Definition and Purpose of INT-140 Form
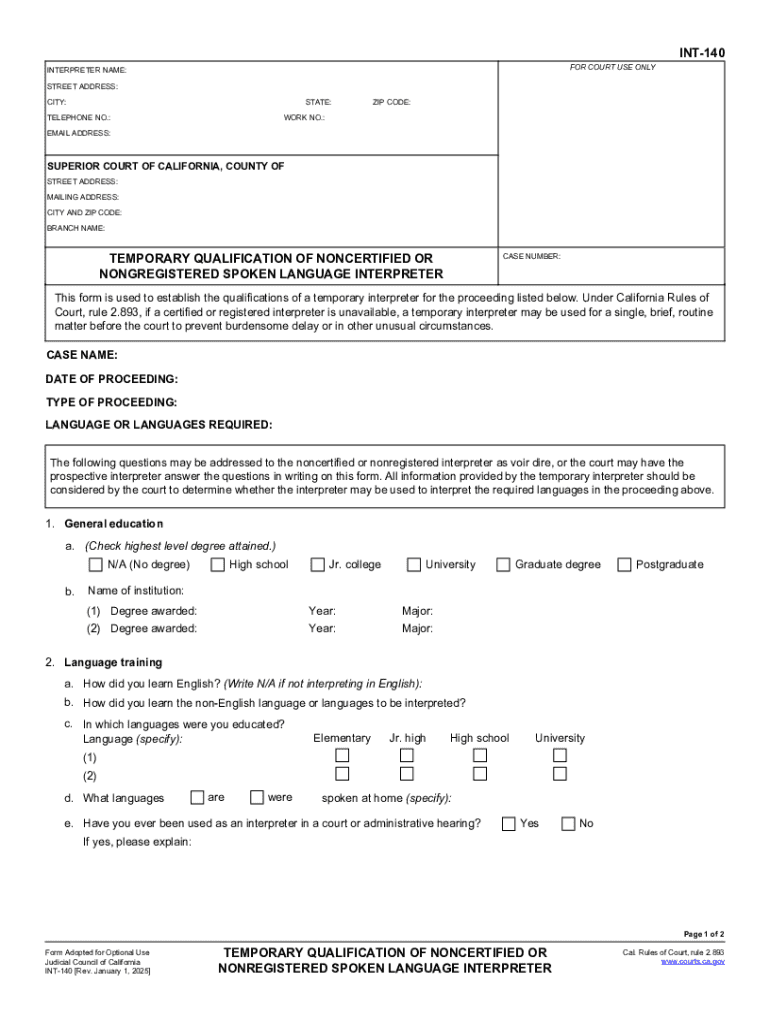
The "INT-140 Temporary Qualification of Noncertified or Nonregistered Spoken Language Interpreter Judicia" form is used predominantly by the Superior Court of California. This document is essential for establishing the temporary qualification of spoken language interpreters who are not certified or registered, specifically for court proceedings. It requires interpreters to provide detailed information about their educational background, language training, and any potential disqualifications. Through this form, the court can officially recognize the interpreter's temporary qualification status when a certified interpreter is not available.
How to Use the INT-140 Form
Utilizing the INT-140 form involves a comprehensive process aimed at documenting the interpreter’s qualifications. The form must accurately reflect the interpreter’s competencies, ensuring the details provided are verifiable and complete. Users should pay close attention to each section, making sure to fill in all mandatory fields to avoid delays or rejections from the court.
Steps to Complete the INT-140 Form
- Personal Information: Enter the interpreter's full name and contact details accurately.
- Education and Training: Detail educational history and specific language training, emphasizing relevant certificates or courses undertaken.
- Professional Experience: Provide a robust account of previous interpreting experiences, including types of events and languages interpreted.
- Declaration: The interpreter must sign and date the form, affirming the truthfulness of the information provided.
- Submission: The completed form should be submitted to the respective court as directed, either through mail, in-person, or as instructed for digital submissions.
Importance of Completing the INT-140 Form
This form serves a key function by ensuring interpreters with non-standard qualifications are still vetted and deemed competent for court duties. Completing the INT-140 form not only contributes to maintaining the integrity of court proceedings but also ensures that justice is accessible to non-English speakers.
Who Typically Uses the INT-140 Form
Main users of this form include court officials requiring interim interpretation services and interpreters who have not achieved full certification or registration. Legal practitioners who handle cases involving non-English speaking clients may also facilitate the form’s use to engage necessary language services.


Legal Considerations of the INT-140 Form
The INT-140 form holds legal weight as it formalizes the appointment of a noncertified or nonregistered interpreter for judicial purposes. This process ensures that interpreters are authorized to perform in legal settings, safeguarding against unqualified interpretations that might jeopardize court rulings.
Key Elements to Include in the INT-140 Form
Critical elements of this form include:
- Interpreter’s Educational Background: Specific details about the interpreter's training and education.
- Language Proficiency: Evidence of proficiency in both English and the target language.
- Professional Experience: Prior interpretation engagements in legal or quasi-legal environments.
State-Specific Guidelines for the INT-140 Form
While the INT-140 form is specific to California, nuances in its application might exist. Courts may have individual mandates on form submission, required additional documentation, or interpreter criteria. It's crucial to verify with local judicial authorities to ensure full compliance with any state-specific adaptations.
Examples of Practical Use of the INT-140 Form
In practice, the INT-140 is often utilized in cases where immediate linguistic assistance is essential, such as:
- Emergency Hearings: When certified interpreters are unavailable.
- Small Claims Court Sessions: Where rapid and accurate language assistance is required.
- Traffic Violation Hearings: Ensuring defendants or witnesses who do not speak English clearly understand the proceedings.
By addressing these common scenarios, the form demonstrates its practical application within the judicial system, providing necessary language support efficiently.