Definition & Meaning of Form Losses 2017
Form losses 2017 refers to a document used to report various financial losses incurred during the 2017 tax year, primarily for tax purposes. Understanding this form is crucial for taxpayers wishing to accurately report their income and properly account for any financial setbacks they experienced. Key aspects of this form include:
-
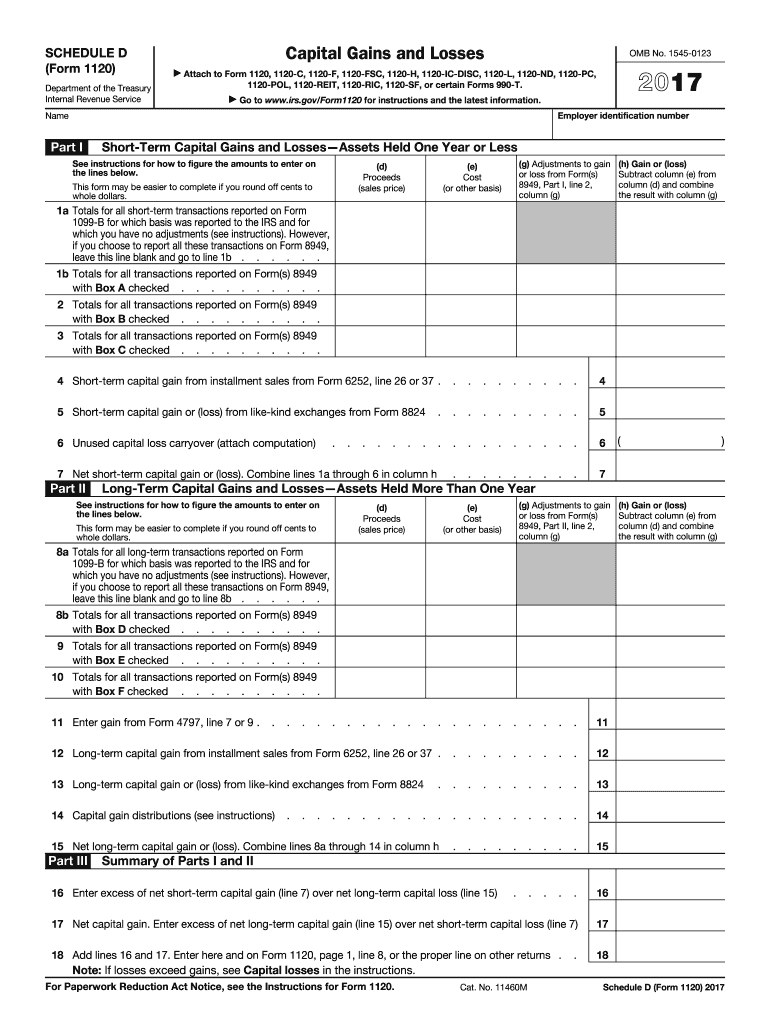
Capital Losses: This is a primary category that involves losses from the sale of an asset, such as stocks or real estate. Taxpayers can use these losses to offset capital gains, reducing their taxable income.
-
Business Losses: If a business operated at a loss, those losses can potentially be used to offset other income. Proper reporting on form losses 2017 allows businesses to ensure they receive the tax benefits available.
-
Personal Losses: In certain circumstances, personal losses (e.g., losses from a theft or casualty) might also be reported, although the criteria can be more stringent for these types of deductions.
Accurate completion and understanding of form losses 2017 not only assist in complying with tax obligations but also maximize potential tax savings.
How to Use the Form Losses 2017
Using form losses 2017 effectively involves understanding its structure and properly documenting losses to maximize tax benefits. Here are important steps to follow:
-
Gather Documentation: Collect all necessary records of your losses, such as sales receipts, brokerage statements, and any relevant financial statements. This documentation will support the entries made on the form.
-
Identify Relevant Sections: Familiarize yourself with the sections of the form dedicated to different types of losses. For example, ensure you distinguish between capital losses and business losses, as they may have different implications for your tax return.
-
Input Loss Amounts: Accurately report the amounts for each loss category. Careful calculations are essential, as inaccuracies can lead to complications or delays in processing your return.
-
Cross-reference with Other Forms: Integrate information from related tax forms, such as Schedule D for capital gains and losses, where applicable. This can help in ensuring consistency and accuracy across your documents.
-
Review Before Submission: Ensure all entries are accurate and backed by documentation. Double-check for any potential errors or omissions that could affect your tax return.
By following these steps, users can ensure they use the form loss effectively to optimize their tax filings.
Steps to Complete the Form Losses 2017
Completing form losses 2017 involves a structured approach to accurately report financial losses. The following enumerated steps provide a clear pathway:
-
Download the Form: Obtain the latest version of form losses 2017, which is typically available on the IRS website or through tax software.
-
Complete Identification Information: Fill in personal or business information, including your name, Social Security number, or Employer Identification Number (EIN).
-
Report Losses: Enter the amounts of each loss in the appropriate sections. This includes:
- Short-term losses: Losses on assets held for one year or less.
- Long-term losses: Losses on assets held for more than one year.
-
Calculate Total Losses: Sum up the reported losses to determine the total amount to report on your tax return. If you have capital losses, ensure these match the figures reported on Schedule D.
-
Sign and Date the Form: Once all information is filled out, review it for accuracy, then sign the form. A signature certifies that the information provided is complete and truthful.
Completing these steps diligently ensures that all potential losses are accounted for and can lead to substantial tax benefits.
Important Terms Related to Form Losses 2017
Understanding the terminology associated with form losses 2017 can streamline the completion of the form and enhance overall comprehension. Key terms include:
-
Capital Gain: The profit realized from the sale of an asset. It's essential to contrast this with capital losses, as losses can offset gains.
-
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): The total income earned, minus specific deductions. This figure plays a role in determining eligibility for certain tax credits.
-
Net Operating Loss (NOL): A situation where a taxpayer's allowable deductions exceed their income. Reporting an NOL can help reduce taxable income in subsequent tax years.
-
Carryforward and Carryback: Terms used to describe the ability to apply losses to past (carryback) or future (carryforward) tax years. This can maximize tax benefits from losses in the current year.
Fostering a robust understanding of these terms helps in correctly filling out the form and strategically planning for future tax implications.
IRS Guidelines for Form Losses 2017
The IRS has established guidelines specific to form losses 2017, ensuring that losses are reported accurately and in compliance with tax laws. Consider the following key points:
-
Eligibility for Deductions: Not all losses may qualify for deductions. The IRS provides criteria that must be met for losses to be deductible, including the nature of the loss and the type of entity involved.
-
Holding Period Rules: The IRS details specific holding periods that differentiate between short-term and long-term capital gains and losses. Understanding these rules is necessary to ensure proper classification.
-
Recordkeeping Requirements: The IRS mandates that taxpayers maintain adequate documentation to substantiate any claims made on their form losses 2017. This includes proof of original costs, dates of acquisition, and any relevant financial transactions.
-
Filing Deadlines: Guidance is also provided regarding the deadlines for submitting the form. Taxpayers must ensure that they file their losses timely to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Adhering to IRS guidelines is essential for a successful filing and can help prevent errors or penalties during the audit process.