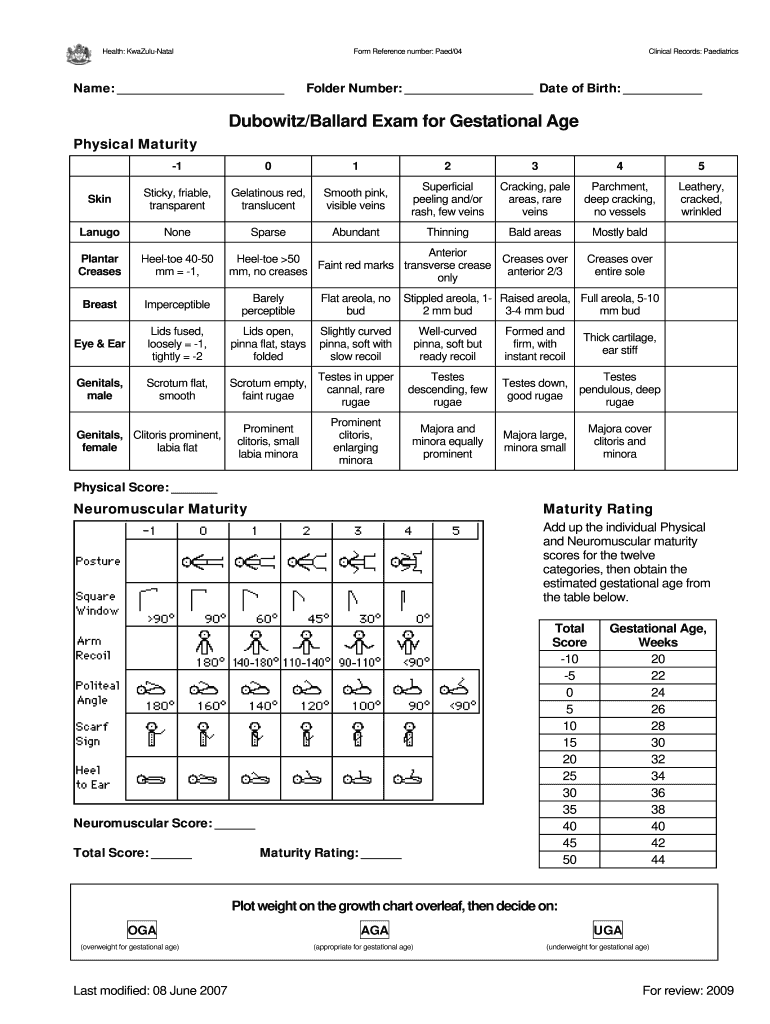
Understanding the Ballard Score
The Ballard score is a standardized tool used primarily to assess the gestational age of newborns based on physical and neuromuscular criteria. It is particularly utilized in clinical settings to aid healthcare professionals in determining the maturity of infants. The tool consists of a scoring system that evaluates specific characteristics and behaviors of a newborn, allowing for a more accurate estimation of gestational age.
Key Elements of the Ballard Score
- Physical Maturity: This aspect focuses on observable features of the infant, including skin texture, lanugo density, plantar surface creases, and ear cartilage. Each feature is assigned a score that contributes to the overall assessment.
- Neuromuscular Maturity: This element evaluates the infant's posture, muscle tone, and reflexes, such as the ability to grasp. These observations offer insight into the infant’s neuromuscular development, which is crucial for understanding gestational age.
- Total scoring: The combined scores from both physical and neuromuscular assessments provide a comprehensive view of the infant's maturity level, which can significantly influence medical decisions regarding care and intervention.
How to Use the Ballard Score
To effectively utilize the Ballard score, healthcare providers should follow a systematic approach:
- Gather Required Tools: Ensure that the necessary score sheet is available. This can be in printable PDF format or a digital version integrated into healthcare systems.
- Conduct Assessments: Observe and document the physical characteristics and neuromuscular responses of the newborn at the appropriate time after birth, ideally within the first hours of life.
- Calculate Scores: Assign points to each observed characteristic per the scoring criteria laid out in the Ballard score chart.
- Interpret Results: Analyze the total score to estimate gestational age and classify the infant as appropriate for gestational age (AGA), small for gestational age (SGA), or large for gestational age (LGA).
Importance of the Ballard Score in Clinical Settings
The Ballard score serves as an essential tool for healthcare professionals, offering several benefits:
- Clinical Decision-Making: By providing a reliable estimate of gestational age, the score assists in making critical decisions related to care, such as nutritional support and developmental interventions.
- Standardization: The use of a standardized scoring system allows for consistent assessment across different healthcare providers and institutions.
- Research Applications: The Ballard score also plays a significant role in research settings, contributing to studies on infant development and neonatal care protocols.
Users of the Ballard Score
The primary users of the Ballard score include:
- Pediatricians: Often the first point of contact for newborn assessment, pediatricians utilize the score to guide treatment plans.
- Obstetricians: During the prenatal period, obstetricians may use the score for better planning regarding delivery and immediate care of the newborn.
- Neonatologists: These specialists employ the Ballard score to monitor and manage care for premature or high-risk infants in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
Examples of the Ballard Score Application
The application of the Ballard score can be observed in various clinical scenarios:
- Premature Infants: For an infant born at 28 weeks gestation, the Ballard score may indicate a lower maturity level, prompting specialized care protocols to support growth.
- Term Infants: A full-term infant scoring high on the Ballard assessment indicates appropriate development and may lead to routine care without the need for intensive intervention.
Understanding the Ballard score and its applications is crucial for healthcare providers involved in neonatal care, ensuring that infants receive the appropriate support tailored to their gestational age and development.