Definition & Meaning
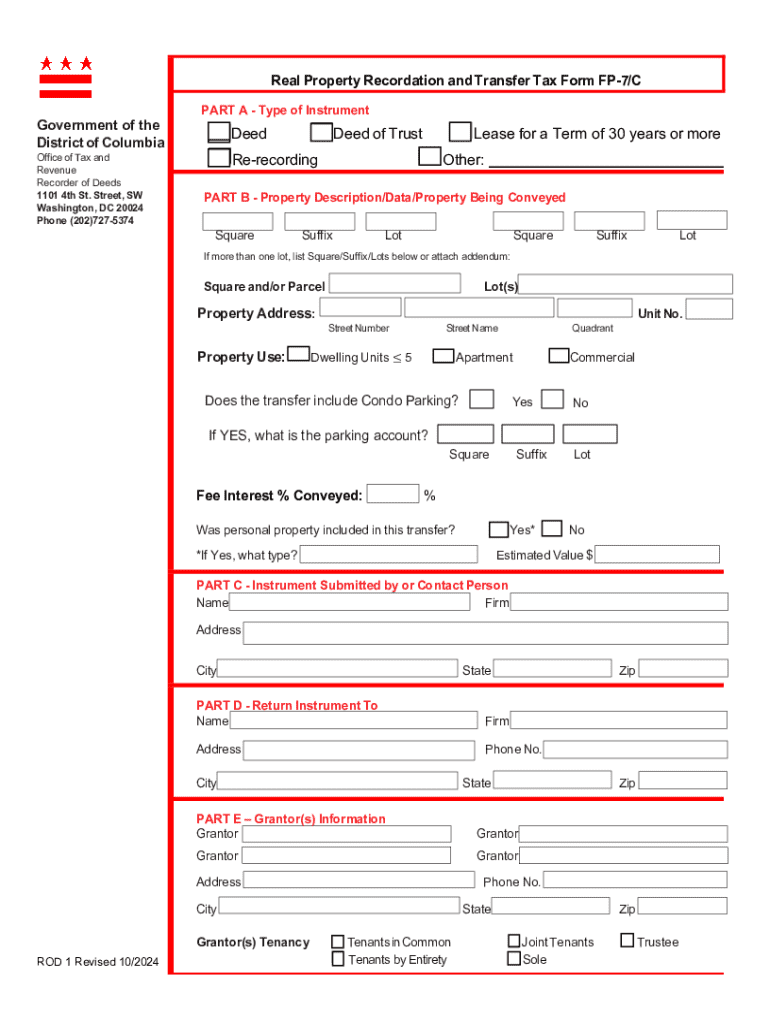
The FP-7/C form is a document used in Washington, D.C. for recording the transfer of property and for computing related real property recordation and transfer taxes. It is primarily used for instruments such as deeds and deeds of trust. The significance of this form lies in its role in helping the local government keep accurate records of property ownership and ensuring that the correct amount of taxes is collected during property transfers.
How to Use the FP-7/C
To use the FP-7/C effectively, the individual or entity involved in a property transaction needs to accurately fill out the form with the relevant details pertaining to the transfer. This involves providing information on the property itself, the parties involved, and the financial aspects of the transaction. Ensuring every required field is completed is crucial to avoid delays or legal issues.
- Property Description: Include details such as the property address and assessor's parcel number.
- Grantor and Grantee Information: Provide full names, addresses, and other identification details of the parties involved.
- Tax Computation: Calculate the amount of tax owed based on the property value and transfer type.
Steps to Complete the FP-7/C
- Gather Required Information: Collect all necessary details about the property, transaction, and parties involved.
- Complete Personal and Property Sections: Fill in the grantor and grantee names, addresses, and full legal description of the property.
- Compute Taxes: Accurately compute the taxes due, considering any exemptions or special cases.
- Review for Accuracy: Double-check all entered information to ensure there are no errors or omissions.
- Submit the Form: Provide the completed form to the Office of Tax and Revenue, along with any required payments and supporting documents.
Why Use the FP-7/C
The FP-7/C is essential for formalizing and recording property transfers in Washington, D.C. It ensures that property transactions are legally documented and the appropriate taxes are assessed and paid. This form also helps protect both parties in the transaction by maintaining an official record of the change in ownership, which can be crucial in resolving potential disputes.
Legal Use of the FP-7/C
Using the FP-7/C legally requires adherence to all filing guidelines set by the District of Columbia. Legal compliance necessitates completing the form fully and truthfully, ensuring the correct tax amount is calculated and submitted, and filing the form within any established deadlines. Failure to comply with these requirements can lead to penalties or legal challenges.
Key Elements of the FP-7/C
- Affidavit Requirements: Completion of sections that may require notarization, especially when claiming tax exemptions.
- Exemption Claims: Details on specific circumstances under which the transaction may be partially or fully exempt from taxes.
- Signatures: Signatures of all parties to affirm the accuracy and completeness of the information provided.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Adhering to the prescribed filing deadlines is vital. The FP-7/C should typically be filed at the time of closing on a real estate transaction. Any delays in filing could result in penalties or additional interest charges. It's advisable to verify the specific deadlines applicable for both reporting and payment as they can impact the cost and legality of the transaction.
Required Documents
The submission of the FP-7/C form must be accompanied by pertinent documents, which may include:
- The Deed or Deed of Trust: The actual document transferring property ownership must be provided.
- Proof of Consideration Paid: Documentation showing the financial details of the transaction.
- Exemption Documentation: If applicable, documents justifying any claimed exemptions need to be included.
Submission Methods
The FP-7/C form can typically be submitted in multiple ways, including:
- Online Submission: Some jurisdictions may permit electronic submission through dedicated portals.
- Mail: Physical mailing of the form and accompanying documents.
- In-Person: Submission at the local taxation office, which might offer the advantage of immediate feedback or receipt acknowledgment.
These options provide flexibility, allowing individuals or entities to choose the method most convenient for them while ensuring timely compliance with local property laws.