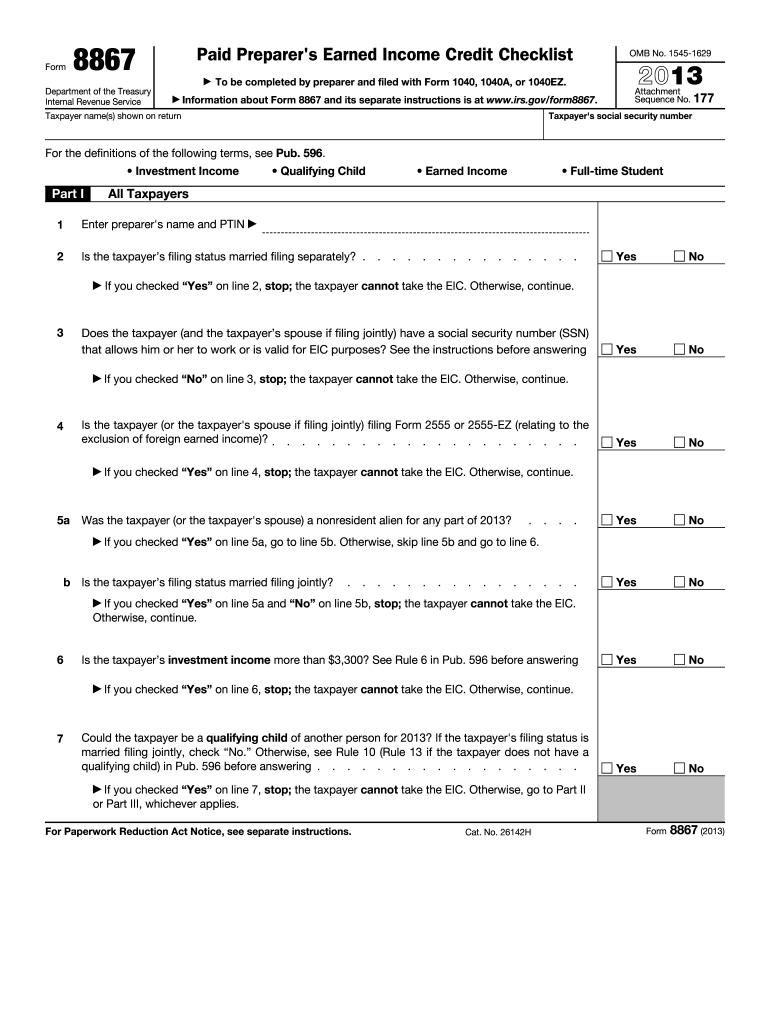Definition and Importance of the 2 Form
The 2 form, officially known as the Paid Preparer's Earned Income Credit (EIC) Checklist, is a crucial document mandated by the IRS for tax preparers. It serves to ensure that tax preparers conduct thorough due diligence when assessing a client's eligibility for the Earned Income Credit (EIC). The EIC is a significant financial support mechanism designed to assist low-to-moderate-income individuals or families, providing them with a tax benefit that can alleviate economic hardship. Its primary purpose is to encourage work and support families in raising children.
The form consists of various questions that focus on a taxpayer's filing status, income, and qualifying children, which are essential criteria for the EIC. By completing this checklist, preparers can substantiate their claims regarding a taxpayer's eligibility, thus safeguarding both the preparer and the taxpayer from potential issues with the IRS concerning improper EIC claims.
How to Use the 2 Form
Utilizing the 2 form effectively requires understanding its structure and purpose. Tax preparers must follow these steps when employing the form:
- Obtain the form: The form can be accessed through the IRS website or tax preparation software that includes it.
- Identify clients eligible for EIC: Analyze the client’s annual income, number of dependents, and other relevant factors to determine if they qualify for the EIC.
- Complete the checklist: Answer all questions specified in the form diligently, ensuring that each section accurately reflects the client's situation. This includes verification of all claimed dependents and their income.
- File the form alongside the tax return: The completed 8867 form must be submitted with the client’s tax return when claiming the EIC.
Thoroughly completing the checklist not only fulfills the IRS requirements but also provides a safeguard for tax preparers against penalties for non-compliance.
Steps to Complete the 2 Form
Completing the 2 form is a multi-step process that requires careful attention to detail. Follow these procedures to ensure the checklist is filled out accurately:
- Gather necessary documentation: Collect income statements, tax returns from previous years, and social security numbers for qualifying children.
- Fill in taxpayer information: Provide the taxpayer’s name, Social Security number, and any other identifying details in the appropriate sections.
- Address eligibility criteria: Answer all questions in the individual checklist items:
- Confirm the taxpayer's filing status.
- Verify the number of qualifying children.
- Ensure that income thresholds are met.
- Review for accuracy: Before submitting, double-check all entries for correctness and completeness to minimize errors.
- Maintain records: Keep a copy of the completed form, along with supporting documentation, for your records, as this may be necessary for future audits or inquiries.
By meticulously following these steps, tax preparers can not only comply with IRS regulations but also provide better service to their clients.
Important Terms Related to the 2 Form
Understanding key terminology associated with the 2 form is essential for effective use. Some notable terms include:
- Earned Income Credit (EIC): A benefit for working people with low to moderate income, designed to incentivize employment.
- Qualifying Child: A child who meets specific criteria related to age, relationship, residency, and support.
- Due Diligence: The responsibility of tax preparers to ensure accuracy in preparing tax returns and claiming credits like the EIC.
- Filing Status: Determines the rate at which income is taxed and is influenced by marital status and family structure.
- Supporting Documentation: Evidence such as W-2s or other income sources required to substantiate claims made on tax returns.
An in-depth comprehension of these terms enables tax preparers to navigate the complexities of tax filing more effectively.
Legal Use of the 2 Form
The legal use of the 2 form is firmly rooted in IRS regulations that stipulate its necessity for tax preparers who assist clients in claiming the EIC. Tax preparers are legally obligated to:
- Exercise Due Diligence: Document all steps taken to confirm a taxpayer’s eligibility for the EIC, ensuring compliance with the law.
- Maintain Confidentiality: Protect clients’ sensitive personal and financial information as required by law.
- Report Claiming Errors: If discrepancies or uncertainties arise while completing the checklist, preparers must seek further documentation or clarification instead of proceeding with an unchecked claim.
Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to penalties, including fines and potential suspension of the preparer’s professional license. Therefore, adherence to legal requirements is vital for all preparers involved in handling the 8867 form.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates Related to the 2 Form
Being aware of the relevant deadlines is critical when dealing with the 2 form. These ensure timely filing and compliance with IRS regulations:
- Tax Filing Deadline: Individual tax returns, including those claiming the EIC, are generally due by April 15 each year (unless it falls on a weekend or holiday).
- Extended Deadline: Taxpayers filing for an extension must submit their returns by October 15, but the 8867 form must still be adhered to during this period.
- Early Filing Incentives: Taxpayers encouraged to file early should be prepared for additional documentation, especially regarding their EIC claims, to ensure all deadlines are met.
Understanding these deadlines helps taxpayers and preparers avoid last-minute issues and penalties associated with late filings.
Examples of Using the 2 Form in Real Scenarios
Illustrating real-world examples of the 2 form's application can clarify its necessity and functionality:
-
Single Parent Scenario: A single mother with two qualifying children earning below the income threshold can use the 8867 form to document her eligibility for the EIC. By carefully filling in the details of her children and income, she secures a tax refund that significantly assists with household expenses.
-
Multiple Jobs Case: A working father with multiple part-time jobs must use the 8867 form to claim the EIC effectively. Upon correctly completing the checklist based on his diverse income sources, he can validate his claims, ensuring compliance while maximizing his refund.
These practical examples demonstrate how the form aids individuals in leveraging the EIC to enhance their financial situations based on their unique circumstances.
IRS Guidelines for the 2 Form
The IRS outlines specific guidelines that govern the use of the 2 form. Preparers must adhere strictly to these protocols:
- Prior Compliance Checks: Preparers should ensure clients have not previously claimed the EIC due to ineligibility, as repeated claims could classify them as harmful actors.
- Continuous Education: Tax preparers are encouraged to undergo regular training to stay updated with IRS changes regarding the EIC and related documentation.
Following these guidelines not only fulfills legal obligations but also safeguards preparers from potential audits and penalties.