Definition and Meaning of Physical and Chemical Changes
Physical and chemical changes are fundamental concepts in chemistry that describe how substances interact and transform. A physical change involves alterations in physical properties such as shape, size, state, or appearance without changing the substance's chemical composition. Common examples include melting ice, dissolving sugar in water, and breaking glass.
In contrast, a chemical change results in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties. This type of change occurs during chemical reactions, where the bonds between atoms are broken and reformed. Examples of chemical changes include burning wood, rusting iron, and mixing vinegar with baking soda, leading to the production of carbon dioxide gas.
Understanding these changes is crucial for various applications in science and industry, enabling individuals to predict how materials will behave under different conditions. Students can explore these concepts through a physical and chemical changes worksheet, which aids in identifying and categorizing examples of each type of change.
How to Use the Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheet
Using a physical and chemical changes worksheet can enhance understanding of these concepts through practical application. Here are steps to effectively utilize the worksheet:
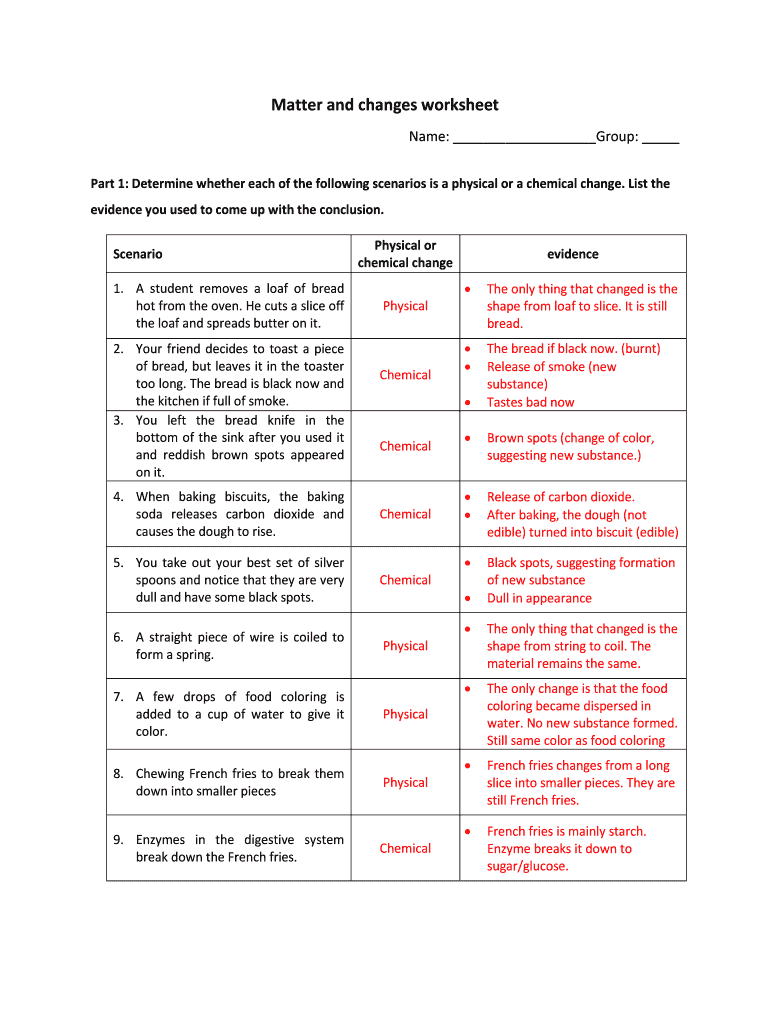
- Identify Examples: Begin by reviewing a list of various scenarios or substances provided in the worksheet. Categorize each example as either a physical or chemical change based on its characteristics.
- Document Evidence: For each identified change, provide supporting evidence. Consider questions such as: What observable changes occurred? What new substances were formed during a chemical change?
- Explore Properties: Definitions of physical and chemical properties are often included. Use these to differentiate between the two changes, reflecting on how these properties help verify the type of change.
- Suggest Alterations: The worksheet may prompt users to propose methods for inducing physical or chemical changes. This encourages deeper analytical thinking about how substances can be manipulated in different contexts.
Through this structured approach, the worksheet serves as a valuable tool in both educational and professional environments.
Steps to Complete the Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheet
Completing a physical and chemical changes worksheet can be done systematically to ensure thorough understanding. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Read Instructions Carefully: Begin by thoroughly reading all instructions to understand what is expected for each section of the worksheet.
- Categorize Changes: For each scenario presented, identify whether it represents a physical or chemical change. Use the definitions provided as a guide.
- Record Observations: Write down specific observations that indicate the type of change. Look for clues such as color changes, temperature changes, or the production of gas.
- Fill in the Answer Key: If the worksheet includes an answer key section, complete it after working through the examples. This will help verify your understanding.
- Review and Reflect: Once completed, review your classifications and observations. Consider what you learned about the nature of substances and transformations.
This structured approach not only helps in achieving the objectives of the worksheet but also solidifies the foundational knowledge of chemical and physical changes.
Examples of Using the Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheet
Examples illustrate how to apply concepts of physical and chemical changes in real-world scenarios. These situations commonly found in a physical and chemical changes worksheet can include:
- Combustion of Wood: This exemplifies a chemical change as new substances, such as carbon dioxide and ash, are produced alongside heat and light.
- Melting Ice: A physical change because the substance retains its composition as water despite changes in form.
- Dissolving Salt in Water: This is also a physical change, as the salt can be recovered by evaporating the water, thus demonstrating the retention of chemical identity.
- Rust Formation on Iron: A classic chemical change, resulting from iron reacting with oxygen and moisture to form iron oxide.
By analyzing these examples, students can gain a better grasp of the underlying principles and practical implications of physical and chemical changes.
Important Terms Related to Physical and Chemical Changes
Familiarity with key terminology enhances comprehension of physical and chemical changes. Here are crucial terms commonly featured in the context of a physical and chemical changes worksheet:
- Physical Properties: Characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the substance’s identity, such as color, odor, melting point, and solubility.
- Chemical Properties: Features that determine how a substance will react with other substances, such as flammability and reactivity with acids or bases.
- Chemical Reaction: A process where reactants undergo a transformation to become products, leading to the formation of new substances.
- Phase Change: A transition between solid, liquid, and gas states, filling a crucial role in understanding physical changes.
- Reactants and Products: Terms that describe the substances present before (reactants) and after (products) a chemical change.
Understanding these terms allows individuals to navigate discussions about physical and chemical changes more fluently, ultimately enriching their learning and application of the concepts.