Understanding the 2005 Form W-9
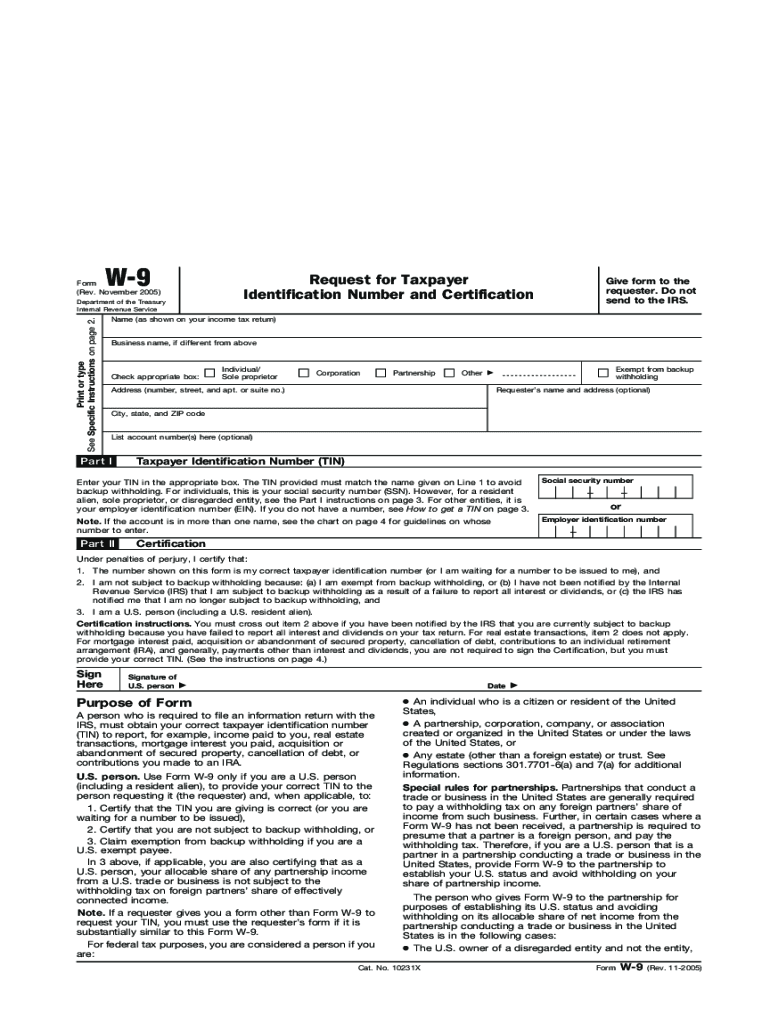
The 2005 Form W-9 is a request for taxpayer identification number and certification that allows U.S. persons to provide their taxpayer identification number (TIN) to entities that need to report income paid to them. This form is essential for ensuring accurate tax reporting and compliance. It facilitates the collection of necessary information required by businesses and individuals to properly file income and tax returns.
Frequent Uses of the 2005 Form W-9
The form is used in various situations, including:
-
Freelancers and Contractors: Independent contractors use the Form W-9 to provide their TIN to clients for whom they perform services. This enables the client to report payments made to the contractor to the IRS.
-
Financial Institutions: Banks and other financial institutions request a W-9 from customers to report interest payments or other income earned.
-
Real Estate Transactions: The W-9 may be needed during the closing process of real estate to report payments received by the seller.
Obtaining the 2005 Form W-9
The 2005 Form W-9 can be obtained through various sources, including:
-
IRS Website: The official IRS website is the primary source. Users can download the form directly from the IRS forms page.
-
Tax Preparation Software: Many tax preparation programs include digital copies of the W-9 form, making it accessible during tax season.
-
Financial Institutions: Banks or tax professionals may also provide copies upon request.
Completing the 2005 Form W-9
Filling out the 2005 Form W-9 requires careful attention to detail. Key steps include:
-
Enter Your Name: Write your full name as shown on your tax return.
-
Business Name (if applicable): If you have a business, enter its name in the applicable field.
-
Address: Provide your full address, including city, state, and ZIP code.
-
Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): Input your TIN, which can be your Social Security Number (SSN) for individuals or Employer Identification Number (EIN) for businesses.
-
Certification: Sign and date the form to confirm that the information is accurate and that you are not subject to backup withholding.
Important Terms Related to the 2005 Form W-9
Understanding specific terms associated with the W-9 form will help users navigate the document effectively:
-
Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): A unique number used by the IRS to identify taxpayers, which can be either an SSN or an EIN.
-
Backup Withholding: A tax withholding requirement imposed on certain payments when the taxpayer does not provide a correct TIN.
-
Certification: The act of signing the form to confirm the accuracy of the provided information.
Legal Compliance and Penalties for Non-Compliance
The 2005 Form W-9 plays a critical role in legal tax compliance. Failing to provide accurate information on the W-9 can result in:
-
Penalties: The IRS may impose penalties for failure to furnish accurate information or if there is a failure to report income correctly.
-
Backup Withholding: If the TIN is not provided or is incorrect, the payer may be required to withhold a percentage of income as backup withholding.
Filing Deadlines and Submission Methods
While the W-9 itself does not have a direct filing deadline since it is not submitted to the IRS, here’s how it is typically used in relation to deadlines:
-
When Requested: Respond promptly to requests for a W-9, as it may be needed for immediate income reporting.
-
Submission Methods: The completed form can be submitted to the requester via:
- Email (if allowed)
- Fax
Keeping these guidelines in mind ensures that the use of the 2005 Form W-9 is compliant and effective in fulfilling tax reporting obligations.