Definition and Meaning of the Business Registration Office
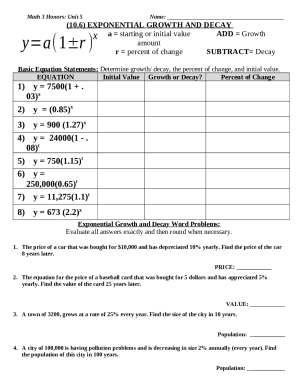
The Business Registration Office serves as a formal place where businesses are officially recorded and authorized to operate legally. The term "Business Registration Office" implies the governmental or administrative entity responsible for managing and processing business registrations. This includes maintaining records of facts such as the legal name, business structure, and ownership. The primary purpose of the Business Registration Office is to ensure that businesses comply with local laws and regulations while fostering an environment of transparency and accountability. Registration typically involves a variety of forms and documentation depending on the jurisdiction.
How to Use the Business Registration Office
To effectively utilize the services of the Business Registration Office, individuals or business entities must first determine the exact documentation required for their specific type of registration. This often involves:
- Identifying the appropriate business structure (e.g., LLC, S-Corp, partnership).
- Gathering necessary personal and business information.
- Completing registration forms accurately and thoroughly.
- Submitting forms through appropriate channels, which may include online submissions, postal mail, or in-person visits.
Once registered, the office often provides a certificate of registration, confirming the legal status of the business entity within the jurisdiction.
Steps to Complete the Business Registration Office Process
- Determine Your Business Structure: Choose whether your entity will be a sole proprietorship, corporation, partnership, or limited liability company (LLC).
- Gather Required Documents: Collect personal identification, articles of incorporation (if applicable), business addresses, and relevant financial information.
- Complete Application Forms: Fill out the specific registration forms required by the state or local jurisdiction. Ensure all information is accurate and complete.
- Submit the Forms: Deliver your application through the designated submission method (online, by mail, or in-person). Digital submissions are often encouraged for faster processing.
- Pay the Required Fees: Registration usually requires a fee payable by credit card, check, or electronic transfer, contingent on the submission method and type of business.
- Receive Confirmation and Certificate: Upon successful registration, receive a formal acknowledgment and an official certificate, permitting the lawful operation of your business.
Importance of the Business Registration Office
Registering with the Business Registration Office is crucial for several reasons:
- Legal Compliance: Ensures businesses operate within the law and meet regulatory requirements.
- Business Identity: Allows a business to establish a unique identity and protect its business name legally.
- Consumer Confidence: Registered businesses are more likely to be trusted by consumers, enhancing reputation and legitimacy.
- Access to Banking and Financing: Many banks require proof of registration to open business accounts or secure loans.
Who Typically Uses the Business Registration Office
The primary users of the Business Registration Office include:
- Entrepreneurs and startups seeking to establish a new business entity.
- Large corporations registering branches or subsidiaries.
- Legal professionals assisting clients with business registrations.
- Accountants and financial advisors managing compliance and operational registrations.
- Non-profit organizations needing official recognition and status.

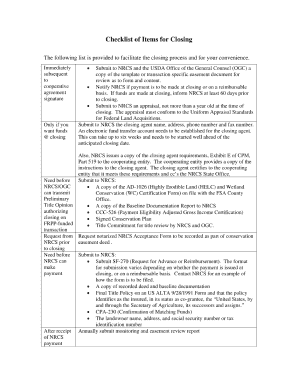
Key Elements of the Business Registration Office
Understanding the components of business registration helps to streamline the process:
- Name Registration: Ensures the business name is unique and not already in use.
- Tax Identification Numbers: Obtains various tax-related identifiers necessary for business operation, including EIN for federal tax purposes.
- Licensing and Permits: Depending on industry and location, additional licenses or permits may be required.
- Articles of Incorporation: For corporate entities, these documents outline the formation and operation structure.
State-Specific Rules for Business Registration
While the general process is similar, specific rules and requirements can vary:
- Filing Fees: Different states have varying fee structures.
- Renewal Periods: Registration may need renewal yearly or bi-yearly, depending on the state.
- Specific Forms: Unique forms might be required, such as those for local taxes or environmental compliance.
- Business Structure Regulations: Some states have unique definitions or rules for specific business types.
Examples of Using the Business Registration Office
Real-world scenarios illustrate the importance and function of business registration:
- Tech Startups: Silicon Valley-based startups often begin by acquiring an LLC status through the California Secretary of State for liability protection while gaining credibility with investors.
- Retail Establishments: A new boutique might register as an S-Corp to benefit from potential tax benefits and stock issuance options.
- Consultancy Services: A consulting firm might select a partnership structure for flexible management and operational decisions.
IRS Guidelines on Business Registration
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides valuable insights and requirements for businesses:
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): Essential for tax filing; the application process involves detailed business activity disclosures.
- Tax Classification: Ensures proper alignment of entity type with federal tax obligations.
- Reporting Requirements: Each business structure has unique tax reporting obligations, necessitating alignment with both federal and state guidelines.