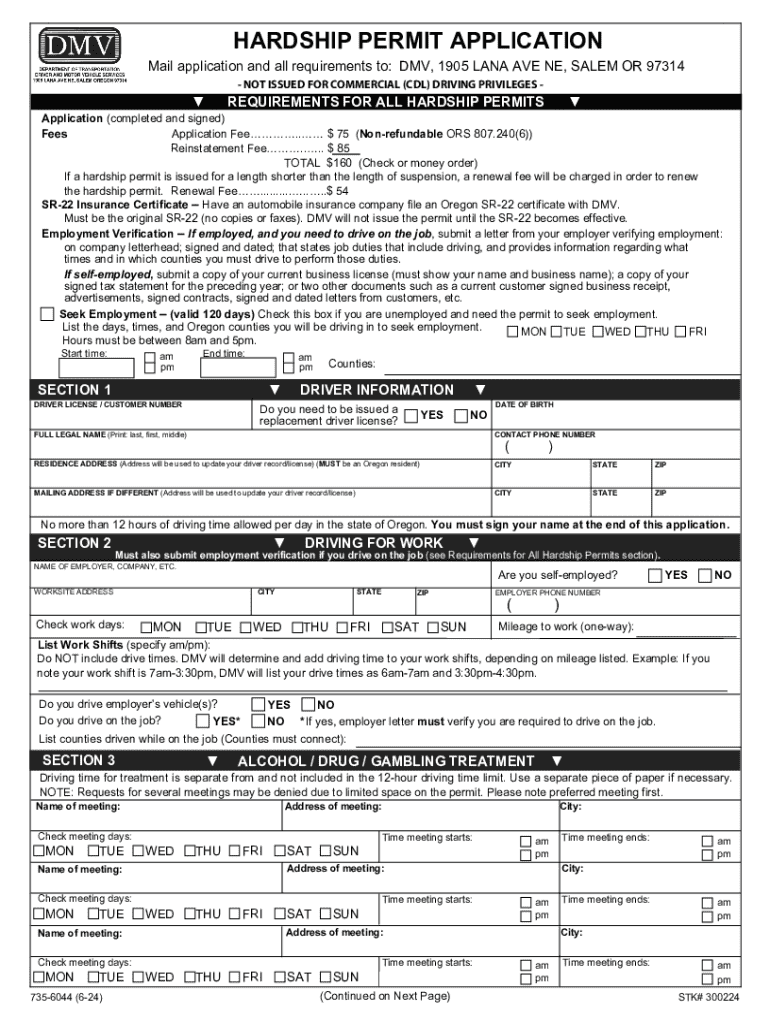
Definition and Meaning of Form
Form is an essential document utilized primarily within the transportation sector. The form is generally associated with vehicle-related applications and approvals, including permits and certifications required by state authorities or relevant departments. Its core function is to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and to facilitate the orderly management of vehicular operations.
Understanding Its Purpose
- Form serves as a critical tool for validating legal and regulatory requirements.
- It is often mandatory for specific operations, including commercial transport activities, where adherence to state laws and guidelines is imperative.
- The document helps streamline the paperwork process, reducing the administrative burden on applicants by standardizing information submission.
How to Use Form
Instructions for Proper Use
- Review the Requirements: Ensure that you fully understand the instructions provided with the form. This includes pre-requisites such as fees, identification documents, and other materials that must accompany the application.
- Complete All Sections: Fill out each required field with attention to detail, ensuring accuracy to avoid processing delays.
- Verification and Submission: Double-check the form for completeness, ensuring all certifications and attestations are signed and dated as required.
Real-World Scenarios
- Transport companies typically need to submit this form when applying for new vehicle permits.
- Individuals might use it to transfer vehicle ownership under specific circumstances where state approval is necessary.
Steps to Complete the
Comprehensive Completion Guide
- Gather Documents: Collect all necessary documentation such as identification, proof of address, and any supporting materials mentioned in the form's instructions.
- Fill in Personal Details: Complete sections related to personal and contact information. Ensure consistency with official records.
- Provide Vehicle Information: Enter all relevant details about the vehicle in question, ensuring they reflect current and accurate records.
- Meet Certification Requirements: If applicable, secure appropriate certifications or endorsements from authorized parties.
- Review and Sign: Authenticate your application with signatures where specified and verify accuracy and completeness before submission.
Edge Cases and Exceptions
- Some applicants might need to provide additional documentation if the vehicle has unique attributes or is customized for special use.
- Legal guardians may complete the form on behalf of minors where pertinent to family-based or guardianship-related vehicle registrations.
Who Typically Uses the


Primary Users
- Commercial Vehicle Operators: Companies operating fleets commonly utilize this form for regulatory compliance, including logistics and transport enterprises.
- State Agencies: Departments managing vehicle registrations and certifications require this form to process and verify compliance with legal obligations.
Inclusion of Secondary Users
- Private individuals engaging in vehicle sales or transfers might also be mandated to use this form.
- Collectors or restorers handling vintage or specialty vehicles often need this document for registration and certification purposes.
Required Documents for
Essential Documentation
- Identification: Government-issued ID or driver's license for applicant verification.
- Proof of Ownership: Title or bill of sale for the vehicle to establish rightful possession.
- Certification or Inspection Reports: Where required, up-to-date vehicular inspection certificates must accompany the form.
Details and Omissions
- Documentation may vary based on state-specific mandates, highlighting the importance of consulting local guidance.
- Failure to include mandatory documents can lead to rejection or extended processing times.
Form Submission Methods (Online / Mail / In-Person)
Available Options
- Online Submission: Utilize state transportation department portals to upload and submit digital versions of the form and accompanying documents.
- Mail-in Submission: Complete the form and send it along with required documents to the specified address. Ensure mail tracking for proof of submission.
- In-Person Submission: Visit local DMV or equivalent office to submit forms directly, allowing for immediate assistance and verification.
Pros and Cons
- Online submissions offer convenience and speed but may depend on internet access and digital proficiency.
- Mailing provides physical records of submission but is prone to postal delays.
- In-person submissions afford immediate confirmation of receipt but require scheduling and attending appointments, potentially leading to longer wait times.
Penalties for Non-Compliance with
Legal and Financial Implications
- Fines and Penalties: Failure to submit Form when required can result in monetary fines and affect vehicle operation legality.
- Revocation of Privileges: Non-compliance may lead to suspension or revocation of licenses or permits associated with the vehicle served by the form.
- Legal Action: Persistent non-compliance could result in further legal challenges, potentially affecting commercial operations adversely.
Mitigation and Resolution
- Ensure timely and accurate submission to avoid penalties.
- Proactively address any notices or flags from regulatory bodies related to delays or form inaccuracies.