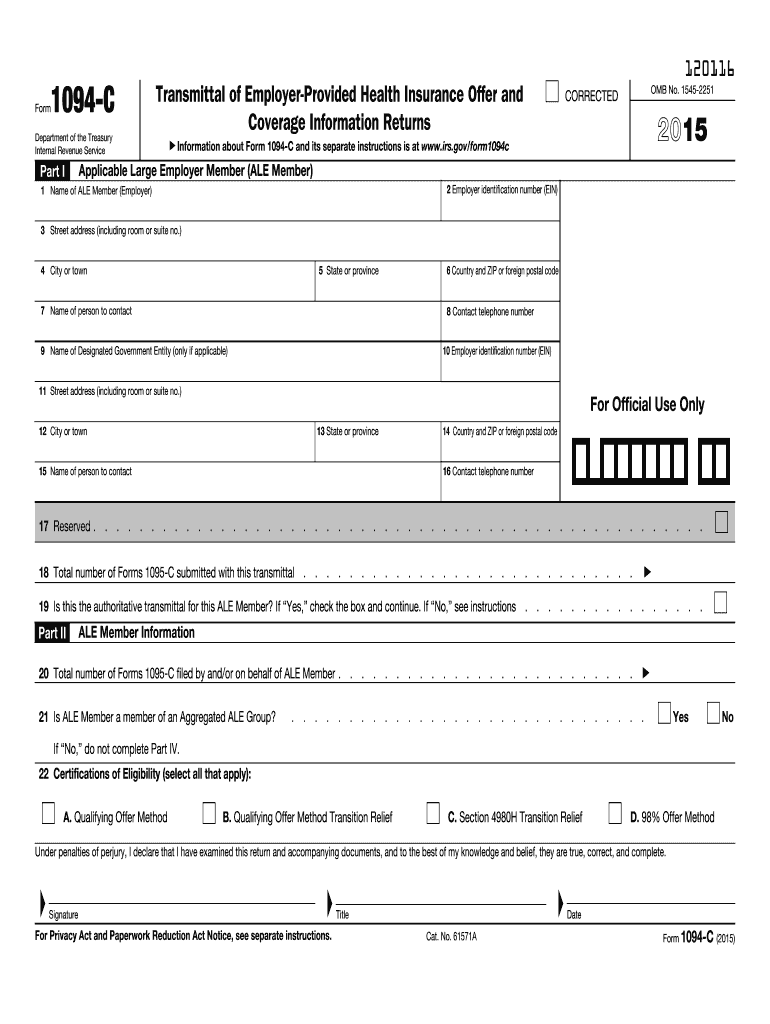
Definition and Purpose of the 2-C Form
The 2-C form is a crucial document used by Applicable Large Employers (ALEs) under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) to report health insurance offers and coverage information to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This form serves as a transmittal for Forms 1095-C, which provide detailed information about the health coverage offered to employees. By completing the 2-C, employers demonstrate compliance with ACA reporting requirements, helping to ensure that employees receive the necessary health coverage that they are eligible for.
The form contains multiple sections designed to capture specific information:
- Employer Identification: This includes the employer's name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN). Accurate information here is critical, as it allows the IRS to easily identify the reporting employer.
- Contact Information: Employers must provide contact details for a designated representative who the IRS can reach out to for questions or further information regarding the filings.
- Monthly Employee Count: This section requires employers to report the number of full-time employees for each month of the calendar year, aiding the IRS in monitoring compliance with ACA requirements.
Understanding the definition and purpose of the 2-C form is essential for any business that is categorized as an ALE, as failing to file this form correctly can lead to penalties and compliance issues.
Steps to Complete the 2-C Form
Completing the 2-C form involves multiple steps to ensure accurate reporting to the IRS. Employers must gather relevant data and fill out the form carefully. Here are the detailed steps:
-
Gather Necessary Information: Collect all data regarding the health insurance coverage offered, details from Forms 1095-C, and the employer's identification information, including the EIN and contact details.
-
Complete Section I:
- Enter the employer's legal name, address, and EIN.
- Provide the total number of Forms 1095-C that are being submitted alongside the 1094-C.
-
Choose the Appropriate Reporting Method:
- Decide whether to report based on full-time employees overall or if applying special rules.
-
Fill Out Section II:
- Indicate the applicable transition relief codes and checkboxes relevant to the employer’s reporting situation.
- This section should be completed based on employer size and employee count to reflect compliance obligations accurately.
-
Final Review: Carefully review all entries for accuracy, ensuring that all required sections are filled out correctly to prevent delays or penalties.
-
Submit the Form: After reviewing, submit the completed 2-C form to the IRS, either electronically or via mail, ensuring that it meets the filing deadlines.
Employers should keep a copy for their records and ensure they understand how their health coverage offerings align with ACA requirements.
Who Typically Uses the 2-C Form?
The 2-C form is primarily used by Applicable Large Employers (ALEs) under the ACA guidelines. ALEs are defined as employers who have fifty or more full-time equivalent employees in the prior calendar year. The following entities typically use this form:
- Corporations: Both large and medium-sized corporations that provide health coverage to their employees are required to file.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Larger nonprofit organizations with sufficient employee counts are also obligated to report using the 1094-C.
- Local and State Governments: Government entities that offer health insurance to their employees must report their coverage to ensure compliance with ACA requirements.
- Employers with Multiple Locations: Companies with several establishments often consolidate reporting through the 2-C to simplify compliance.
Understanding who must use the 2-C form is essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential penalties associated with non-filing or incomplete filing.

IRS Guidelines for the 2-C Form
The IRS has outlined specific guidelines for completing the 2-C form, which are essential for businesses to follow to ensure compliance with federal regulations. These guidelines include:
- Filing Requirements: ALEs must file Form 1094-C along with Forms 1095-C for each full-time employee offered health coverage. The deadline for filing these forms is typically around February 28th for paper submissions or March 31st for electronic submissions.
- Electronic Filing: Employers with 250 or more Forms 1095-C must file electronically. The IRS provides a specification guide that details the technical requirements for electronic submissions.
- Correct Use of Codes: Employers need to accurately enter the correct codes to signify the type of health coverage offered. This includes codes for various affordability and minimum essential coverage metrics.
- Accuracy and Compliance: All information reported must be accurate to prevent any penalties associated with incorrect filing. The IRS mandates that employers keep records of their health insurance offerings for a minimum of three years.
Adhering to these IRS guidelines ensures that employers fulfill their reporting obligations effectively and avoid any legal complications.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Filing deadlines for the 2-C form are crucial for employers to understand to ensure timely submissions and compliance. The following are key dates to keep in mind:
- January 31: This is typically the deadline for employers to provide Forms 1095-C to employees. Employers should ensure that all employees have received their Forms 1095-C by this date, as it contains important information about health coverage.
- February 28: The deadline for filing the 2-C and 1095-C forms with the IRS via paper submission.
- March 31: If filing electronically, employers have until this date to submit Forms 1094-C and 1095-C to the IRS.
Employers need to plan ahead to meet these deadlines, taking into account the time required to gather information and prepare the necessary documentation. It is advisable to begin the process well in advance of the deadlines to avoid any last-minute issues.