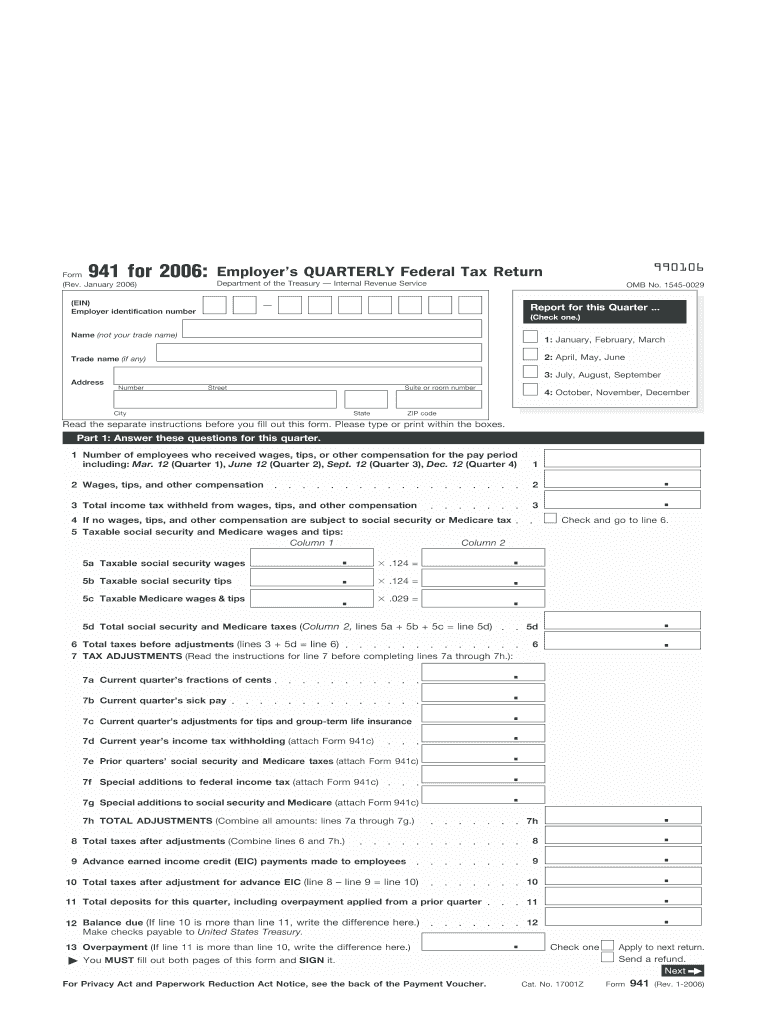
Definition and Meaning of the 2006 941 Form
The 2006 941 form, officially known as the Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return, is a pivotal document utilized by employers in the United States to report wages paid to employees along with the federal taxes withheld. This form serves as a formal declaration to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) detailing not only wages but also other important information regarding tax liabilities for each quarter. It specifically encompasses the reporting of social security and Medicare taxes, in addition to federal income tax withheld.
Form 941 is integral for maintaining compliance with federal tax requirements. It is mandatory for most employers, and failure to submit it accurately or on time can result in penalties or interest charges. By compiling a comprehensive overview of payroll taxes, the form helps ensure that employers correctly report their tax obligations and make timely payments. Understanding the nuances of this form is essential for any employer to avoid complications with tax authorities.
Steps to Complete the 2006 941 Form
Completing the 2006 941 form involves several key steps that ensure accurate reporting of employee wages and tax withholdings.
-
Gather Information:
- Collect details of wages, tips, and other compensation paid to employees during the quarter.
- Compile records of federal income tax withheld, as well as both employer and employee portions of social security and Medicare taxes.
-
Fill in Basic Information:
- Provide your employer identification number (EIN), and report the name and address of the business.
- State the total number of employees who received pay during the quarter.
-
Report Wages and Taxes:
- Enter total wages and tax amounts in the designated sections of the form, including Line 1 for total remuneration and Lines 2-5 for detailed obligations regarding taxes withheld.
-
Calculate Tax Liabilities:
- Use the completed information to determine total tax liabilities, ensuring all calculations align with the IRS guidelines.
-
Payments:
- Review whether you have made timely payments of estimated federal taxes, providing accurate entries on Line 9 for adjustments.
-
Sign and Date the Form:
- Ensure that the form is signed by an authorized individual within the company, affirming the completeness and accuracy of the information provided.
IRS Guidelines for the 2006 941 Form
The IRS provides detailed guidelines for accurately completing the 2006 941 form. This information is crucial for ensuring that all entries are compliant with federal tax regulations.
-
Reporting Periods: Employers are required to file the 941 form quarterly, with payments for federal tax withheld due by the end of each reporting period. This includes January to March (Q1), April to June (Q2), July to September (Q3), and October to December (Q4).
-
Filing Methods: Employers can submit the form either electronically or via mail. Electronic submissions are strongly encouraged as they are processed more swiftly and can minimize errors.
-
Amendments: If errors are discovered after filing, employers can amend their returns using Form 941-X, ensuring that records accurately reflect the true tax liabilities.
-
Recordkeeping: Employers must retain copies of their filed forms for a minimum of four years from the date of the tax due or paid, whichever is later. This retention policy supports transparency and accountability during potential audits.
Who Typically Uses the 2006 941 Form
The primary users of the 2006 941 form are employers operating within various sectors across the United States. This includes:
-
Small Businesses and Startups: Many small employers, especially those new to payroll, rely on the form to fulfill their tax reporting obligations.
-
Corporations: Larger businesses use Form 941 for reporting substantial wage disbursements and related tax withholdings.
-
Non-Profit Organizations: Non-profits with employees must comply with federal tax withholding, making the 941 form an essential part of their tax management processes.
-
Partnerships and LLCs: These entities also utilize this form when they employ individuals to streamline their tax reporting.
Comprehending the use and function of the 2006 941 form is crucial for any employer, regardless of the business size or sector.

Filing Deadlines for the 2006 941 Form
Understanding the deadlines for filing the 2006 941 form is critical for employers to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with federal guidelines.
-
Quarterly Filing Deadlines: Employers must submit their Form 941 on or before the last day of the month following the end of each quarter:
- Q1 (January to March): Due by April 30
- Q2 (April to June): Due by July 31
- Q3 (July to September): Due by October 31
- Q4 (October to December): Due by January 31 of the following year
-
Penalties for Late Filing: Delaying the submission can result in penalties, which can accumulate quickly. The failure-to-file penalty may be assessed based on the amount of tax owed and the number of days the return is late.
-
Extensions and Special Cases: While extensions are typically not available for Form 941, particular considerations may apply for employers with special circumstances, such as those impacted by natural disasters, which may grant temporary relief.
Timely filing and payment are crucial components of an employer's responsibilities in maintaining compliance with IRS requirements.