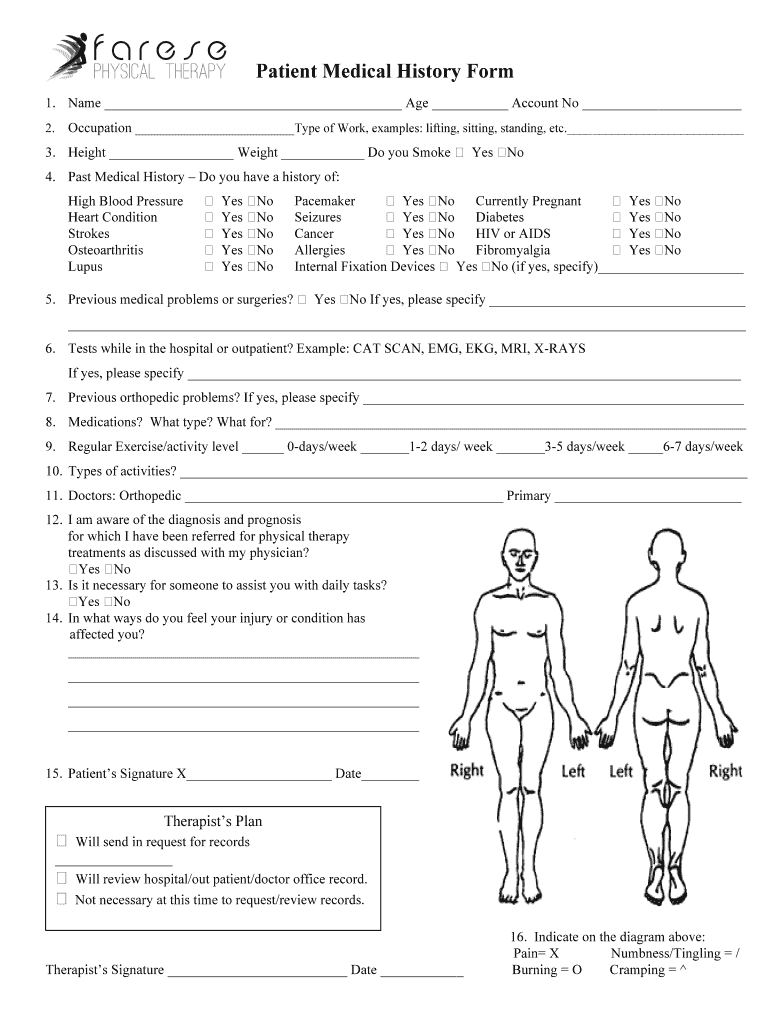
Definition and Importance of Patient Medical History
Patient medical history refers to the comprehensive record of a patient's medical background and health information. This document typically includes personal details, past illnesses, treatments received, family medical history, and current medications. The significance of maintaining a thorough patient medical history lies in its role in providing healthcare professionals with crucial insights into a patient's health status, which informs diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Key elements often included in a patient medical history are:
- Personal Information: Basic details such as name, age, gender, and contact information.
- Medical History: Records of previous illnesses, surgeries, and hospitalizations.
- Medications: A list of current prescriptions and over-the-counter medications, including dosages.
- Family History: Health issues faced by immediate family members, which might indicate genetic predispositions.
- Social History: Lifestyle factors, including smoking, alcohol consumption, exercise habits, and occupation.
- Allergies: Documenting known allergies to medications, foods, or environmental factors.
A well-documented medical history allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions that can lead to better patient outcomes. It also facilitates communication between multiple healthcare professionals involved in a patient's care.
Steps to Complete the Patient Medical History
Completing a patient medical history is a structured process that requires careful attention to detail. Here are the steps typically involved:
- Gather Personal Information: Start by collecting essential information, including patient’s full name, date of birth, and contact details.
- Document Medical History: Include all relevant past medical events, surgeries, and ongoing health conditions, ensuring to capture the timeline and any significant changes.
- List Current Medications: Note all medications the patient is currently taking, specifying dosages and the prescribing physician’s name.
- Collect Family Health History: Inquire about the health of immediate family members, focusing on any chronic diseases or conditions that may affect the patient.
- Assess Social History: Discuss lifestyle choices, work environment, and social habits that may impact the patient’s health.
- Record Any Allergies: Detail any known allergies to medications, foods, or other substances, as this impacts treatment plans.
- Review and Confirm: After gathering all the information, review it with the patient to ensure accuracy and completeness.
This structured approach helps ensure that no vital information is overlooked, ultimately enhancing the quality of care.
Key Elements of the Patient Medical History
Each section of the patient medical history is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s health. Below are the key elements that should be included:
- Identifying Information: Basic demographic data that facilitates patient tracking.
- Chief Complaint: The primary reason for seeking medical attention, which helps guide the initial assessment.
- Present Illness: A detailed description of the current medical issue, including duration and severity.
- Review of Systems (ROS): A systematic review that helps identify any other potential health issues.
- Medications and Treatment History: A thorough account of medication adherence and previous treatment outcomes.
- Past Medical History: Comprehensive details about any past health conditions, surgeries, or hospital admissions.
- Family Medical History: An essential component that can illuminate hereditary health patterns.
- Social and Lifestyle Factors: Information about the patient’s lifestyle choices that may contribute to their health status.
Each of these elements plays an integral role in forming a holistic view of a patient's health, guiding clinical decisions.
Legal Usage of Patient Medical History
The legal considerations surrounding patient medical history are paramount for ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations. Here are key aspects:
- HIPAA Compliance: Protecting patient privacy and ensuring confidentiality according to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- Informed Consent: Patients must be informed about who may have access to their medical history and how it will be used.
- Record Keeping: Healthcare providers are required to maintain patient records for a specific period, which varies by state, to ensure accountability and traceability.
- Disclosure Requirements: Regulations specify when and how patient medical histories can be shared, including circumstances of medical emergencies and legal proceedings.
Understanding the legal frameworks surrounding patient medical history is essential for healthcare providers to protect patient rights while delivering effective care.
Who Typically Uses Patient Medical History?
Various professionals and institutions utilize patient medical history as a critical component in their operations and patient care strategies. Key users include:
- Physicians: Primary care providers, specialists, and surgeons rely on detailed medical histories to inform diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Nurses: Core members of the healthcare team, nurses use patient histories to monitor patient progress and collaborate on care.
- Therapists: Physical and occupational therapists use the medical history to design personalized rehabilitation plans that account for past medical events and medications.
- Healthcare Administrators: Database management and quality assurance personnel utilize aggregated medical histories for improving patient care protocols and operational efficiency.
- Researchers: Clinical researchers often analyze medical histories to study health trends and outcomes in larger populations.
Understanding the roles of these various users highlights the multifaceted importance of patient medical histories across healthcare settings.