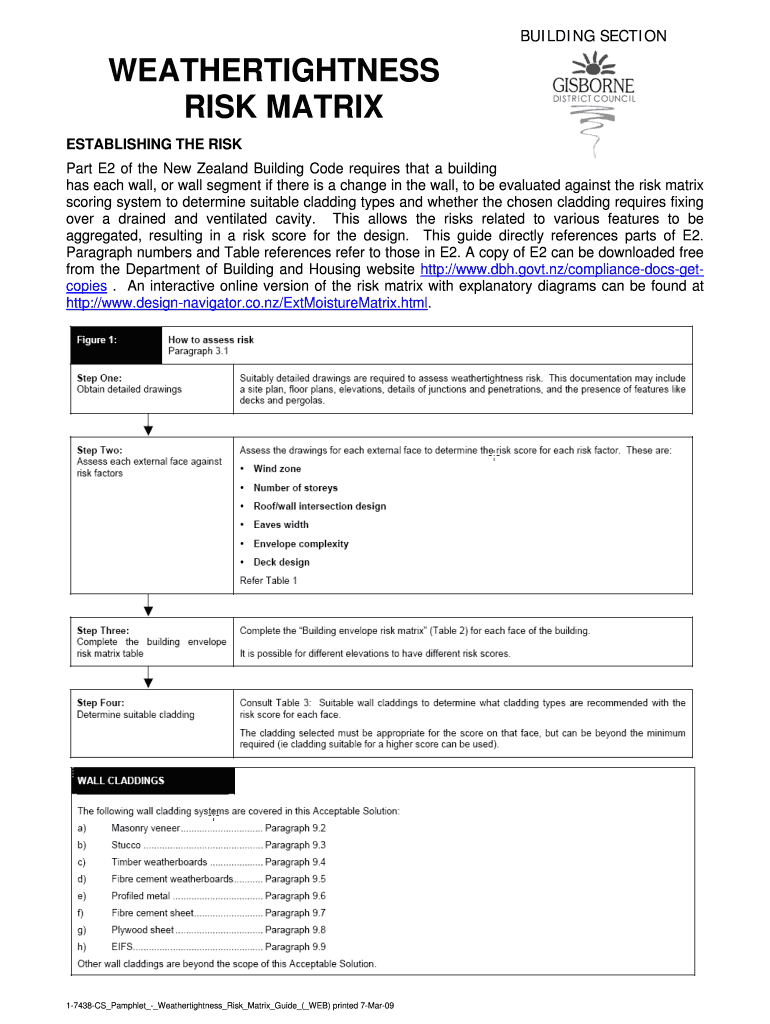
Definition and Meaning of Establishing the Risk
"Establishing the risk" involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks within a project, decision, or operational process. The concept refers to creating a structured framework to analyze potential uncertainties and determine how they might impact the objectives. This step is crucial in risk management as it aids in understanding which risks need attention, their implications, and how they align with the goals and strategy of the organization.
Components of Risk Establishment
- Risk Identification: Involves listing all potential risks that could affect the project or operation. Strategies like brainstorming sessions, SWOT analysis, and risk workshops can be employed.
- Risk Assessment: Entails evaluating the identified risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. This process helps in understanding which risks are most significant.
- Risk Prioritization: Focuses on ranking the risks to create a clear picture of which risks require immediate action, addressing both probability and impact.
- Documentation of Risks: Includes maintaining detailed records of all identified risks, assessments, and potential mitigation strategies.
How to Use the Establishing the Risk Process
Step-by-Step Guide
- Gather Information: Collect data related to the project or operation scope.
- Identify Risks: Brainstorm all possible risk factors with relevant teams.
- Assess Risks: Evaluate each risk for its probability and impact.
- Prioritize Risks: Rank them to determine which pose the greatest threat to objectives.
- Develop Mitigation Plans: Create strategies to address and minimize the risks.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly review and update the risk assessment process.
Practical Application
- Use Case: Project Management: An IT project team conducts a risk assessment workshop to identify potential security risks in their software development life cycle.
- Use Case: Financial Planning: A financial firm uses risk assessment techniques to foresee credit risks in their investment strategies.
Steps to Complete the Establishing the Risk Documentation
Comprehensive Steps Involved
- Define Objectives: Clearly articulate what you aim to achieve with the risk management process.
- Create a Risk Register: Build a structured document that lists and describes all identified risks.
- Evaluate Risk Severity: Use a risk matrix to plot each risk's likelihood versus its impact.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Document planned actions to mitigate, transfer, accept, or avoid risks.
- Review & Update: Set up regular intervals to refine and adjust the risk management plan according to new data or changing dynamics.
Case Example
- Scenario: A manufacturing company developing a new product line performs risk documentation to anticipate potential disruptions in supply chain logistics.
Key Elements of the Establishing the Risk Process
Core Elements
- Risk Matrix: A visually intuitive tool used to map out risks based on probability and impact, helping stakeholders to comprehend risk severity quickly.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Ensures that all relevant parties contribute insights and acknowledge risk management strategies.
- Risk Ownership: Assigns specific risks to designated individuals who are responsible for managing and mitigating them.
- Communication Plan: Maintains open lines of communication regarding risk status and resolution efforts across all levels of the organization.
Detailed Breakdown
- Risk Analysis Methods: Includes qualitative and quantitative approaches to evaluate risk levels, like Monte Carlo simulations or scenario analysis.
- Documentation Tools: Utilizes software applications for compiling and visualizing risk data, ensuring accessibility and up-to-date information.
Legal Use of the Establishing the Risk Process
U.S.-Centric Legal Considerations
- Compliance: Aligns with U.S. regulations pertinent to industry-specific standards, such as those enforced by OSHA or the SEC.
- Contractual Obligations: Ensures legal risk management strategies are documented within business contracts, protecting parties from foreseeable risks.
- Liability and Accountability: Establishing risk processes clarify who holds responsibility for risk management outcomes, minimizing legal exposure.
Implications
- Contract Clauses: Contracts may include clauses specifying risk management obligations and remediation actions for potential breach scenarios.
- Regulatory Compliance: Businesses must ensure risk management practices meet federal standards to maintain licensing and avoid fines.
Who Typically Uses the Establishing the Risk Process


Common Users
- Project Managers: To identify and mitigate risks in timelines and deliverables.
- Financial Analysts: Evaluating investment risks to enhance portfolio performance.
- Safety Officers: Implement strategies to reduce workplace hazards.
- Compliance Officers: Ensure that business practices align with industry regulations.

Sector-Based Applications
- Healthcare Sector: Manages patient safety risks and regulatory compliance concerns.
- Technology Firms: Address cybersecurity threats and system vulnerabilities.
Important Terms Related to Establishing the Risk Process
Key Terminology
- Risk Appetite: The amount and type of risk an organization is willing to take to meet its goals.
- Residual Risk: The level of risk that remains after all mitigation strategies have been implemented.
- Risk Transfer: Shifting risk to a third party, commonly through insurance or outsourcing.
- Contingency Plan: Pre-defined actions to take if a risk materializes.
Examples
- Residual Risk in Banking: Post-mitigation credit risks are assessed to ensure open positions conform to corporate risk appetite.
- Risk Transfer in Construction: A construction firm acquires insurance policies to mitigate financial implications of potential project delays.
Software Compatibility for Establishing the Risk
Tools and Integrations
- Risk Management Software: Platforms like TurboTax or QuickBooks that integrate risk tracking features for financial assessments.
- Collaborative Platforms: Use of Google Workspace to document and share risk assessments effectively across teams.
Real-World Scenarios
- QuickBooks Integration: A small business uses it to track financial risks based on real-time accounting data.
- Google Workspace: Teams seamlessly update risk documents, enhancing collaboration and accuracy in risk tracking.
Providing comprehensive coverage of "Establishing the Risk" processes ensures stakeholders adopt a systematic, data-driven approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks effectively.