Overview of the Rumke Table in Hematology
The Rumke table is a vital tool in the field of hematology, particularly when analyzing blood cell types. This table provides reference ranges for proportions of various white blood cells, which are crucial for diagnosing conditions like infections, leukemia, and other hematologic disorders. Understanding how to use and interpret the Rumke table can significantly enhance laboratory outcomes and patient care.
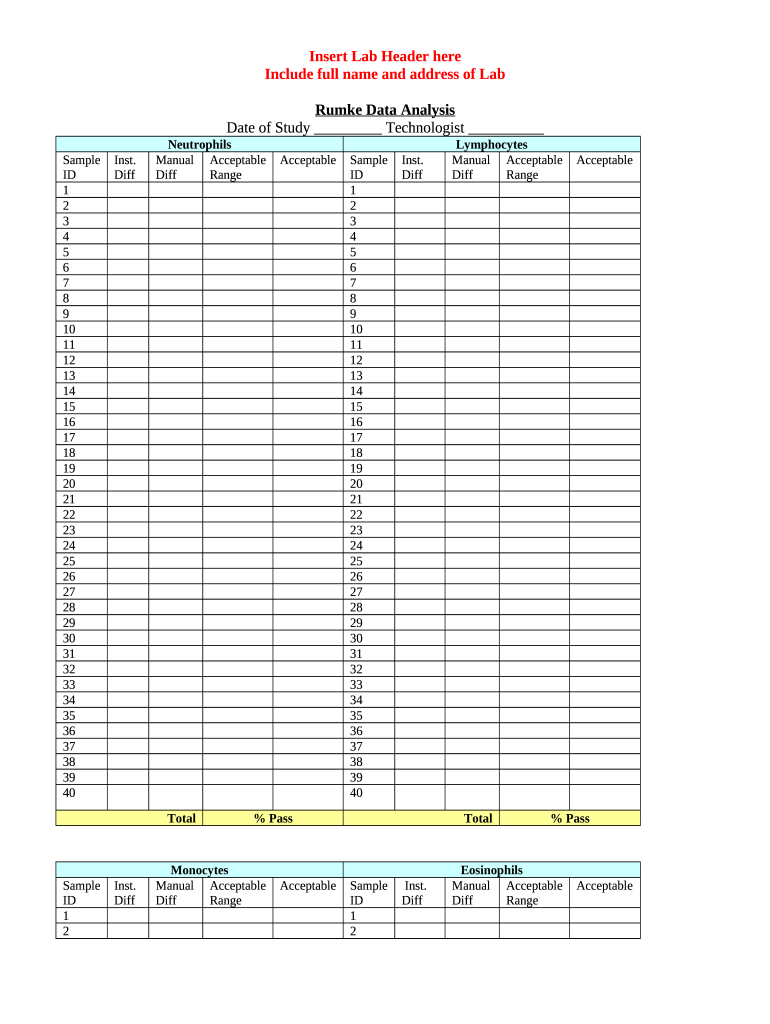
Key Components of the Rumke Table
The Rumke table typically includes the following components:
-
Cell Types: The table outlines different types of blood cells, including:
- Neutrophils
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
-
Reference Ranges: Each cell type is associated with acceptable reference ranges, which may vary based on demographics and clinical context.
-
Sample IDs: Each entry in the table corresponds to specific sample IDs that facilitate the tracking and identification of test results.
Using the Rumke Table for Hematology Differential
The Rumke table hematology differential is designed to assist laboratory technicians in examining and categorizing blood cell populations. Here’s how to effectively utilize this tool:
-
Collection of Blood Samples: Proper collection techniques are essential to avoid contamination and ensure accurate results. Use of EDTA tubes is recommended for preserving cellular integrity.
-
Manual Differential Counts: Once blood smears are prepared, manual counts can be performed under a microscope. Each white blood cell type is counted to determine its percentage relative to the total white blood cell count.
-
Interpreting Results: Compare obtained values against the reference ranges in the Rumke table. Clinicians can identify abnormalities based on deviations from normal ranges.
Practical Applications of the Rumke Table
The Rumke table holds various practical applications in clinical settings:
-
Diagnosis: It aids in diagnosing infections, anemia, or hematologic malignancies by providing a clear reference point for white blood cell counts.
-
Monitoring: Healthcare providers can utilize the Rumke table as a monitoring tool for patients undergoing treatment for conditions like leukemia, where white blood cell counts may fluctuate.
-
Education: The table serves as an educational resource for hematology students and professionals, allowing them to grasp the significance of each blood cell type and its clinical implications.
Common Variants and Formats
The Rumke table can be found in several formats for convenience, including:
- PDF Version: Ideal for printouts in the laboratory for quick reference.
- Excel Format: Allows for data manipulation and electronic record keeping, enhancing tracking of patient results.
There are also adaptations of the Rumke table that cater to specific populations, such as pediatric or geriatric patients, considering the variance in normal ranges across different age groups.
Important Considerations for Using the Rumke Table
When using the Rumke table, several factors should be carefully considered:
-
Patient Demographics: Normal ranges can vary based on age, sex, and ethnicity. Always consider the patient's profile when interpreting results.
-
Clinical History: A comprehensive clinical history is essential as it can provide context for interpreting white blood cell abnormalities.
-
Methodological Variances: Different laboratories may employ varied methodologies in counting cells, which can influence results. It is important to standardize procedures for consistency.
Understanding how to effectively use the Rumke table can greatly enhance diagnostic and monitoring capabilities in hematology, providing a framework for accurate analysis and informed clinical decisions.