Definition and Importance of the Nevada MBT
The Nevada Modified Business Tax (MBT) is a tax levied on businesses operating within the state, calculated based on their total gross wages. This tax applies primarily to employers who are subject to Nevada's Unemployment Compensation Law. Understanding the MBT is crucial for compliance and financial planning, as it affects cash flow and overall business expenses.
The MBT is designed to support state funding, including essential services such as education and infrastructure. Therefore, the revenue generated from this tax is vital for maintaining these services, making it a key component in the state's budget. Businesses must grasp the implications of the MBT to ensure they manage their tax obligations effectively.
Who Typically Uses the Nevada MBT
Businesses of various types and sizes operating within Nevada are subject to the MBT. This includes:
- Corporations: Traditional corporations must adhere to MBT regulations as part of their operational costs.
- Limited Liability Companies (LLCs): Many LLCs are also required to file and pay MBT, particularly if they have employees.
- Partnerships and Sole Proprietorships: Individuals running businesses with employees are likewise included under the MBT regulations.
Understanding who falls under these categories helps businesses determine their liability under Nevada tax laws.

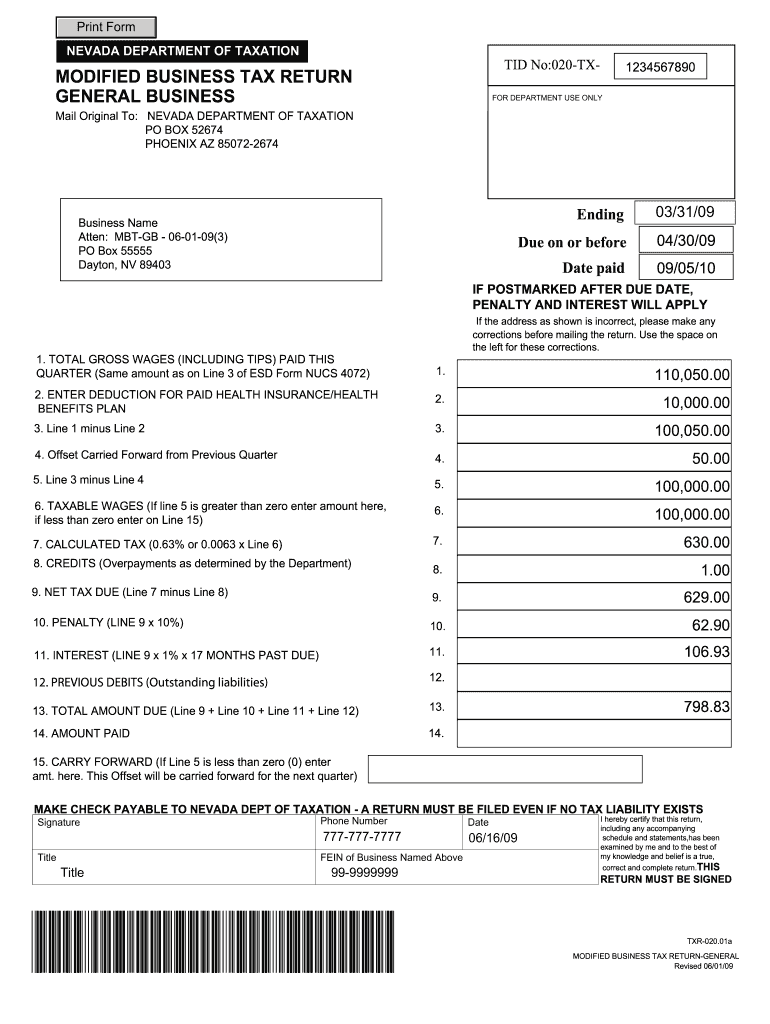
Steps to Complete the Nevada MBT Form
Completing the Nevada Modified Business Tax Form requires careful attention to detail and adherence to specific guidelines.
- Gather Financial Records: Collect all necessary documentation, including payroll records and any deductions applicable for health benefits.
- Determine Total Gross Wages: Calculate the total gross wages paid to employees during the reporting period.
- Identify Deductions: Review available deductions, notably health benefits, which can be subtracted from the gross wages to lower taxable income.
- Fill Out the Form: Enter the calculated figures into the appropriate sections of the Nevada MBT form, ensuring accuracy in every entry.
- Review and Submit: Double-check all calculations and information before submission. This step is crucial to avoid potential penalties due to incorrect filings.
Each of these steps is critical to ensure compliance and avoid issues with the Nevada Department of Taxation.
Important Terms Related to the Nevada MBT
Understanding key terms associated with the Nevada MBT is essential for effectively managing tax obligations:
- Total Gross Wages: The full amount paid to employees before any deductions, which forms the base for the MBT calculation.
- Deductions: Specific amounts that can be subtracted from gross wages, such as health benefits, helping lower the overall MBT liability.
- Taxable Amount: The amount remaining after deductions, which is subject to the MBT rate.
- Penalties: These can apply for late payments or failures in compliance with filing requirements.
Grasping these terms aids in navigating the filing process and determining tax responsibilities.
State-Specific Rules for the Nevada MBT
Nevada has unique rules regarding the Modified Business Tax that businesses must abide by to ensure compliance:
- Filing Frequency: Most businesses are required to file annually, but those that exceed certain benchmarks must file quarterly.
- Payments: Taxes owed must be remitted according to the set schedules to avoid penalties.
- Health Benefits Deduction Cap: There are limits on how much can be deducted in health benefits, so it's essential to verify current regulations.
- Owner-Operated Businesses: Unique considerations apply to businesses where the owner also serves as an employee regarding tax calculations.
Awareness of these state-specific rules can significantly impact tax planning and compliance for businesses.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Meeting the deadlines for filing the Nevada MBT is crucial for ensuring compliance. Key dates include:
- Quarterly Filings: Deadlines are typically within the first month after each quarter, requiring businesses to plan accordingly.
- Annual Filings: Businesses must file their annual MBT returns by a specified date each year, with extensions available under certain conditions.
Failure to adhere to these dates can result in penalties and interest on unpaid taxes, highlighting the need for a well-managed filing schedule.