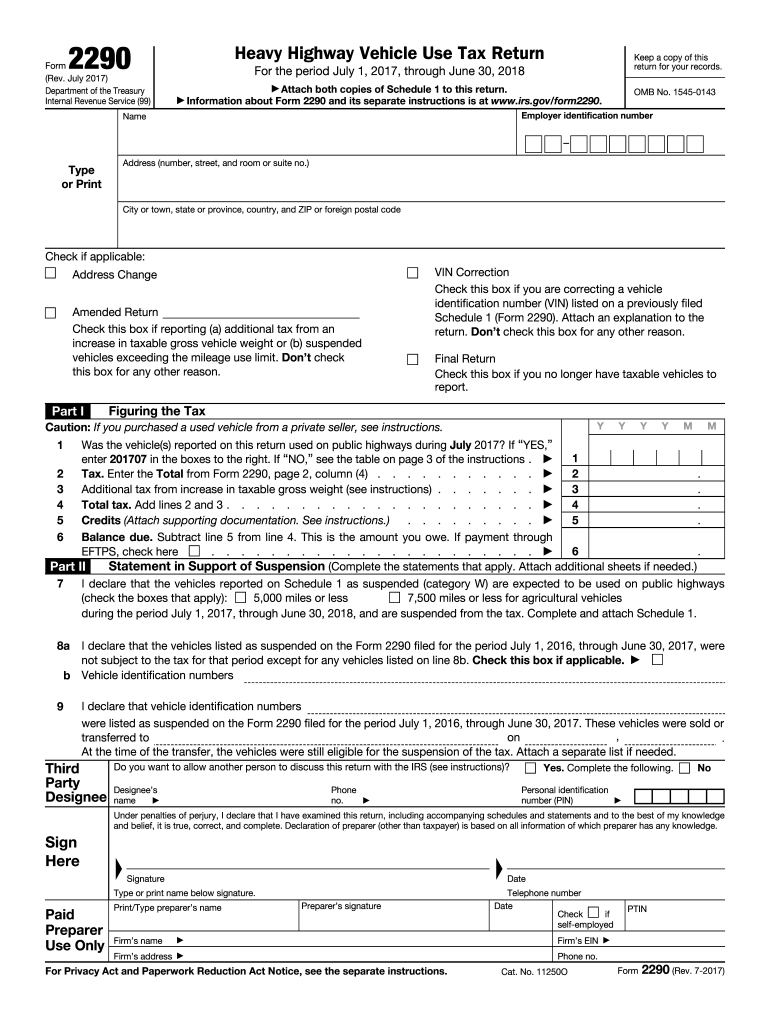Definition & Meaning
The IRS Form 2290, known as the Heavy Highway Vehicle Use Tax Return, is specifically designed for owners of heavy highway vehicles. This form is used to report and pay the annual tax for vehicles operating on public highways with a taxable gross weight of 55,000 pounds or more. The tax period covered by the 2017 version of this form extends from July 1, 2017, to June 30, 2018.
Form 2290 serves multiple purposes, including calculating the amount of tax due, enabling users to make necessary corrections, and providing Schedule 1, which is a crucial attachment for proof of payment. Completing this form accurately is essential for vehicle registration and compliance with federal tax obligations.
How to Use the 2 Form
To effectively utilize the 2290 Form for the 2017 tax year, vehicle owners should follow a systematic approach:
-
Determine Vehicle Eligibility: Ensure that your vehicle is required to be reported on Form 2290. Typically, this includes trucks, tractors, and buses with a taxable gross weight of 55,000 pounds or more.
-
Calculate the Tax Due: Use the form to calculate the tax based on the vehicle's weight, using the IRS-provided tax rates. Be accurate in weight calculations to avoid penalties.
-
Complete Vehicle Information: Fill in necessary vehicle details, such as VIN and weight category. This data is crucial for tax calculation and compliance.
-
Submit Schedule 1: Attach Schedule 1 with your submission for official IRS acknowledgement, which serves as proof of tax payment.
-
Review and Send: Double-check all entries for accuracy before submitting either electronically or via mail.
How to Obtain the 2 Form
Obtaining the 2290 Form for 2017 can be accomplished through several methods:
-
IRS Website: Download the form directly from the official IRS site in a fillable PDF format.
-
Tax Software Providers: Utilize accounting software that supports tax form downloads and submissions.
-
IRS Offices: Contact or visit the nearest IRS office to request a physical copy.
Make sure to gather this form well before any deadlines to ensure a timely submission.
Steps to Complete the 2 Form
Filling out the Form 2290 involves several crucial steps:
-
Provide Personal Information: Enter your business name, Employer Identification Number (EIN), and contact details.
-
Vehicle Information: Accurately list all vehicles subject to the tax, including each VIN and weight category.
-
Calculate Tax Due: Utilize provided tables to determine the tax amount based on the vehicle's specifications.
-
Schedule 1 Completion: Fill out Schedule 1, marking down all applicable vehicle data.
-
Submit Payment Voucher (Form 2290-V): If paying by check or money order, complete this voucher to accompany your payment.
-
Review and File: Ensure all parts are correct, and submit the form either electronically or by mailing it to the IRS.
Required Documents
When filing IRS Form 2290 for 2017, ensure you have these documents:
- Vehicle Registration Documents: Verify details such as VIN and weight class.
- Proof of Business Ownership: Present relevant paperwork like business licenses or incorporation documents.
- Previous Year’s Schedule 1: If applicable, reference the earlier year's proof of tax payment for continuity.
These documents support the accuracy and completeness of your submission.
IRS Guidelines
Adhering to IRS guidelines for the 2290 Form ensures compliance:
- Earliest Filing Date: The form can be filed starting on July 1 of the tax year.
- Payment Methods: Taxes can be paid via check, money order, or electronic funds withdrawal directly from a bank account.
- Error Correction Process: If an error is found after filing, use Form 2290 Amendment to make corrections relating to vehicle weight or mileage category adjustments.
Follow these guidelines closely to prevent compliance issues.
Filing Deadlines / Important Dates
Understanding the timeline for Form 2290 is crucial:
-
Annual Deadline: Generally falls on August 31 for new forms related to tax periods starting July 1.
-
Deadline for Exemptions: If your vehicle has been exempted and later meets tax requirements, ensure submission by the last day of the month after the exemption ends.
Missing these deadlines can lead to penalties and interest on unpaid taxes.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with the filing and payment of Form 2290 can result in:
-
Late Filing Penalty: Typically 4.5% of the total tax due, assessed monthly until paid.
-
Late Payment Penalty: Usually 0.5% of the unpaid tax per month.
-
Interest Charges: Accrues on unpaid taxes from the due date until the full payment is made.
To avoid these penalties, ensure timely submission and accuracy of information on your 2290 Form.