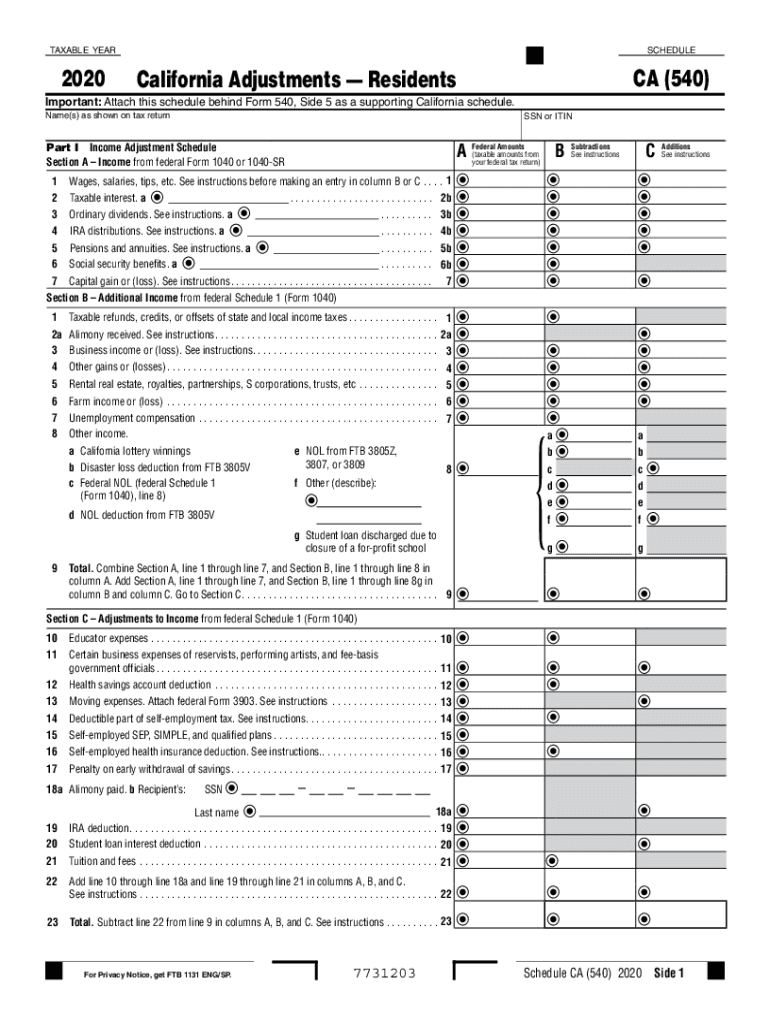
Definition and Meaning of Schedule CA (540)
The Schedule CA (540) is a form used by residents of California to report adjustments to income and deductions that may differ from federal tax information reported on Form 1040. This schedule outlines various California-specific tax rules and is crucial for accurately calculating state tax obligations. Taxpayers utilize this form to ensure compliance with state requirements, particularly when adjustments arise from sources of income not recognized at the federal level or state-deductible items.
Purpose of the Schedule CA (540)
- Income Adjustments: Taxpayers may need to adjust their total income based on California regulations. These adjustments can include state-specific deductions and credits.
- Deductions and Credits: Allows for modifications related to federal itemized deductions and state-specific deductions, ensuring that only those applicable in California are counted.
- Compliance with State Tax Laws: Essential for maintaining adherence to California tax statutes, reducing the risk of audits and penalties.
How to Use the Schedule CA (540)
Using the Schedule CA (540) involves several key steps and considerations. Understanding the structure of the form is vital to ensure correct completion.
Understanding the Form Structure
- Sections: The form is organized into sections, each targeting specific adjustments to income and deductions.
- Part I: Income adjustments that may reduce federal adjusted gross income (AGI).
- Part II: Adjustments to itemized deductions, affecting how the taxpayer’s total itemized deductions are calculated.
- Part III: Covers additional information and other adjustments that might be unique to the taxpayer's situation.
Steps to Fill Out the Schedule CA (540)
- Gather Required Documents: Collect all relevant tax documents, including your federal tax return and any applicable documentation supporting your adjustments.
- Complete Part I: Detail income adjustments, ensuring each line item corresponds with supporting documentation.
- Complete Part II: Adjust federal itemized deductions based on California law and ensure that differences are correctly recorded.
- Review Part III: Make any necessary disclosures and additional adjustments needed for your tax situation.
Important Terms Related to Schedule CA (540)
Familiarity with key terms associated with the Schedule CA (540) aids in proper usage and understanding of the document.
Commonly Used Terms
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): The total income earned before tax deductions. Adjustments are often made to AGI to figure state-specific modifications.
- Itemized Deductions: Expenses such as medical expenses, state taxes, and mortgage interest are eligible for deductions that may vary from federal standards.
- Franchise Tax Board (FTB): The state agency responsible for tax collection and enforcement, including the issuance of the Schedule CA (540).
Legal Use of the Schedule CA (540)
The Schedule CA (540) is legally required for anyone who needs to report state income tax in California. Completing this form accurately ensures that taxpayers meet their obligations under California law, which can help in avoiding potential penalties for non-compliance.
Steps to Complete the Schedule CA (540)
Detailed comprehension of each step necessary to complete the Schedule CA (540) assists in ensuring accuracy during the filing process.
Detailed Completion Process
- Determine Eligibility: Confirm if you are required to file the Schedule CA (540) based on your residency status and income sources.
- Access the Form: The form can be obtained from the Franchise Tax Board website or through tax preparation software.
- Fill Out Personal Information: Provide identifying information, including name, address, and Social Security number.
- Report Income Adjustments: As specified in Part I, report all forms of income, including wages, interest, and rental income, and make necessary adjustments.
- Adjust Itemized Deductions in Part II: Carefully enter deduction modifications to comply with state law, ensuring that all calculations are made according to the most recent California tax guidelines.
Examples of Using the Schedule CA (540)
Understanding practical applications of the Schedule CA (540) enhances appreciation of its role in tax preparation.
Practical Scenarios
- Self-Employed Individual: A freelance graphic designer may need to adjust both income and deductible expenses since certain expenses not recognized federally are deductible in California.
- Homeowner: A taxpayer may modify their itemized deductions to reflect mortgage interest adjustments unique to California tax rules, such as limits on the deductibility of mortgage interest based on the home equity.
- Retiree: A retiree receiving pension income may have to adjust that income depending on whether it meets the criteria for California tax adjustments, as some public pensions are exempt.
Filing Deadlines and Important Dates for Schedule CA (540)
Being aware of deadlines is crucial for timely filing and compliance.
Key Dates
- Tax Filing Deadline: Typically April 15 for the annual tax return, including the Schedule CA (540).
- Extensions: California residents may file for an extension, but any taxes owed must still be paid by the original due date to avoid penalties and interest.
Required Documents for Schedule CA (540)
Having the necessary documentation on hand is essential for completing the Schedule CA (540) accurately.
Documentation Checklist
- Form 540: The primary tax form for California residents that the Schedule CA (540) supports.
- W-2s and 1099s: These forms report income earned, which is essential for accurate adjustment reporting.
- Receipts and Statements: Documentation for claimed itemized deductions, such as mortgage interest statements and proof of charitable contributions.
- Previous Year Tax Return: Helpful for reference, especially for adjustments based on trend changes.
Digital vs. Paper Version of Schedule CA (540)
Each format has distinctive advantages and considerations that can impact the filing process.
Advantages of Digital Submission
- Convenience: Digital formats allow for easy access and submission directly through tax software or FTB online services.
- Immediate Validation: Tax software often includes automatic error-checking features, reducing the risk of filing mistakes.
- Faster Processing: Electronic submission typically results in quicker processing times compared to paper filings.
Ensuring thorough understanding and complete preparation is vital when dealing with tax documents. The Schedule CA (540) plays an integral role in aligning taxpayer obligations with California’s specific tax laws.