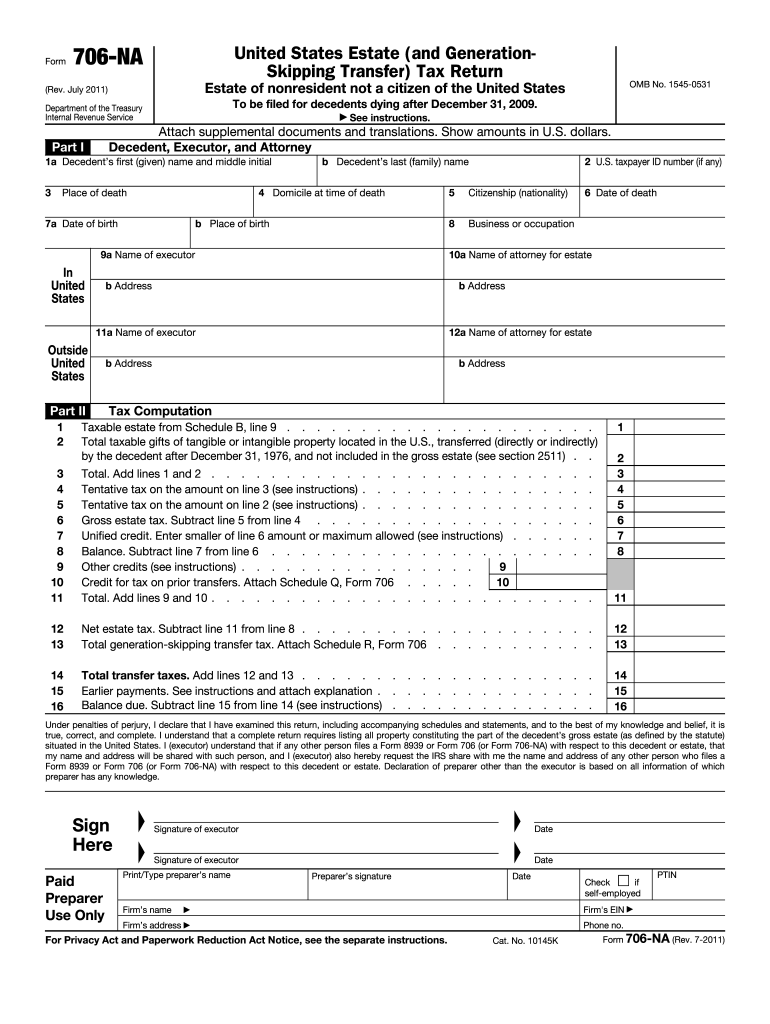Definition and Meaning of Form 706-NA
Form 706-NA, also known as the United States Estate (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax Return, must be filed for nonresident decedents who died after December 31, 2009. This form is essential for reporting and assessing estate and generation-skipping transfer taxes on property within the United States. The primary objective of this document is to ensure that the IRS adequately gathers information regarding the decedent's U.S. assets for correct tax computation.
Steps to Complete Form 706-NA
-
Gather Necessary Documents: Collect documents proving ownership and valuation of the decedent's U.S.-based assets. Examples include real estate deeds, bank statements, and appraisals.
-
Filling Out Personal Information: Enter details such as the decedent's name, date of death, and taxpayer identification number in the form's introductory section.
-
Asset Valuation: List and value each asset according to IRS guidelines. Include market values as of the date of death.
-
Claiming Deductions: Identify applicable deductions, such as debts and funeral expenses, and ensure accurate entries in the deductions section.
-
Calculating Tax Liability: Use the provided IRS schedules to calculate estate and generation-skipping taxes based on the final asset valuation figures.
-
Signature and Submission: The executor of the estate must sign the completed form and submit it according to IRS submission guidelines.
Required Documents for Form 706-NA
- Proof of the decedent's non-U.S. citizenship.
- Legal documents proving ownership of assets within the U.S.
- Valuation reports including appraisal certificates.
- Death certificate and any applicable court orders.
- Documentation for claimed deductions, such as invoices for debts and funeral expenses.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
- Form 706-NA is generally due nine months after the decedent's date of death.
- Estate representatives may request a six-month filing extension using IRS Form 4768 if additional time is needed.
Failure to comply by the prescribed deadlines may result in penalties and interest on unpaid taxes.
Eligibility Criteria
Form 706-NA applies to nonresident alien decedents whose estates include U.S.-located assets. Only estates with a value above the exemption threshold (determined by IRS regulations at the time of death) are required to file. Executors must ensure the estate meets these criteria before proceeding with preparations.

Penalties for Non-Compliance
-
Failure to File Penalty: Estates not filing on time may encounter a penalty of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is late, with a maximum of 25%.
-
Failure to Pay Penalty: This consists of 0.5% of the unpaid tax per month, increasing to 1% for taxes overdue by more than ten days following a notice of intent to levy.
To avoid penalties, timely filing and full payment of taxes due are crucial.
Key Elements of the Form 706-NA
-
Part I - Decedent Information: Captures essential details about the deceased and their estate representative.
-
Schedule A - Real Estate: Provides for listing and valuing U.S. real estate items.
-
Schedule B - Stocks and Bonds: Records details of stocks and bonds held in the U.S.
-
Schedule C - Cash and Other Assets: Includes cash, savings, insurance funds, and other personal effects.
-
Schedule D - Deductions: Allows the entry of deductions such as claims against the estate and funeral expenses.
-
Tax Computation: Summarizes taxes owed after accounting for applicable deductions and credits.
How to Obtain Form 706-NA
Form 706-NA is available for download on the IRS website. Libraries and post offices no longer carry physical forms, emphasizing the importance of digital access. Estate representatives can also consider using tax preparation software that includes government form libraries for easy access to tax documents.