Definition & Meaning
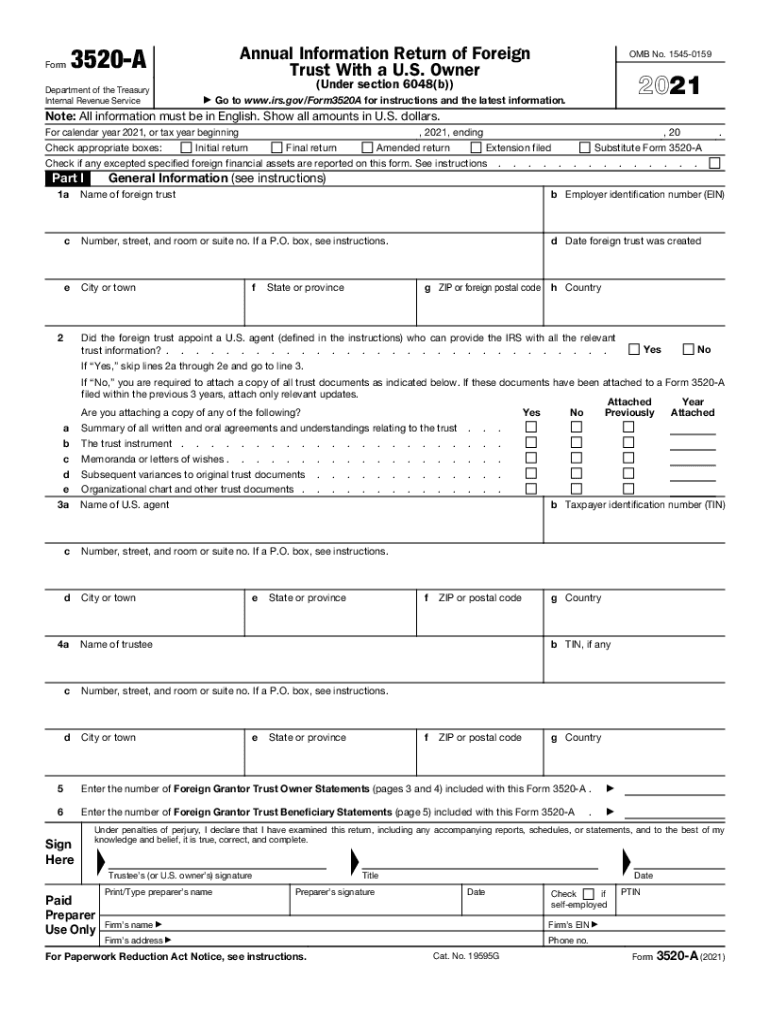
Form 3520-A is designated by the IRS as the Annual Information Return of Foreign Trust With a U.S. Owner. This document is essential for collecting details about foreign trusts owned by U.S. taxpayers. It serves a regulatory purpose by capturing comprehensive information on the foreign trust's establishment, structure, and financial activities. Form 3520-A is necessary for transparency and to ensure compliance with U.S. tax obligations. It provides data that include the trust's income, expenses, distributions to U.S. persons, and overall financial health.
How to Use Form 3520-A
Form 3520-A is primarily submitted by the trustee of a foreign trust with a U.S. owner. The document ensures compliance with IRS regulations by reporting financial data and distributions to U.S. beneficiaries. The process involves accurate completion of various sections, which include detailing the trust's financial operations and identifying U.S. beneficiaries. U.S. owners relying on trustees for form completion should ensure the document accurately reflects all transactions during the tax year. Failure to comply can lead to penalties.
Steps to Complete Form 3520-A
- Gather Information: Collect data regarding the trust's income, expenses, and distributions throughout the year.
- Identify U.S. Owners: Ensure all U.S. owners and beneficiaries are correctly listed.
- Complete Financial Statement Sections: Fill out the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of distributions.
- Review for Accuracy: Double-check all entries for accuracy and completeness.
- Submission: The trustee files the form with the IRS by the due date, typically March 15th.
Who Typically Uses Form 3520-A
Foreign trusts with one or more U.S. owners are required to use Form 3520-A. Trustees of such trusts are responsible for completing and submitting the form. This ensures that U.S. persons with beneficial interest maintain transparency in accordance with the IRS regulations. This form is also crucial for U.S. taxpayers who are beneficiaries or contributors to foreign trusts, as it reflects their financial interests and obligations accurately.
Key Elements of Form 3520-A
- Trust Financial Information: Ensures that financial statements, such as income statements and balance sheets, are detailed and accurate.
- U.S. Owner Identification: Specifies owners and beneficiaries, highlighting those with U.S. tax obligations.
- Distribution Details: Details how income and capital are distributed to U.S. beneficiaries.
- Trustee's Certification: An affirmation of accuracy and compliance with IRS regulations, crucial for validation.
Filing Deadlines / Important Dates
Form 3520-A must be filed annually by the 15th day of the third month after the trust's tax year ends, often March 15th for calendar year trusts. Failure to submit the form by the deadline could result in substantial penalties. Extensions may be requested through Form 7004, providing additional time if necessary, but should be sought proactively to avoid potential non-compliance issues.
IRS Guidelines
The IRS provides detailed instructions for submitting Form 3520-A, highlighting the importance of precision in financial disclosures. Guidelines specify which financial documents are necessary, how to report transactions with U.S. beneficiaries, and how to handle unique financial scenarios. They also address common errors that can lead to penalties, underscoring the need for accurate and complete submissions.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Significant penalties apply for failing to file Form 3520-A or providing inaccurate information. Penalties can be as high as 5% of the gross value of the involved trust assets if the form is not filed timely or is incomplete. The IRS emphasizes the importance of compliance, offering detailed guidance to alleviate ambiguity. Avoiding these penalties requires meticulous attention to form requirements and deadlines.
Examples of Using Form 3520-A
- Asset Reporting: A U.S. taxpayer owns a foreign trust that generates income from property rentals. Form 3520-A explains the trust's income distribution to U.S. beneficiaries.
- Trust Formation: When a trust is established, all U.S. beneficiaries must be listed, ensuring they are aware of potential tax responsibilities.
- Intermediary Reporting: A trust distributing assets among multiple beneficiaries using Form 3520-A ensures transparency and compliance for U.S. tax purposes.