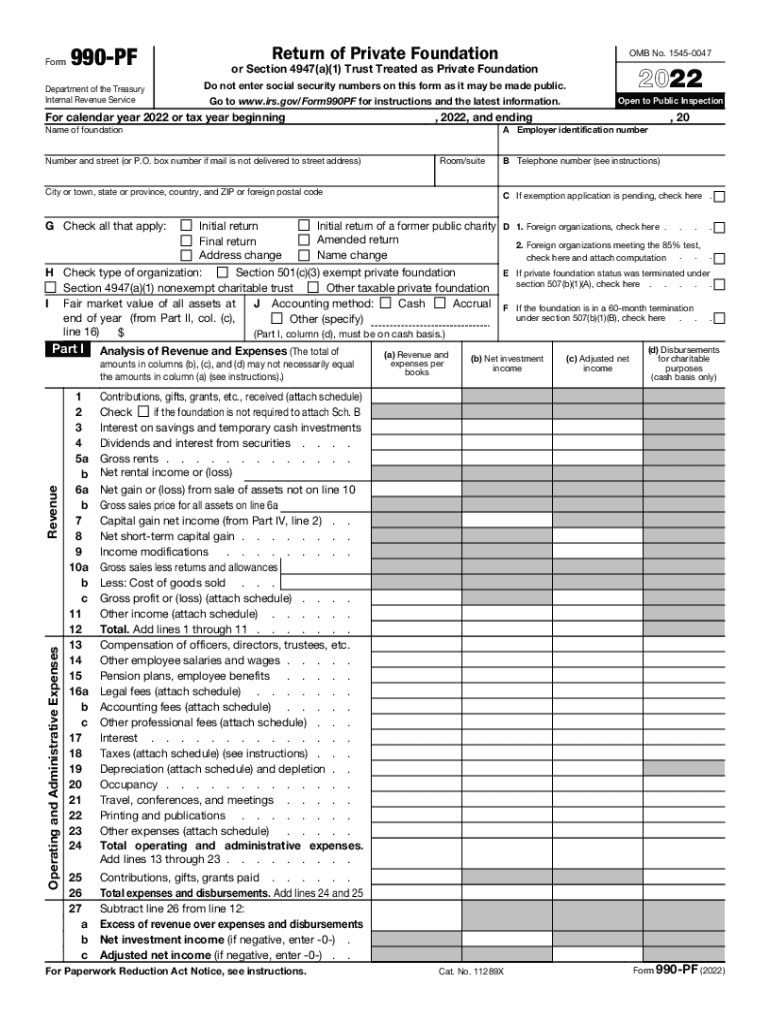
Definition & Purpose of 2022 Form 990-PF
The 2022 Form 990-PF, also known as the IRS tax form for private foundations, is essential for nonprofit entities to report their financial activities. This form requires foundations to detail their annual revenue, expenses, and distributions made for charitable purposes. It serves as a comprehensive financial statement, ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
Key Elements of Form 990-PF
- Revenue Reporting: Foundations must disclose all contributions received and other income sources.
- Expense Accounting: Detailed reporting on operating expenses, including administrative costs.
- Charitable Distributions: Lists grants and other distributions made for charitable activities.
- Balance Sheets: A snapshot of the foundation’s financial position, including assets and liabilities.
- Capital Gains Information: Report capital gains and losses that impact the foundation’s finances.
- Excise Taxes: Foundations must calculate and report excise taxes on investment income.
- Officer & Director Information: Disclosure of information regarding key individuals within the foundation.
How to Use the 2022 Form 990-PF
Using Form 990-PF requires a thorough understanding of different sections that align with the foundation’s financial data. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process to accurately fill out and submit this form.
Steps for Completing Form 990-PF
- Gather Financial Documents: Include bank statements, receipts, grant applications, and proof of donations.
- Fill out Revenue Details: Start with Part I, which records revenue from contributions, investments, and other miscellaneous sources.
- Detail Operating Expenses: Ensure comprehensive logging of administrative and program-related expenses.
- Document Distributions: Accurately list all distributions made for philanthropic purposes in Part VII.
- Complete Balance Sheets: Utilize Part II to reflect assets and liabilities accurately.
- Calculate Investment Income Tax: Use Part VI to report and calculate any applicable excise taxes.
- Submit Officer Information: Provide complete information about the foundation’s managers to ensure transparency.
How to Obtain the 2022 Form 990-PF
Obtaining the 2022 Form 990-PF is straightforward through several IRS-sanctioned channels, ensuring accessibility and efficiency.
Available Channels
- IRS Website: Download directly from the IRS’s official site in PDF format.
- Local Libraries: Some public libraries provide tax forms during the filing season.
- Financial Advisors or Accountants: Often provide copies to clients who need to complete this form.
- Tax Software Programs: Integrated directly into platforms like TurboTax or QuickBooks, allowing for digital completion.
Legal Use of the 2022 Form 990-PF
Form 990-PF is legally required by private foundations to ensure transparency and accountability in their financial operations. Noncompliance can lead to significant penalties and jeopardize a foundation’s tax-exempt status.
Compliance and Requirements
- Accuracy: Ensuring all information is correct and reflective of the foundation’s financial status.
- Timeliness: Adhering to the specified filing deadlines to avoid late fees or penalties.
- Disclosure of All Financial Activities: Comprehensive reporting of all financial activities to maintain transparency.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates
Adhering to filing deadlines is crucial for private foundations. The IRS generally sets precise due dates to maintain uniformity.
Critical Filing Information
- Typical Deadline: April 15th of the year following the close of the taxable year.
- Extension Possibility: Foundations can apply for a six-month extension if necessary, moving the deadline to October 15th.
- Late Filing Penalties: Failing to file on time can result in penalties ranging from financial fines to more severe consequences.
Required Documents for Filing
Successful filing of Form 990-PF requires compiling specific documents to substantiate the information provided.
Documentation Checklist
- Donation Records: Include all receipts and acknowledgment letters for donations received.
- Financial Statements: Income statements, balance sheets, and any schedules supporting tax filings.
- Investment Documentation: Statements showing interest, dividends, capital gains, or losses.
- Payroll Records: If applicable, especially if there are paid staff within the foundation.
Form Submission Methods
Private foundations have multiple avenues to submit completed Form 990-PF, allowing for flexibility based on preferences and resources.
Submission Options
- Electronic Filing: Preferred method, utilizing e-filing systems through tax software for efficiency.
- Mailing Paper Forms: Traditional mailing to the IRS processing center specified for nonprofit tax filings.
- Consulting Services: Financial advisors or tax preparers can manage the paperwork and submit on behalf of the foundation.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with IRS regulations regarding Form 990-PF can lead to penalties, impacting a foundation’s financial and legal standing.
Types of Penalties
- Monetary Fines: Charged per day until the foundation resolves the non-compliance.
- Tax-Exempt Status Risks: Repeated non-compliance could endanger the status, affecting donations and operations.
- Public Disclosure: Non-filing can result in mandatory public disclosure of non-compliance, tarnishing the foundation’s reputation.