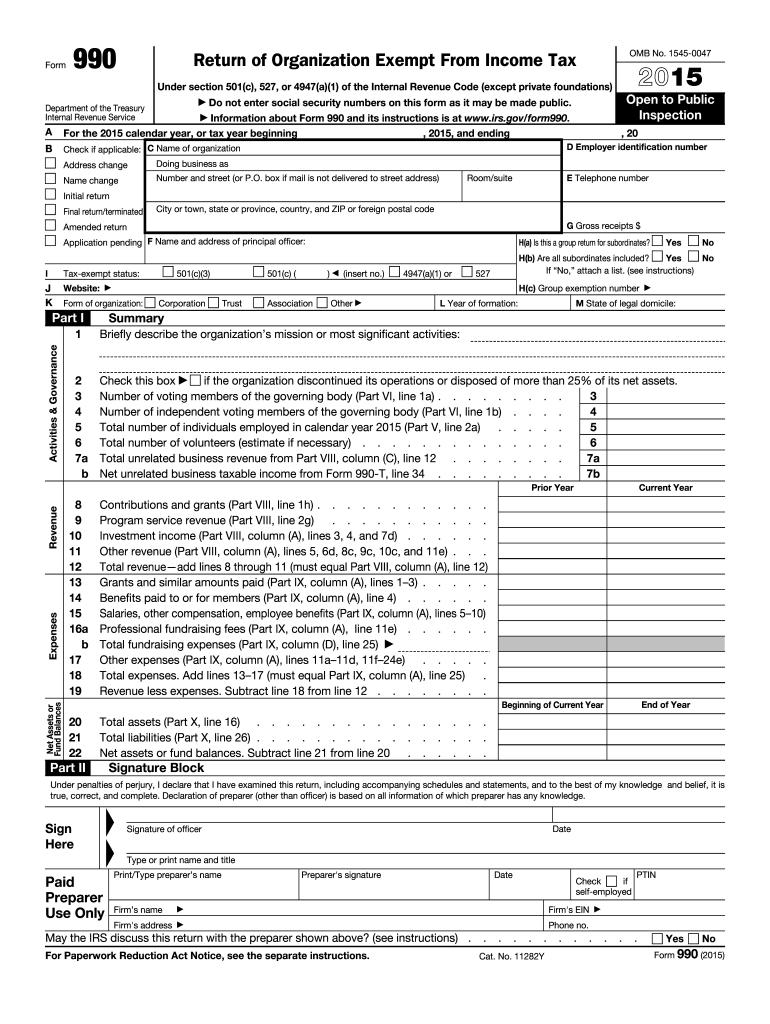Definition and Meaning
Form 990 for the year 2015 is a pivotal document used by tax-exempt organizations in the United States. Filed annually with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), this form is mandatory for organizations that fall under sections 501(c), 527, or 4947(a)(1) of the Internal Revenue Code. It primarily serves to provide the IRS and the public with detailed information about an organization’s financial health, governance, and operational transparency. This includes specifics about revenue generation, functional expenses, net assets, and program service accomplishments. Moreover, disclosures regarding officer compensations and political engagements are also part of the reporting. Form 990 acts as a tool to maintain transparency and ensure accountability among tax-exempt bodies.
Key Elements of the IRS 2015 Form 990
The Form 990 is structured to extract comprehensive data from organizations. Core elements include:
- Part I: Summary – Presents a snapshot of the organization's mission, suitability, and key financials.
- Part III: Statement of Program Service Accomplishments – Lists the organization's main activities and achievements during the year.
- Part VII: Compensation of Officers, Directors, Trustees, Key Employees, Highest Compensated Employees, and Independent Contractors – Requires detailed disclosures of compensation arrangements.
Additionally, the form delves into sections that address governance details, such as board members and operational policies, providing insight into the transparency of the organization’s internal processes.
How to Use the IRS 2015 Form 990
Using Form 990 correctly is essential for compliance and transparency. Here are steps to guide through its use:
- Gather Required Information: Before beginning, collect all necessary financial documents, including revenue statements, expense reports, and details of compensations.
- Complete Relevant Sections: Depending on the organization's structure and activities, not all parts of the form need to be completed. Focus on sections that apply directly to the organization’s activities.
- Ensure Accuracy: Verify all financial data thoroughly to avoid discrepancies that could lead to penalties or queries from the IRS.
- Consult with Experts: If uncertain about any part of the form, contacting an accountant or a tax advisor can be beneficial for accurate filing.
Steps to Complete the IRS 2015 Form 990
Completing Form 990 requires careful attention to detail. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Correct Version: Choose the applicable version of Form 990, as organizations with different revenue levels may file Form 990, 990-EZ, or 990-N.
- Fill Out Identification Information: Enter the organization’s legal name, address, employer identification number (EIN), and tax year at the form's outset.
- Provide Financial Details: Enter financial data, including revenue and expenses, as accurately as possible.
- Complete Governance Information: Detail the governance structure, including names and roles of board members and any significant changes in policies.
- Review and Double-Check All Entries: Ensure all sections are complete, and the information is accurate to prevent delays or inquiries.
- Submit the Form: Decide on the mode of submission—mail, electronic filing, or in-person. Electronic submissions are often faster and facilitate quicker processing.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Timeliness is key to maintaining good standing with the IRS. The regular deadline for Form 990 is the 15th day of the fifth month following the end of the organization's accounting period. For a calendar-year filer, this typically means May 15. Extensions are possible but must be requested before the initial deadline. Missing these crucial dates can lead to penalties, so maintaining an organized schedule for compliance is vital.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to file Form 990 on time can result in significant financial penalties. Organizations can incur fines up to $100 per day of lateness, with a maximum penalty reaching $50,000 each year. Repeated failures can lead to revocation of tax-exempt status, severely impacting the organization's operations and public trust. Therefore, it's critical that all organizations adhere to IRS deadlines and filing procedures with diligence.
Legal Use of the IRS 2015 Form 990
The IRS mandates the use of Form 990 to uphold legal and ethical standards within tax-exempt organizations. The form's disclosure requirements ensure not only compliance with federal tax laws but also alignment with broader governance and transparency obligations. Accurately reporting on finances and governance—such as listing significant donations or political contributions—helps maintain the organization's accountability and public trust.
IRS Guidelines
The IRS provides comprehensive guidelines for Form 990, which outline who must file, which version to use, and essential instructions for completion. These guidelines are indispensable for ensuring accuracy and compliance. Organizations are encouraged to review the latest IRS instructions each year, as regulations or reporting requirements can change. Tax professionals or consultants can also provide valuable insight into applying these guidelines to specific organizational contexts.