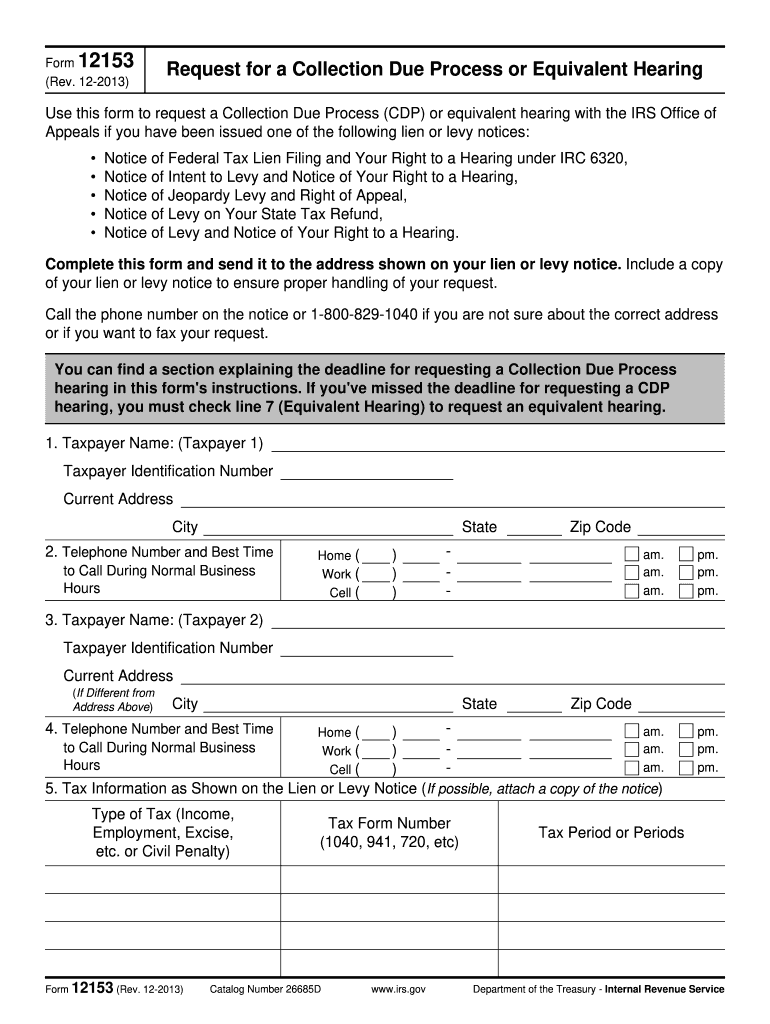
Understanding IRS Form 12153: Definition and Purpose
IRS Form 12153, formally known as the Request for a Collection Due Process (CDP) or Equivalent Hearing, is a crucial document for taxpayers who wish to challenge IRS lien or levy actions. This form allows individuals to request a hearing with the IRS Office of Appeals concerning notices received for liens or levies. By utilizing Form 12153, taxpayers can formally assert their rights to appeal against the IRS's collection actions, ensuring they have an opportunity to present their case and explore alternative options.
The importance of this form lies not only in its function as an appeal tool but also in its role in preserving taxpayers’ rights. The completion of Form 12153 provides a structured way for individuals to communicate their specific concerns regarding the IRS’s collection actions. Additionally, it includes sections for taxpayers to articulate the reasons for their dispute, such as financial hardships or discrepancies in the IRS's claims.
How to Use IRS Form 12153: Steps for Submission
Submitting Form 12153 requires careful attention to detail. The process is as follows:
-
Obtain the Form: You can access IRS Form 12153 from the IRS website or various tax assistance platforms. Ensure you have the latest version of the form to avoid issues with outdated regulations.
-
Complete the Form: Fill in the required information accurately. This includes:
- Taxpayer's name and contact details
- Social Security number or Employer Identification Number
- Specific tax periods affected by the lien or levy
- Reasons for disputing the IRS action, citing any relevant facts or documentation.
-
Attach Supporting Documents: If applicable, include any additional documents that support your case. This could include financial statements, tax returns, or correspondence with the IRS.
-
Submit the Form: After ensuring the form is complete and all documents are attached, send it to the appropriate IRS office as indicated in the instructions.
-
Follow-Up: Keep a record of your submission and monitor for any correspondence from the IRS regarding your request.
Key Elements of IRS Form 12153: A Detailed Breakdown
IRS Form 12153 contains several essential components, which assist in the effective processing of your request. The key elements include:
-
Taxpayer Information: This section captures personal details necessary for the IRS to identify your tax account. Accurate information here is critical to prevent delays.
-
Tax Periods: Clearly indicate the tax periods involved. This helps the IRS understand the context of your request for a hearing.
-
Basis for Request: This critical component allows taxpayers to explain their reasons for disputing the lien or levy. Providing clear and concise descriptions can significantly affect the outcome of your case.
-
Preferred Hearing Type: Taxpayers can specify whether they prefer a face-to-face meeting, a telephone conference, or a correspondence hearing, enabling them to choose the format most comfortable for them.
-
Signature and Date: Completing the form is not enough without a signature and date. This step verifies that the request is official and aligns with IRS protocols.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates for IRS Form 12153
Timeliness is vital when submitting IRS Form 12153. Specific dates and deadlines must be observed to ensure your request is valid. Here are the critical timelines:
-
Request Deadline: Generally, you must file Form 12153 within thirty days of the IRS’s lien or levy notice. Missing this deadline can result in the forfeiture of your right to a hearing.
-
Hearing Scheduling: Once the form is submitted, the IRS aims to schedule a hearing within a reasonable timeframe, often within a few weeks. You will receive notification about the hearing date, which should be noted and marked on your calendar.
-
Response Time: After the hearing, you can expect the IRS to respond with its decision within a specified period, usually six weeks post-hearing. Monitoring this timeline is essential to maintain communication regarding your case.
Common Scenarios for Using IRS Form 12153
Understanding the various scenarios that may lead to a use of IRS Form 12153 can help taxpayers identify their eligibility and need for this form. Common situations include:
-
Financial Hardship: If a taxpayer is experiencing financial difficulties that hinder their ability to pay their tax debt, they may use this form to argue against aggressive IRS collection actions.
-
Disputed Tax Amounts: If a taxpayer believes the amount owed is incorrect due to errors in reporting or calculation, Form 12153 serves as a platform to present this challenge to the IRS.
-
Incorrect Filing Issues: Taxpayers who face liens or levies that result from misfiled or fraudulent tax returns can also utilize Form 12153 to seek remediation.
Importance of Understanding Legal Use of IRS Form 12153
Awareness of the legal implications surrounding IRS Form 12153 is imperative for taxpayers:
-
Compliance with IRS Regulations: Filing this form ensures that taxpayers adhere to IRS guidelines concerning disputed tax collection actions.
-
Protection of Taxpayer Rights: By using this form, individuals actively engage in protecting their rights against potential overreach by the IRS, thereby fostering a more transparent tax system.
-
Statutory Rights to Appeal: Taxpayers have the statutory right to request a hearing on collections, and using Form 12153 is a formal recognition of this right.
By comprehensively understanding these facets of IRS Form 12153, taxpayers can effectively navigate the complexities of IRS collections and secure their appeal rights with confidence.