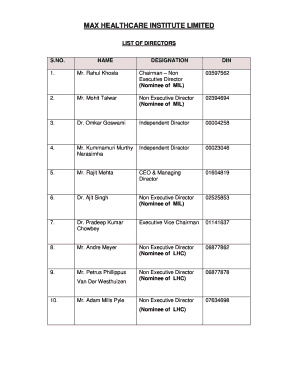
Definition and Purpose of a Logging Business Plan
A logging business plan is a comprehensive document outlining the strategies, objectives, and operational framework for a logging company. Primarily, it serves as a roadmap for establishing and running a successful logging business. This plan details the scope of operations, including the scale of the logging activities, type of equipment used, and the number of crews needed. It also includes financial projections, market analysis, and a marketing strategy to ensure the business not only thrives but also competes effectively in the marketplace.
- Scope of Operations: Large-scale operations might include mechanized logging and extensive logistic support.
- Financial Components: Incorporates budget planning, investment requirements, and projected revenues.
- Market Strategy: Identifies target markets, pricing strategies, and competitive positioning.
Steps to Complete the Logging Business Plan
Creating a robust logging business plan involves several key steps, ensuring that every aspect of the business is thoroughly planned.
- Research and Analysis: Conduct a detailed market analysis to understand industry trends and consumer demands.
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline short-term and long-term business goals.
- Outline Operational Plans: Describe operational workflow, from logging techniques to delivery methods.
- Financial Planning: Develop budgets and financial forecasts, including funding requirements and ROI estimates.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks and create mitigation strategies.
- Review and Revise: Regularly review the plan and update it based on market changes or business growth.
Key Elements of the Logging Business Plan
A successful logging business plan should include several critical elements that provide a clear picture of the business strategy.
- Executive Summary: Gives a snapshot of the company and its mission.
- Business Description: Details the nature of the logging business and its operational strategy.
- Market Analysis: Provides insights into the industry landscape and competitiveness.
- Organization and Management: Describes the business structure and management hierarchy.
- Sales and Marketing Strategy: Outlines plans to reach potential customers and retain existing ones.
- Funding Request: If applicable, includes a formal request for funding with detailed use of funds.
How to Use the Logging Business Plan
The logging business plan is a dynamic tool that guides business decisions and helps secure financing.
- Internal Guidance: Use it as an operational blueprint for decision-making and strategy formulation.
- Securing Investment: Present it to investors and banks to showcase the viability and profitability of the venture.
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly compare actual performance against plan projections to assess business health.
Who Typically Uses the Logging Business Plan
Various stakeholders find the logging business plan beneficial for different purposes.
- Business Owners and Entrepreneurs: Plan and manage their logging operations effectively.
- Investors and Financiers: Evaluate the feasibility of investing in the business.
- Managers and Employees: Understand the business objectives and their roles in achieving them.

Important Terms Related to Logging Business Plan
Understanding specific terms associated with logging business plans ensures precise communication and execution.
- Harvesting Schedule: The timeline and techniques used for cutting timber.
- Yield Projection: Expected output of timber based on logging practices.
- Sustainability Practices: Methods ensuring environmental responsibility in logging.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Management of resources from logging site to final delivery.
Legal Considerations in Logging Business Plans
Operating a logging business involves navigating various legal frameworks, particularly in environmental compliance and land use.
- Permits and Licenses: Ensure all necessary legal permissions for logging activities.
- Environmental Regulations: Adhering to laws that protect forest ecosystems.
- Labor Laws: Compliance with workforce safety and fair labor standards.
Examples of Using the Logging Business Plan
Several real-world scenarios demonstrate the utility of a well-crafted logging business plan.
- Startup Ventures: New businesses utilize plans to structure their entry into the logging industry.
- Expansion Projects: Existing companies use these plans to navigate adding new regions of operation or increasing production capacity.
- Operational Overhaul: A change in business strategy, such as adopting new technology, is guided by revisions in the business plan.
Business Types that Benefit Most from a Logging Business Plan
While a logging business plan is critical for most logging operations, several business types see particular advantages.
- Independently Owned Logging Firms: Need detailed plans for scaling and financial tracking.
- Logging Cooperatives: Benefit from coordinated efforts in marketing and operations.
- Timber Exporters: Rely on comprehensive plans to handle international trade logistics and compliance.