1120-SF is a critical process for settlement funds to ensure tax compliance. Here’s a breakdown of how to effectively use this form:
-
Gather Required Information: Before beginning to fill out the form, gather all necessary documentation, including financial statements, income reports, and records of distributions made to claimants.
-
Complete Identification Sections: Fill out the identifying information about the settlement fund, including the name, address, and EIN. Accurate identification is essential to avoid issues during processing.
-
Report Income: Enter the total income earned by the fund for the tax year. This may include interest income, dividends, and any other forms of revenue. Ensure that all income sources are documented.
-
Deduct Eligible Expenses: Identify and deduct all allowable expenses related to the operation of the fund. These may involve necessary administrative costs, legal fees, or any other expenses directly related to the fund’s operation.
-
Balance Sheet Information: Provide a balance sheet as of the end of the tax year, which will list the fund's assets, liabilities, and equity. This information is crucial for assessing the fund's overall financial health.
-
Distribution Reporting: Detail the distributions made to claimants throughout the year to ensure that all funds are accounted for and that claimants are properly classified for tax purposes.
-
Review and Submit: Carefully review all sections of the completed form for accuracy before submission. Submission can be done electronically or via mail, depending on IRS guidelines.
Each of these steps is vital for the accurate completion of Form 1120-SF, promoting compliance and reducing the risk of errors that could lead to penalties or delays.
Key Elements of Form 1120-SF
Form 1120-SF is composed of several key elements that play a crucial role in the reporting process. Understanding these elements can aid fund managers in accurately preparing their tax returns:
-
Identification Section: Captures the essential information about the fund, including legal name, EIN, and address.
-
Income Section: This segment requires detailed reporting of all sources of income the fund receives, broken down by categories as needed.
-
Deductions Section: Allows the fund to list qualifying expenses that reduce its taxable income, which can directly affect the tax liability.
-
Distributions Details: This area must be filled in carefully to reflect how the fund distributes money to claimants. Accurate reporting of these distributions is necessary for both the fund and the claimants’ tax filings.
-
Balance Sheet: A snapshot of the fund’s financial standing at the end of the fiscal year, displaying assets, liabilities, and net worth, providing critical insights into the fund's financial health.
Together, these elements ensure that Form 1120-SF comprehensively captures the necessary financial information required by the IRS for settlement funds.
Important Terms Related to Form 1120-SF
A clear understanding of relevant terminology is essential when working with Form 1120-SF. Below are some important terms that fund managers should be aware of:
-
Settlement Fund: A pool of money established to distribute payments to claimants as a result of legal settlements. These funds must adhere to specific IRS regulations regarding their tax status.
-
Taxable Income: The portion of the fund's income that is subject to taxation after all allowable deductions have been accounted for. Accurate reporting ensures that the fund pays the correct amount of tax.
-
Distributions: Payments made to claimants from the settlement fund. Proper documentation of these transfers is crucial for both the fund and the recipients.
-
Deductions: Certain expenses that can be subtracted from the fund's income, thus reducing the overall taxable income. Examples might include legal fees and administrative costs directly associated with the fund's operation.
Familiarity with these terms enhances the accuracy of the tax reporting process and ensures compliance with IRS regulations.
Filing Deadlines for Form 1120-SF
Form 1120-SF carries specific filing deadlines that are crucial for compliance. Settlement funds should be aware of the following important dates:
-
Initial Filing Deadline: The form must be filed by the 15th day of the third month following the end of the fund’s tax year. For most funds operating on a calendar year, this deadline typically falls on March 15.
-
Extensions: If additional time is needed, funds can apply for an automatic six-month extension by submitting Form 7004. However, this extension only applies to the filing date and does not extend the time to pay any due taxes.
-
Late Filing Penalties: Not adhering to the deadlines can result in penalties. The IRS imposes late filing fees, which can accumulate daily based on the duration of the delay. Therefore, it is essential to submit the form promptly to avoid additional costs.
Understanding and adhering to these deadlines is vital for maintaining compliance and avoiding unnecessary penalties related to the filing of Form 1120-SF.