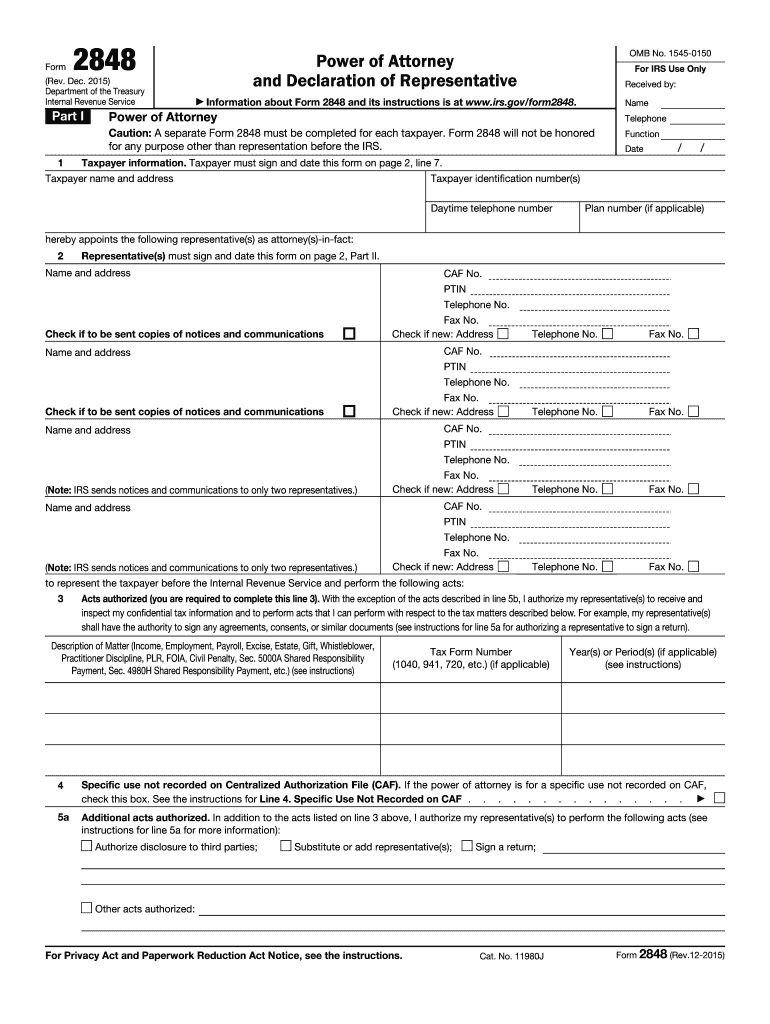
Definition and Purpose of Form 2848
Form 2848, also known as the Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative, is an official document utilized by taxpayers in the United States to authorize individuals to act on their behalf when dealing with the IRS. This form enables the appointed representative to communicate with the IRS regarding tax-related matters for the taxpayer. Without this document, the representative cannot legally discuss or resolve issues concerning the taxpayer’s account, tax returns, or any tax-related inquiries.
- Power of Attorney: The form grants authority for the representative to manage affairs including discussions and meetings with the IRS.
- Declaration of Representative: This section stipulates the qualifications of the representative, ensuring they are eligible to practice before the IRS.
- Representation Limits: Taxpayers can specify which tax years or types of tax the power of attorney covers, allowing for fine-tuned representation.
How to Complete Form 2848
Filling out Form 2848 correctly is essential to ensure representation authorization is accepted by the IRS. The form consists of several sections that each require specific information:
- Taxpayer Information: Initial fields require the taxpayer’s name, address, and Social Security number (or Employer Identification Number).
- Representative Details: This part includes providing the representative's name, address, phone number, and Centralized Authorization File (CAF) number if applicable.
- Authorized Acts: Taxpayers need to specify which acts the representative is authorized to perform. This can include, but is not limited to, tax return preparation, signing documents, and receiving confidential information.
- Signature Section: The taxpayer must sign and date the form, certifying that the information provided is accurate and complete.
Correctly following these steps facilitates a smoother process in gaining IRS representation.
Obtaining Form 2848
Accessing Form 2848 is straightforward:
- Online Access: The form is readily available for download from the IRS website or, for convenience, from DocHub. Taxpayers can simply search for "Form 2848" through an internet search engine.
- In-Person Requests: Taxpayers can also obtain the form directly at local IRS offices.
- Contacting the IRS: Calling the IRS can clarify any questions regarding where to retrieve the form.
Availability in both digital and physical formats ensures wide access for all taxpayers.
Filing Process for Form 2848
Once Form 2848 is completed, the next step is ensuring it is filed correctly with the IRS:
- Submission Methods: The completed form can be submitted via:
- Mail: Send to the specified address for the IRS office designated for power of attorney submissions.
- Fax: If urgent representation is required, taxpayers may choose to fax the form to the appropriate IRS office.
- Processing Time: Generally, the IRS processes Form 2848 within two to four weeks, but this duration can vary based on workload and submissions.
Ensuring proper submission helps avoid delays in representation.
Common Use Cases for Form 2848
Form 2848 is widely used among various groups, including:
- Tax Professionals: Accountants, tax attorneys, and enrolled agents often utilize this form to represent clients in tax matters.
- Business Entities: Corporations and partnerships require representation for audits and disputes with IRS.
- Individuals: Taxpayers who feel overwhelmed by tax responsibilities or disputes frequently seek assistance through appointed representatives.
Each of these cases exemplifies the importance of having clear representation in dealing with federal tax matters.
Key Elements of Form 2848
Understanding the essential components of Form 2848 can help taxpayers navigate its use more effectively:
- Tax Identification Numbers: Including particulars such as Social Security Numbers ensures precisely identifying the taxpayer.
- Authorized Acts: Clearly defined powers allow representatives to act without ambiguity, covering preparation and representation in matters before the IRS.
- Specific Tax Years: Taxpayers can limit the authority to specific years, providing oversight and control over representation.
Awareness of these elements enables both taxpayers and representatives to align their expectations and responsibilities.
IRS Guidelines for Form Submission
The IRS provides specific guidelines regarding the completion and submission of Form 2848:
- Eligibility Requirements: All representatives must be authorized to practice before the IRS, ensuring they meet the criteria for acting on behalf of others.
- Submission Deadlines: Timing becomes crucial; those submitting the form should be aware of any relevant deadlines regarding tax filings or disputes.
- Revocation Procedures: Understanding how to revoke an existing Form 2848 when a change in representation occurs is vital for maintaining control over one’s representation.
Familiarity with IRS guidelines minimizes complications and optimizes the representation experience.
Important Legal Considerations
Legal aspects surrounding Form 2848 bear relevance for both taxpayers and representatives:
- Binding Authority: Understanding that the authority granted through the form must be respected by the IRS is crucial for smooth interactions.
- Confidentiality and Privacy: The IRS is required to keep taxpayer information confidential, but representatives must also ensure they operate within legal boundaries.
- Revocation of Authority: Taxpayers may revoke the power of attorney at any time by submitting a new Form 2848 or a written notice, safeguarding their rights.
Grasping these legal considerations can prevent disputes and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.